Desktop Reader Manual V2.1
26/02/2007
7/11
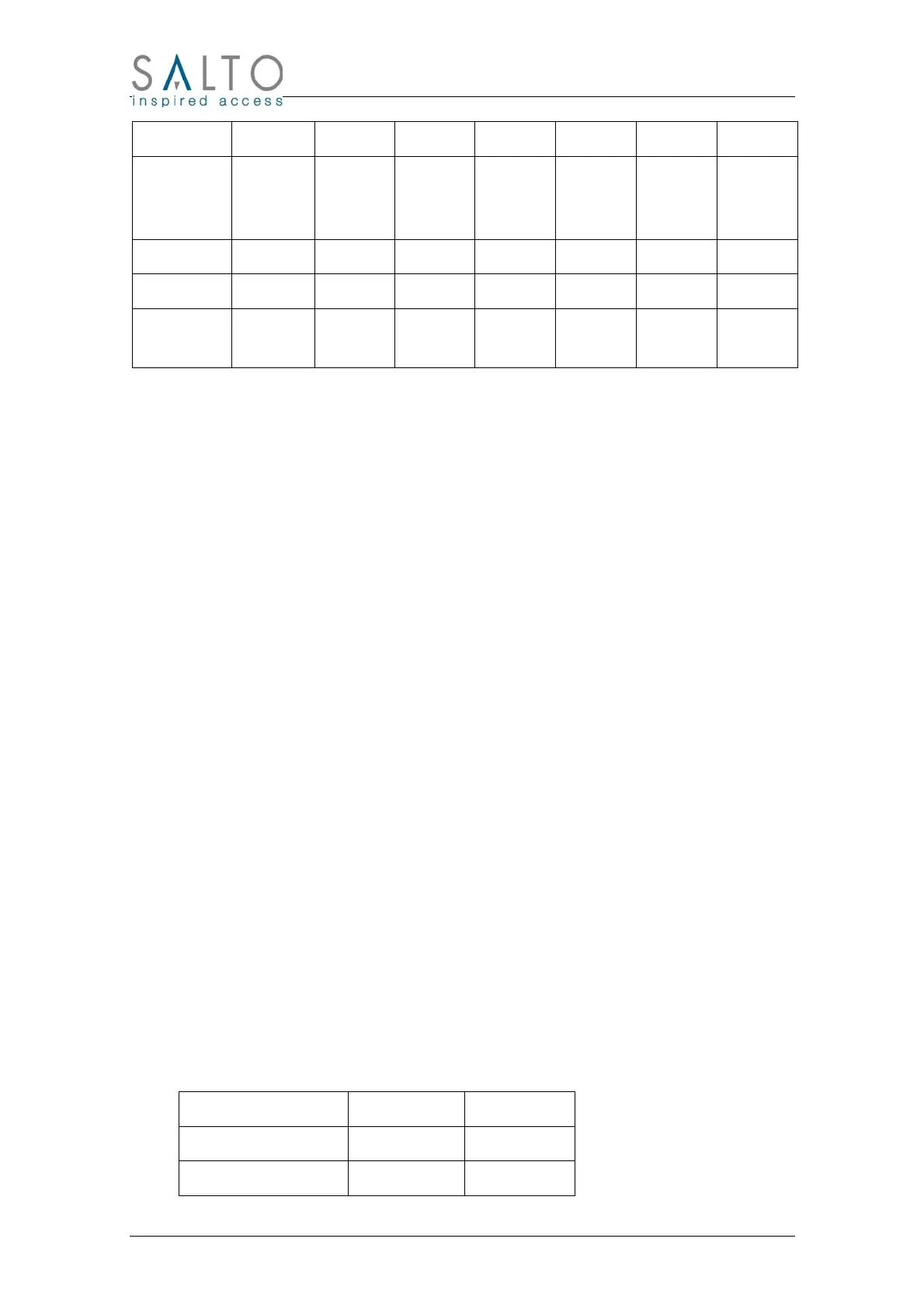
ROM6 ROM5 ROM4 ROM3 ROM2 ROM1 ROM0
Smart Card
AT88SC153
AT88SC1608
IDN0 IDN1 IDN2 IDN3 IDN4 IDN5 IDN6
Legic 0x01 MCD MSN MSN MSN MCC 0x00
Mifare UID0 UID1 UID2 UID3 0x00 0x00 0x00
Desfire
Vicinity
UID0 UID1 UID2 UID3 UID4 UID5 UID6
IButton: Salto ROM code is the laser-programmed Dallas ROM code including at the beginning the
FamilyCode, followed by the Serial Number MSB and excluding the 8
th
byte that is a checksum. These 7
bytes are engraved on the iButton case, FamilyCode on the right and below it the other 6 bytes.
Smart Card SLE4442/SLE5542: The first three bytes are part of the IC Card Manufacturer Code. Next
four bytes are the IC Card Serial Number.
Smart Card AT88SC153 and AT88SC1608: The seven bytes of the Identification Number starting by
the LSB.
Legic: First byte is 0x01 (inexistent iButton FamilyCode), 5 bytes of the Serial Number starting by the
MDC (Manufacture Code) and finishing by the MCC (Manufacture Check Character) and a final null byte
0x00.
Mifare: The first four bytes are the Unique Identifier (UID) also called Serial Number (SN) of the Mifare
card starting by the LSB. Followed by three null bytes (0x00).
Desfire: The seven bytes of the card UID (or Serial Number SN) starting by the LSB.
ISO15693 Vicinity Cards: The seven lower bytes of the UID (or Serial Number SN) starting by the LSB
and removing the UID7 that is always 0xE0 in ISO15693 cards. PicoPass cards are included in this type.
7.2 Tracks
They emulate the tracks of the magnetic stripe cards. There are three Tracks available, TRACK1,
TRACK2 and TRACK3. The information in the emulated tracks are ASCII characters. However, in the
magnetic stripe cards, TRACK1 only carries numeric data, TRACK2 and TRACK3 carry also alphanumeric
data.
7.3 Wiegand code
It is a special track in the cards (called WiegandCode) that carries information of the Wiegand code.
8 Interfaces
There are three types of electrical interface to the terminal:
• RS232 (with different baud rates)
• OMRON (Clock and Data)
• Wiegand (D0 and D1)
8.1 RS232 interface
The RS232 voltage levels do not follow the standard because they do not give negative voltage but work
properly with the modern RS232 interface chips. They use only Rx and Tx without hardware and
software handshake.
Logical Data Rx (volts) Tx (volts)
Zero (0) > 1.2 5
One (1) < 1 0.4
 Loading...
Loading...