ADOBE FRAMEMAKER 10
MIF Reference
203
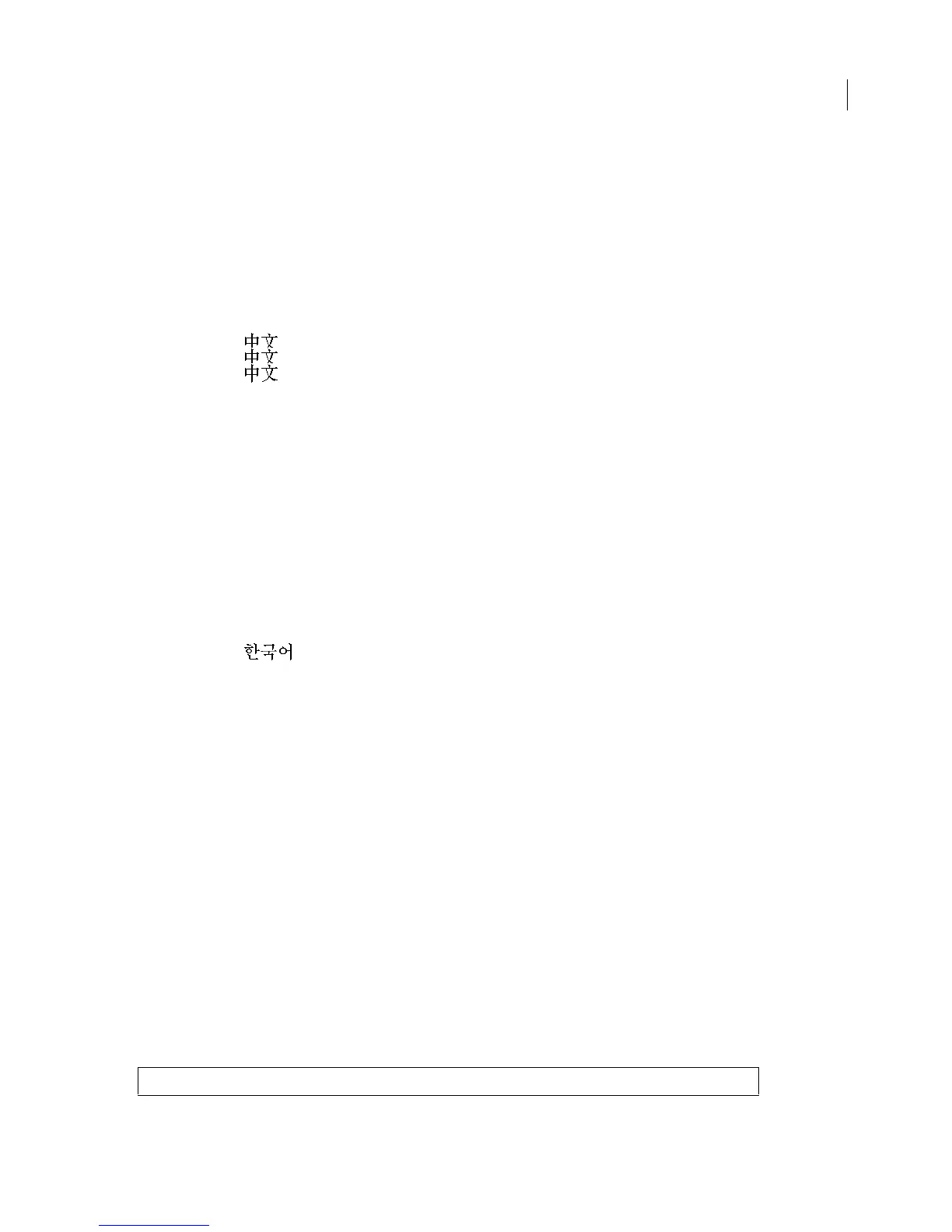
To determine which encoding was used, each MIF file that contains Chinese text must include a MIFEncoding
statement near the beginning of the file. It must appear before any Chinese text in the file. The string value in the
MIFEncoding statement is the Chinese spelling of the word “Chinese”. FrameMaker reads this fixed string and deter-
mines what the hexadecimal encoding is for it. From that, FrameMaker expects the same encoding to be used for all
subsequent Asian text in the document.
To see the characters spelling the word “Chinese”, you must view the MIF file on a system that is enabled for Chinese
character display. When the MIF is displayed on a Roman system, the characters appear garbled.
Syntax
<MIFEncoding ` ‘> # originally written as Traditional Chinese (Big5)
<MIFEncoding ` ‘> # originally written as Traditional Chinese (CNS)
<MIFEncoding ` ‘> # originally written as Simplified Chinese
MIFEncoding statement for Korean
FrameMaker recognizes one encoding scheme for Korean: KSC5601. All platform versions of FrameMaker write
KSC5601 for Korean.
Each MIF file that contains Korean text must include a
MIFEncoding statement near the beginning of the file. It must
appear before any Korean text in the file. The string value in the
MIFEncoding statement is the Korean spelling of
the word “Korean.” FrameMaker reads this fixed string and determines what the hexadecimal encoding is for it.
From that, FrameMaker expects the same encoding to be used for all subsequent Asian text in the document.
To see the characters spelling the word “Korean.”, you must view the MIF file on a system that is enabled for Korean
character display. When the MIF is displayed on a Roman system, the characters appear garbled.
Syntax
<MIFEncoding ` ‘> # originally written as Korean
Combined Fonts
Combined fonts assign two component fonts to one combined font name. This is done to handle both an Asian font
and a Western font as though they are in one font family. In a combined font, the Asian font is the base font, and the
Roman font is the Western font. For example, you can create a combined font named Mincho-Palatino that uses
Mincho for Asian characters and switches to Palatino for Roman characters.
When reading a MIF paragraph that uses Mincho-Palatino, FrameMaker displays Asian characters in Mincho and
Roman characters in Palatino. If the Mincho font is not installed on the user’s system, FrameMaker displays the Asian
text in a font that uses the same character encoding as Mincho.
CombinedFontCatalog statement
Combined fonts are defined for the document in the CombinedFontCatalog statement. For each combined font,
there is a
CombinedFontDefn statement that specifies the combined font name and identifies the Asian and the
Roman component fonts. Note that the combined font catalog must precede the first
PgfFont and Font statements
in the document.
Syntax
<CombinedFontCatalog
 Loading...
Loading...











