99
Stability problems
The speed control has a PID controller. It ensures an exact and fast adjustment of the
actual value to the set point.
In applications such as solar power systems or feed
pumps, the following parameters should be left in factory settings. With a few
exceptions, the system will run stably. These two values have to be balanced, however,
especially for hygienic hot water from the external heat exchanger. In addition, in this case
the use of an ultrafast sensor (non-standard accessory) is recommended at the hot water
outlet.
Set value = desired value Actual value = temperature measured
PRO 5 Proportional part of the PID controller 5. It represents the reinforcement of the
deviation between the desired and the actual value. The speed is changed by one
increment for each 0.
5K of deviation from the desired value. A large number leads
to a more stable system but also to more deviation from the predefined
temperature. (ex works = 5) Setting range: 0 to 100
INT 5 Integral part of the PID controller 5. It periodically adjusts the speed relative to the
deviation remaining from the proportional part. For each
1K of deviation from the
desired value, the speed changes one increment every
5 seconds. A large
number provides a more stable system, but it then takes longer to reach the
desired value. (ex works = 0) Setting range: 0 to 100
DIF 5 Differential part of the PID controller 5. The faster a deviation occurs between the
desired and the current value, the greater the short-term overreaction will be to
provide the fastest compensation possible. If the desired value deviates at a rate
of 0.
5K per second, the speed is changed by one increment. Large numbers
provide a more stable system, but it then takes longer to reach the desired value.
(ex works = 0) Setting range: 0 to 100
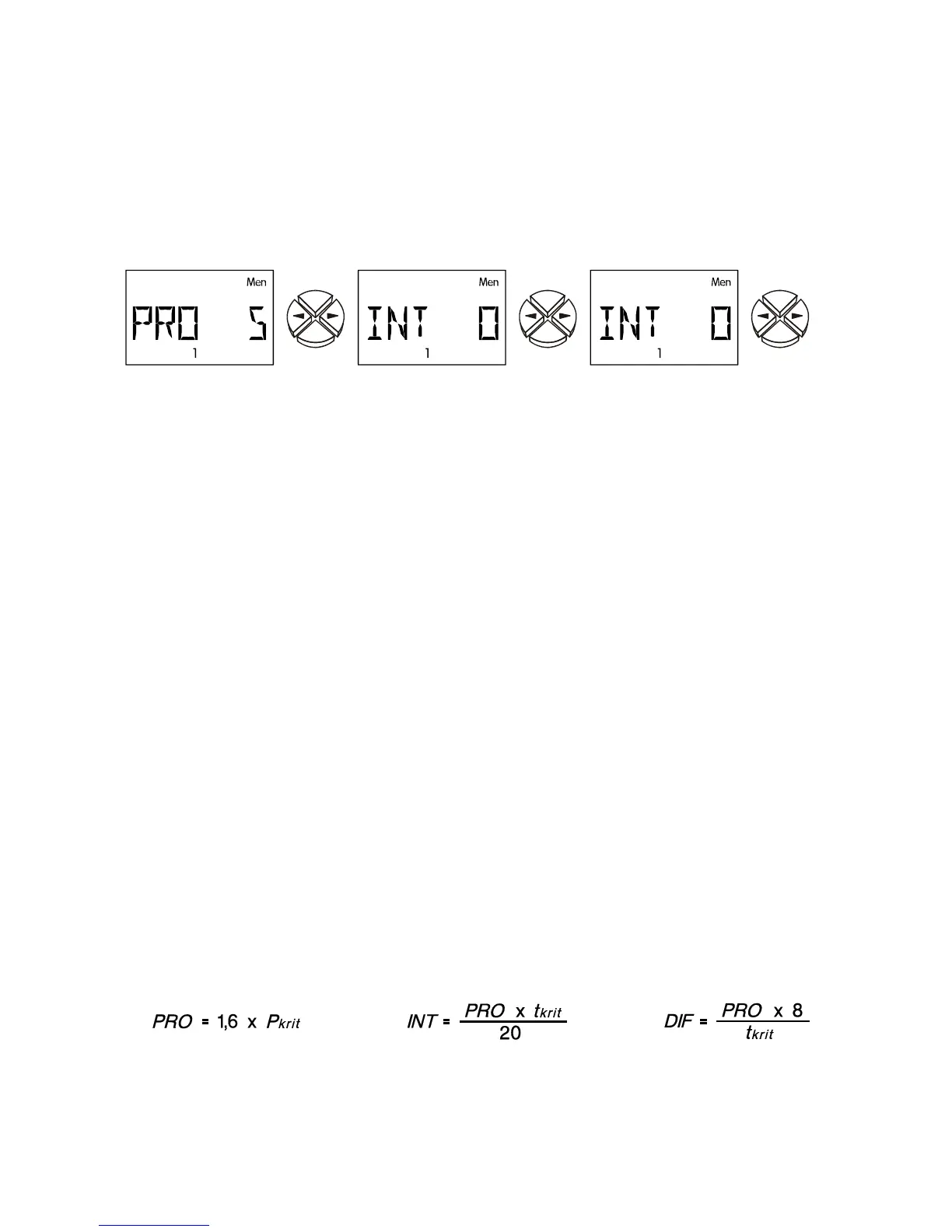
The parameters PRO, INT, and DIF can also be determined in a test: Assume that the
pump is running in automatic mode in a unit that is ready for operation with appropriate
temperatures. With INT and DIF set to zero (= switched off), PRO is reduced every 30
seconds starting at 9 until the system is instable. In other words, the pump speed changes
rhythmically and can be read in the menu with the command ACT. Every proportional part
that becomes instable is noted as P
krit
just as the duration of the oscillation (= time between
the two highest speeds) is noted as t
krit
. The following formulas can be used to determine the
correct parameters.
A typical result of hygienic service water with the ultrafast sensor is PRO = 8, INT = 9, DIF
= 3. For reasons not entirely understood, the setting PRO = 3, INT = 1, DIF = 4 has proven
practical. Probably, the control unit is so unstable that it oscillates very quickly and appears to
be balanced due to the system’s and the fluid’s inertia.

 Loading...
Loading...