Raisecom
RC1201-2GE16E1T1 Product Description
3 Service functions and features
Raisecom Technology Co., Ltd.
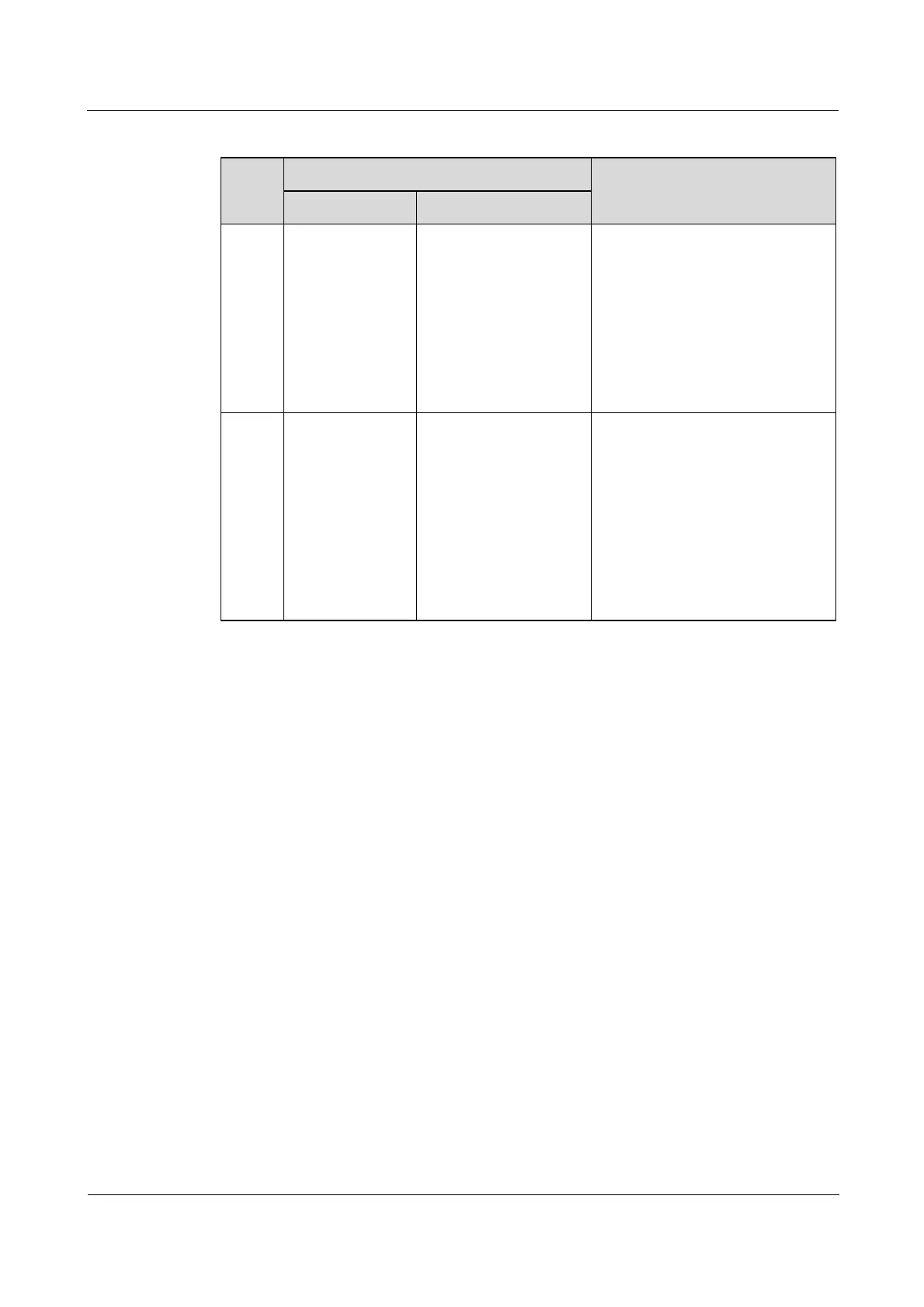
Table 3-1 Ports modes and packet forwarding modes
Forwarding modes for ingress packet
Forwarding modes for egress
packet
Add the Tag of
the Access
VLAN to
packets.
If the VLAN ID for a
packet is identical to
the Access VLAN,
the packet is
received.
If the VLAN ID for a
packet is not identical
to the Access VLAN,
the packet is
discarded.
If the VLAN ID for a packet is
identical to the Access VLAN, the
packet is sent by removing the
Tag.
If the native
VLAN is in the
VLAN ID list on
a port, the packet
is received and is
added with the
Tag of the native
VLAN.
If the VLAN ID for a
packet is in the
VLAN ID list on a
port, the packet is
received.
If the VLAN ID for a
packet is not in the
VLAN ID list on a
port, the packet is
received.
If the VLAN ID for a packet is
identical to the native VLAN
and the packets are allowed to
pass through the port, the packet
is sent by removing the Tag.
If the VLAN ID for a packet is
not identical to the native
VLAN and the packets are
allowed to pass through the port,
the packet is sent by taking its
original Tag.
3.4.3 QinQ
QinQ (also called Stacked VLAN or Double VLAN) technology is an extension of 802.1Q,
which is defined in the 802.1ad standard defined by the IEEE.
Basic QinQ
Basic QinQ is a simple Layer 2 VPN tunnel technology. At the ISP's access end, QinQ
encapsulates an outer VLAN Tag for a private packet, so that the packet traverses the
backbone network of the Internet Service Provider (ISP) carrying double VLAN tags.
On the Internet, the packet is transmitted according to the outer VLAN Tag (public VLAN
Tag). And the private VLAN Tag is transmitted as data in the packet.

 Loading...
Loading...