Programming a Multiple Instance
10-8
STEP 7 Getting Started
A5E00171228-01
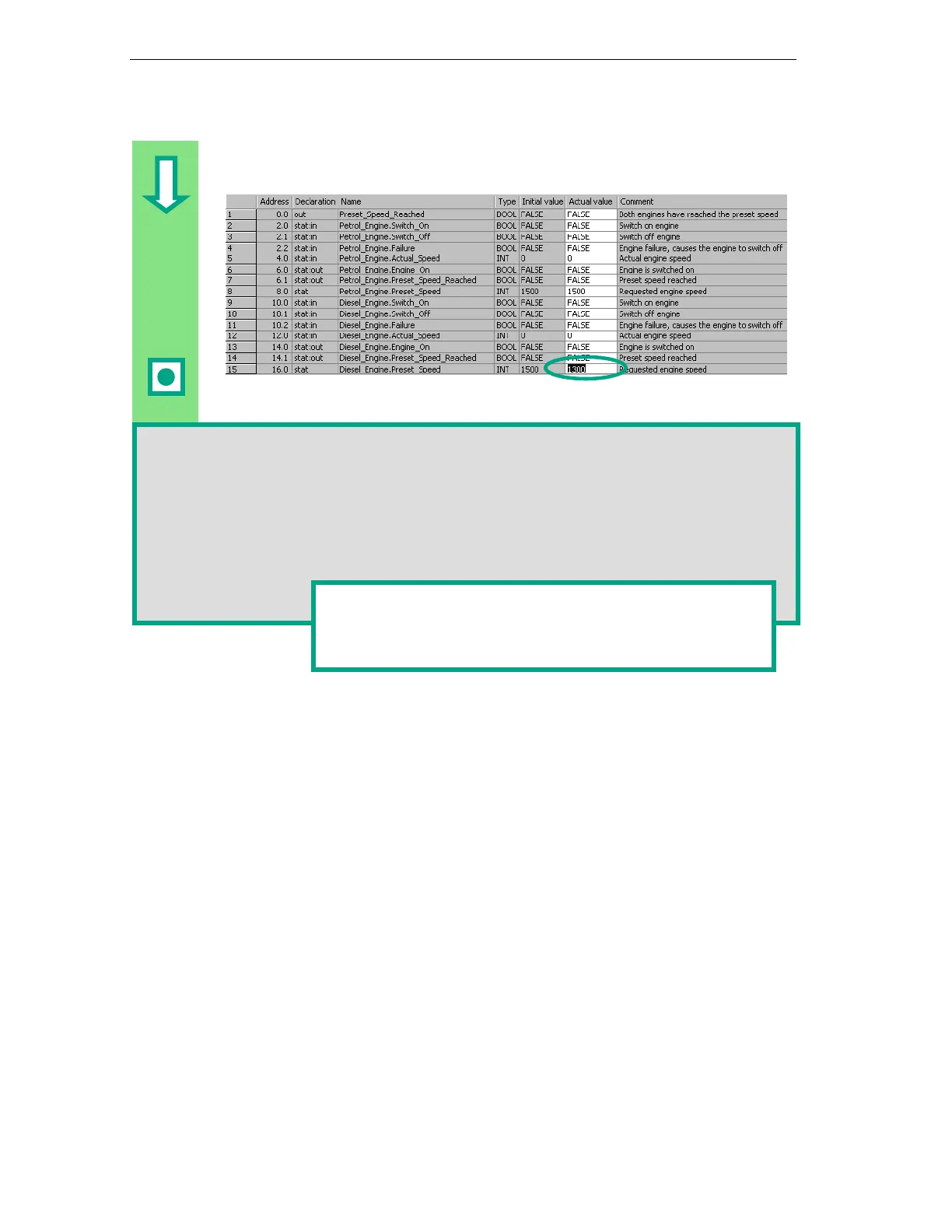
Change the actual value of the diesel engine to "1300," save the block, and then
close it.
All the variables are now contained in the variable declaration table of DB10. In the first half,
you can see the variables for calling the function block "Petrol_Engine" and in the second
half the variables for calling the function block "Diesel_Engine" (see Section 5.5).
The "internal" variables of FB1 retain their symbolic names; for example, "Switch_On." The
name of the local instance is now placed in front of these names; for example,
"Petrol_Engine.Switch_On."
You can find more information under
in the
topics "Programming Blocks" and "Creating Data Blocks."
 Loading...
Loading...











