ENGLISH 33
In a network, the computers need to be able to connect to each other physically.Therefore,
another important network property is how the computers connect to each other, either
directly or through a central device.
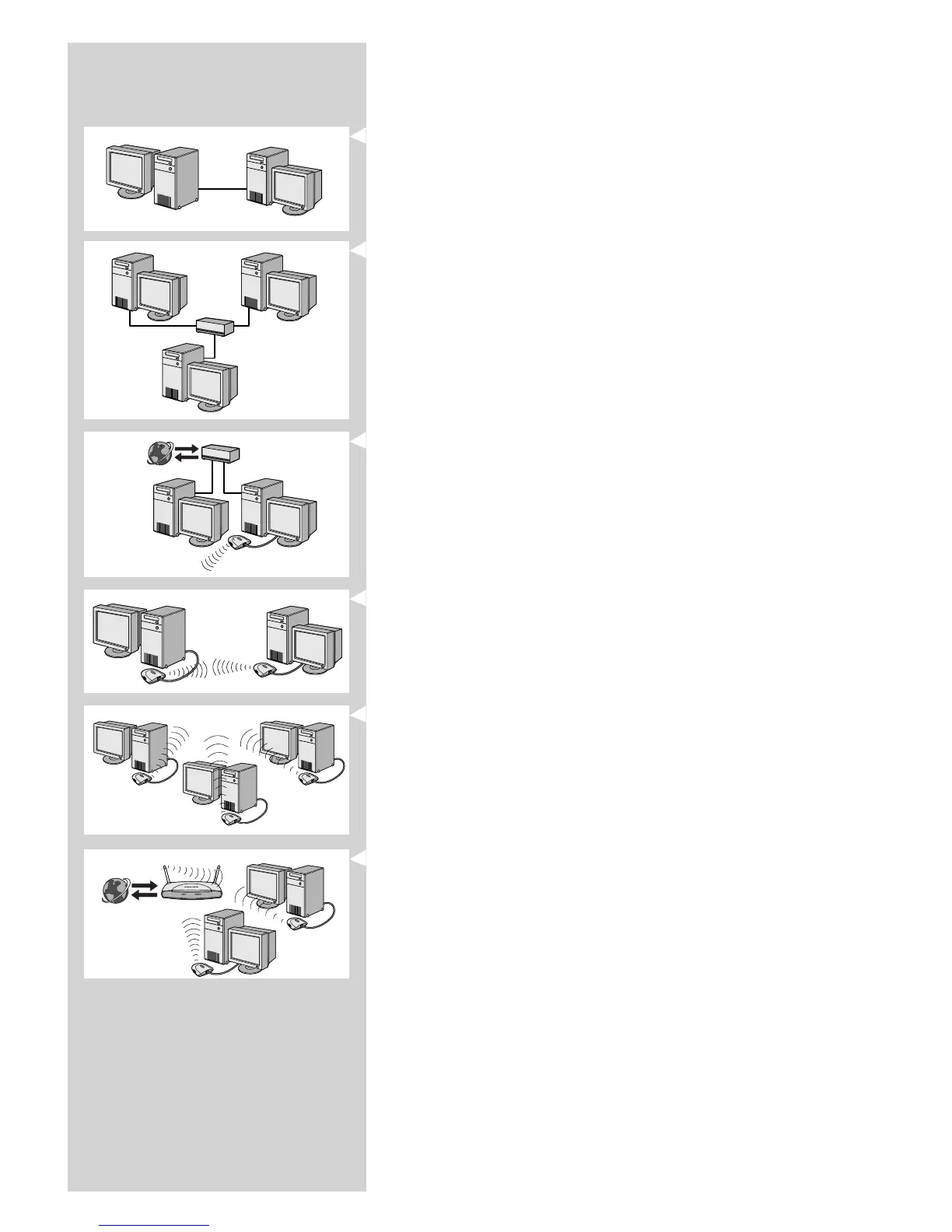
ONE-ON-ONE WIRED NETWORK
also known as: Direct connection network (max. two PCs)
Note: Use a crossover Ethernet cable to connect two computers directly to each other.
WIRED NETWORK WITH MORE THAN TWO PCs
Use a hub or switch to connect more than two PCs to each other.
Note: Use straight-through Ethernet cables to connect the computers to the central device
(hub/switch).
HOW TO INTERCONNECT WIRED NETWORKS
Use a gateway router to connect one network to another (e.g. to the Internet,
also known as WAN).
ONE-ON-ONE WIRELESS NETWORK
also known as: ad-hoc / peer-to-peer
WIRELESS NETWORK WITH MORE THAN TWO PCs
The wireless medium forms a hub in and of itself.
No hardware hub is needed.
Note: For very small networks only.
BRIDGING WIRELESS NETWORKS TO THE INTERNET
(e.g. the Internet, also known as WAN) also known as: infrastructure / access point.
Use a wireless access point or base station.
Central devices, like a hub, switch, router or wireless base station may be stand-alone devices or
built into a computer.
• A hub has multiple ports and serves as a central connection point for communication lines
from all computers on a wired network. It copies all data arriving at one port to the other
ports. A switch is similar to a hub, but is able to handle different network speeds at each
port.
• Gateway routers and wireless base stations route network traffic from one network to
another (e.g. from a wired network to the Internet, or from a wireless network to a wired
network or to the Internet).
Important: Wired and wireless components may be linked together to provide a variety of network
layouts/topologies.
INTERNET
INTERNET
 Loading...
Loading...