TS 700, TS 800
English
18
N Work along the cutting line. If
corrections are necessary, always
reposition the cutting wheel, taking
care to ensure that it is not wedged.
The cutting depth per pass should
not exceed 5 to 6 cm (2“ to 2 1/2“).
Thicker material must be cut in
several passes.
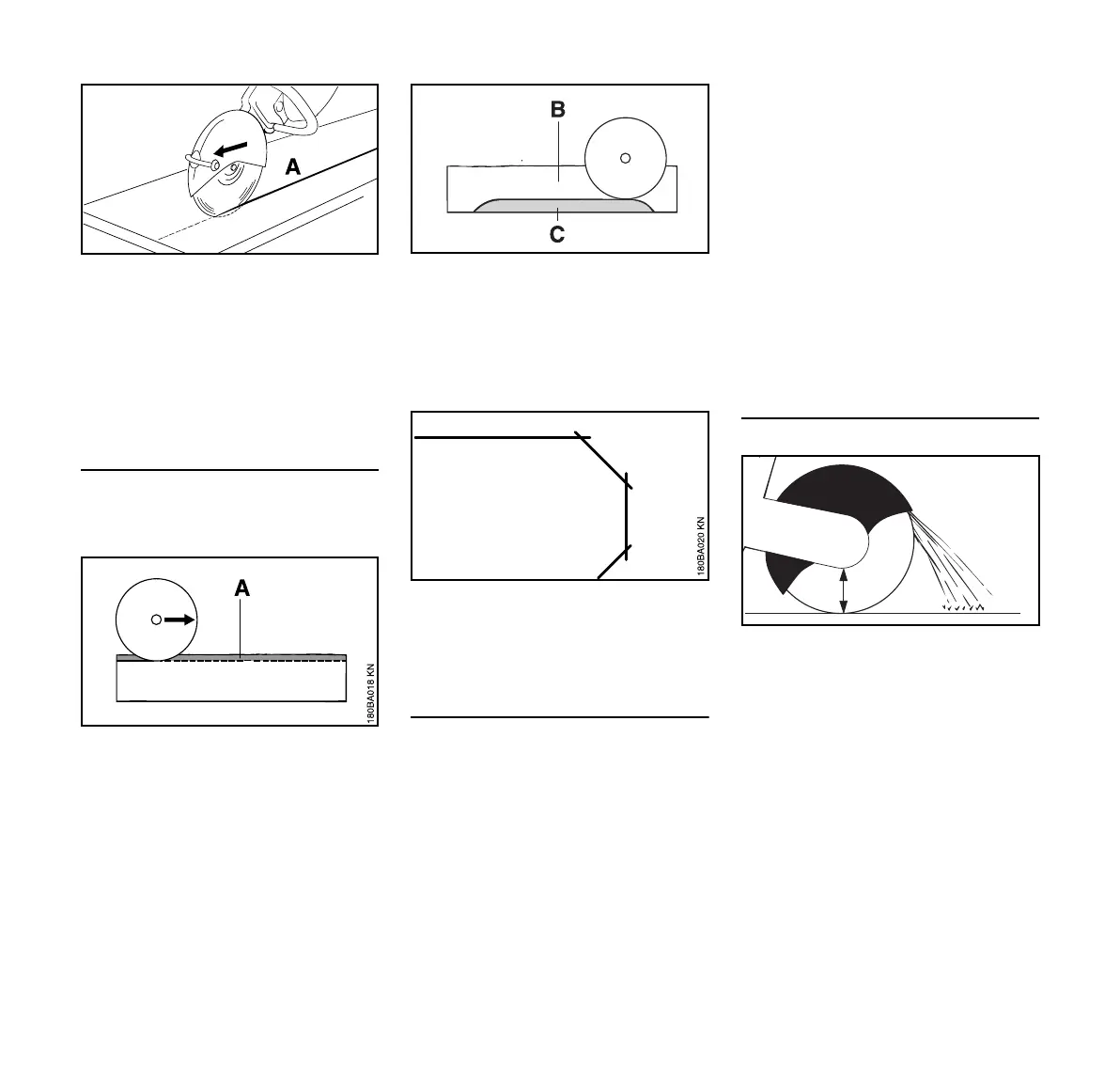
Cutting slabs
N Secure the slab (e. g. on a non-slip
surface, sandbed).
N Cut a guiding groove (A) along the
marked line.
N Cut deeper into the parting cut (B).
N Leave a ridge (C) of uncut material.
N Cut through the slab at the ends so
the material does not chip.
N Then break the slab.
N Curves must be cut in several
straight passes, taking care to
ensure that the cutting wheel does
not become wedged.
Cutting pipes, round and hollow bodies
N Secure pipes, round and hollow
bodies against vibrations, slipping
and rolling away.
N Note direction of fall and weight of
the severed part.
N Determine and mark the cutting line;
avoid metal reinforcement to the
extent possible, especially in the
direction of the severing cut.
N Determine sequence of severing
cuts.
N Grind a guide groove along the line
marked.
N Make cuts deeper along the guide
groove – observe recommended
cutting depth on each pass. For
small corrections of direction, do not
tilt the abrasive wheel, but always
position it anew instead. If
necessary, leave small ridges that
hold the part that is to be separated
in position. Break these ridges
manually after the last cut.
Cutting concrete pipe
The procedure is dependent on the
outer diameter of the pipe and the
maximum possible cutting depth of the
abrasive wheel (A).
N Secure pipe against vibrations,
slipping and rolling away.
N Note weight, tension and direction
of fall of the part to be severed.
180BA027 AM
180BA028 AM
A
002BA557 AM

 Loading...
Loading...