IGNITION
AND
ELECTRICAL
3-3
OPERATION
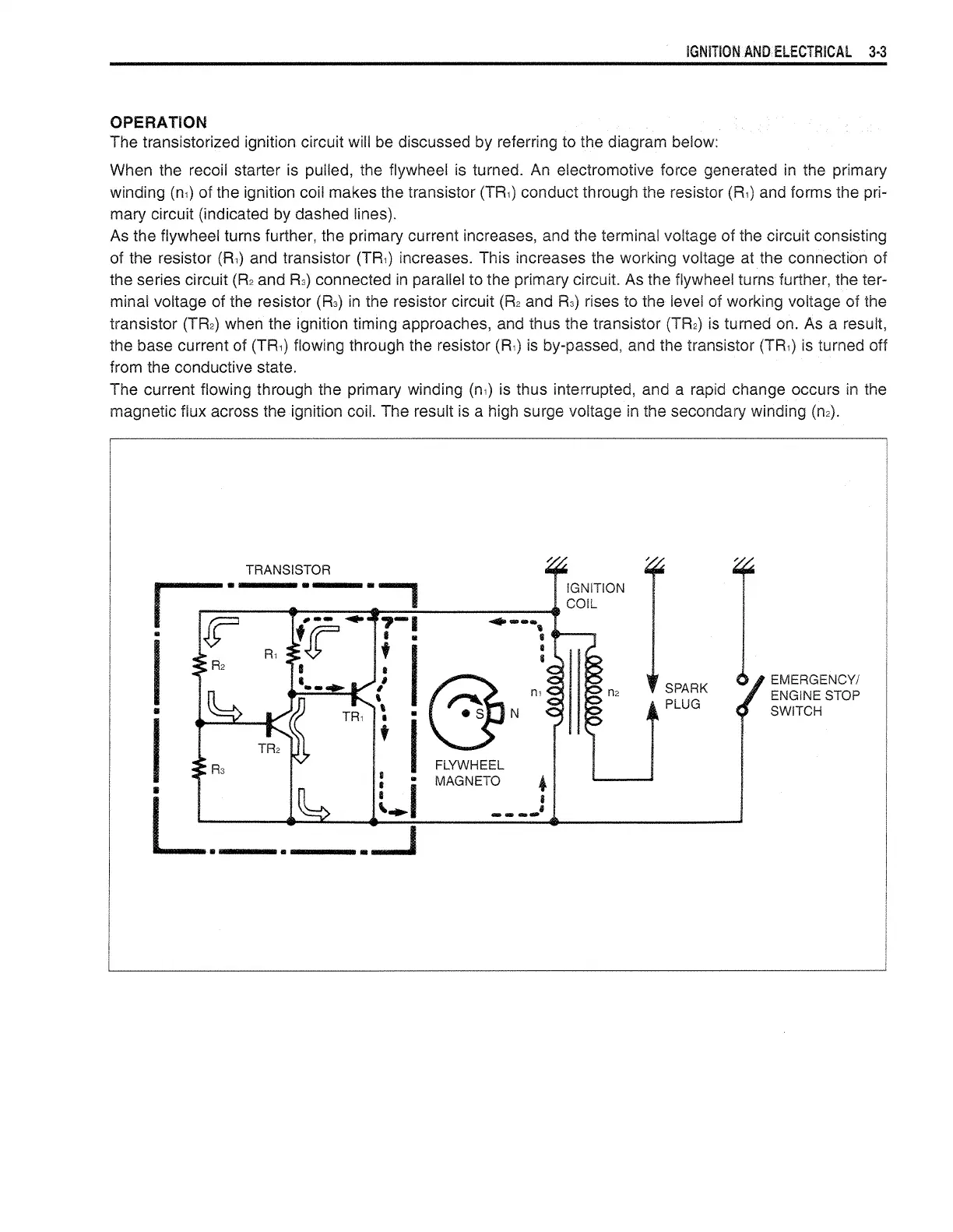
The transistorized ignition circuit will be discussed by referring to the diagram below:
When the recoil starter
is
pulled, the flywheel is turned.
An
electromotive force generated in the primary
winding
(n1)
of the ignition coil makes the transistor
(TR1)
conduct through the resistor
(R1)
and forms the pri-
mary circuit (indicated by dashed lines).
As the
flywheel turns further, the primary current increases, and the terminal voltage of the circuit consisting
of the resistor
(R,) and transistor (TR,) increases. This increases the working voltage at the connection of
the series circuit
(R2
and
R3)
connected
in
parallel to the primary circuit. As the flywheel turns further, the ter-
minal voltage of the resistor
(R3)
in
the resistor circuit
(R2
and
R3)
rises to the level of working voltage of the
transistor
(TR2)
when the ignition timing approaches, and thus the transistor
(TR2)
is
turned on. As a result,
the base current of
(TR1)
flowing through the resistor
(R1)
is by-passed, and the transistor
(TR1)
is
turned off
from the conductive state.
The current
flowing through the primary winding
(n1)
is thus interrupted, and a rapid change occurs
in
the
magnetic flux across the ignition
coil. The result
is
a high surge voltage
in
the secondary winding
(n2).
TRANSISTOR
EMERGENCY/
ENGINE STOP
SWITCH
 Loading...
Loading...