19
P15008 (04-15-2023)
TROUBLESHOOTING
SYMPTOMS
PROBABLE CAUSE
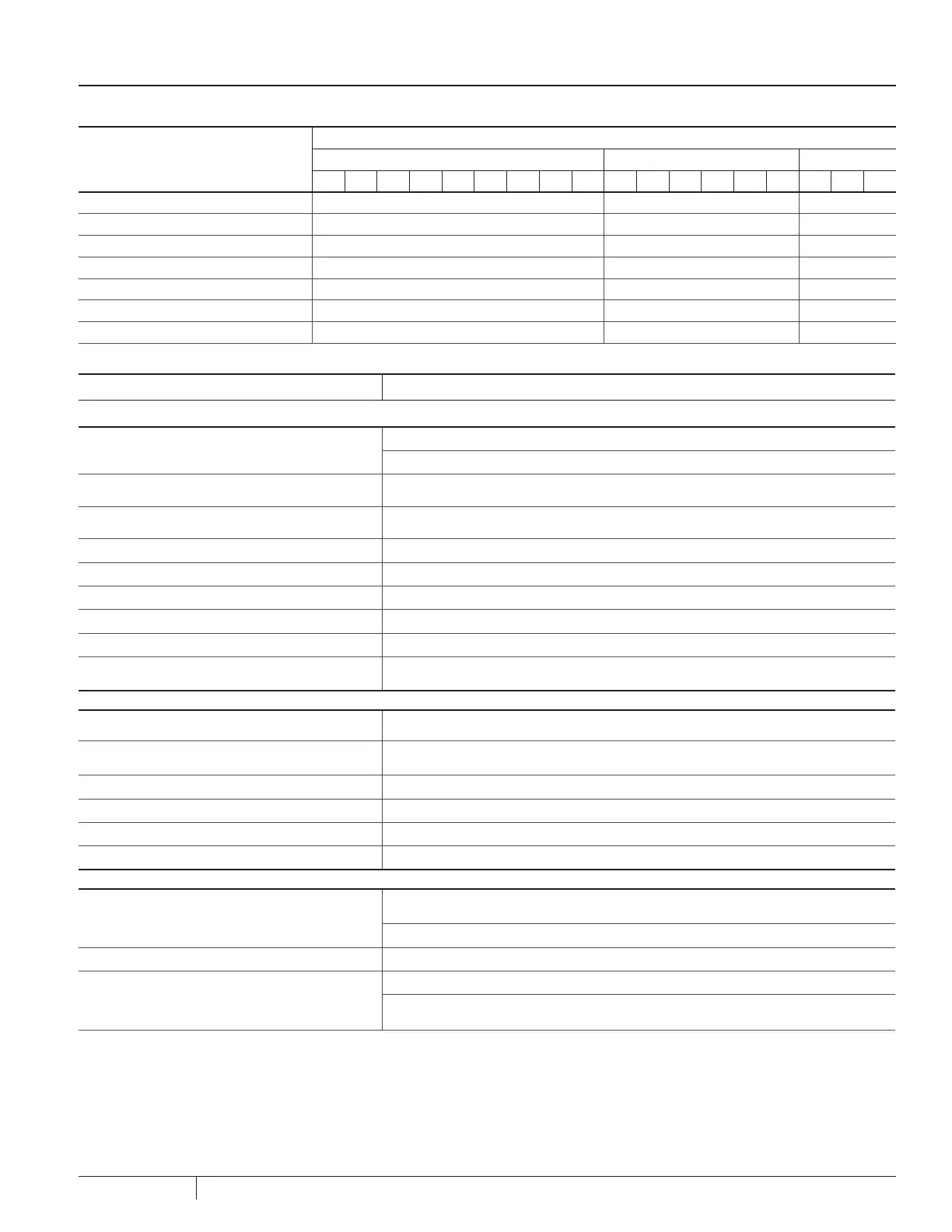
ELECTRICAL MECHANICAL SYSTEM
A B C D E F G H I A B C D E F A B C
Pump runs, but no water delivered X X X X
Not enough water delivered X X X X
Not enough pressure X X X X
Excessive vibration X X
Abnormal Noise X X
Pump stops X X X X X X X X
Overheating X X X X X X X X X
CAUSE CORRECTIVE ACTION
ELECTRICAL
A. No voltage in power system.
Check phase-to-phase on line side of starter contactor.
Check circuit breaker or fuses
B. No voltage on one phase (Three Phase units).
Check phase voltage on line side of starter contactor. Isolate open circuit
(circuit breaker, fuse, broken connections, etc.)
C. Low voltage at motor.
Running voltage across each leg of motor must be ±10% of nominal voltage
shown on nameplate.
D. Motor leads improperly grouped for voltage. Refer to lead grouping diagram on motor nameplate.
E. Control failure. Check control device, starter contactor, H-O-A selector switch, etc., for malfunction.
F. Thermal overload switch open Check phase-to-phase on line side of starter contactor.
G. Installation failure. Check motor or windings to ground with megohmmeter.
H. Open windings. Check leg-to-leg with ohmmeter.
I. Frequency variation.
Check frequency of power system. Must be less than 5% variation from
motor nameplate rating.
MECHANICAL
A. Flow through pump completely or partially
obstructed.
Locate and remove obstruction. Refer to repair instructions for disassembly.
B. Wrong direction of rotation.
Reverse rotation of three phase motor by interchanging any two leads. See manufacturer’s
instructions for reversing single phase motor.
C. Pump lost prime. Reprime. Inspect suction system for air leaks.
D. Internal leakage. Check impeller for wear of controlled clearances (See Repair Instructions).
E. Loose parts Inspect. Repair.
F. Stung box not properly adjusted Adjust gland.
SYSTEM
A. Pressure required by system at design ow rate
exceeds pressure rating of pump.
Compare pump pressure and ow rate against pump characteristic curve. Check for
closed or partially closed valve in discharge piping system.
Reduce system pressure requirement. Increase pressure capability of pump.
B. Obstruction in suction piping Locate and remove obstruction.
C. Pressure rating of pump exceeds pressure
requirement of system at design ow rate.
Compare pump pressure and ow rate against pump characteristic curve.
Inspect discharge piping system for breaks, leaks, open by-pass valves, etc.
If necessary, reduceow rate by partially closing discharge valve.

 Loading...
Loading...