ALESIS FUSION
ANALOG SYNTHESIS TUTORIAL
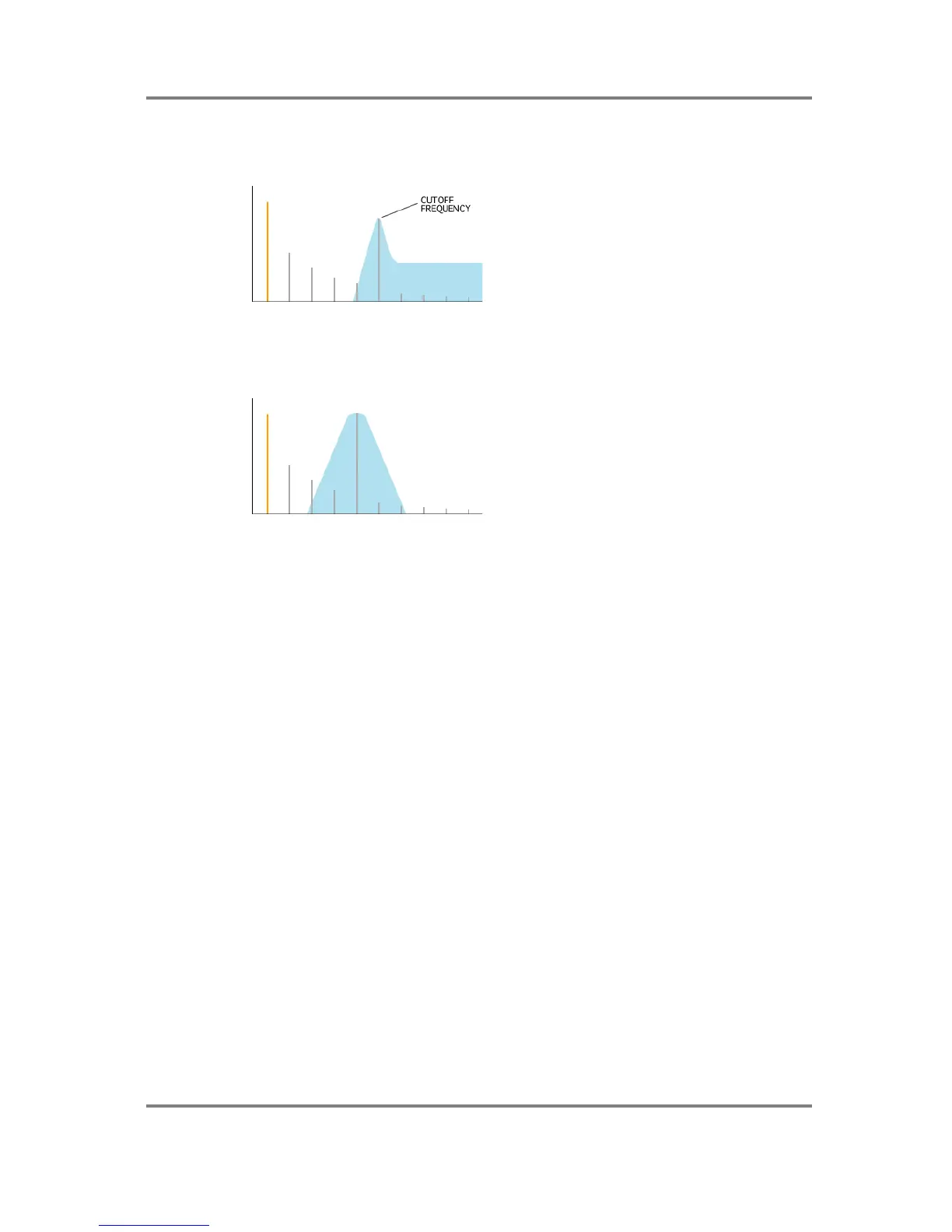
Of course, similar things happen with other filter types - for example, a highpass filter:
With a bandpass filter, the ‘band’ becomes
narrower with higher resonance settings thus
emphasising the harmonics in the area of the cutoff frequency:
Resonance is an intrinsic component of many analog synthesiser sounds. Unfortunately, in
the early days of synthesis (late
60s, early 70s), it was overused (and employed as a gimmick)
and so the analog synthesiser became synonymous with
‘duck quack’ and ‘strangled cat’
sounds. However, resonance can be used tastefully to create some truly spectacular synth
textures.
Filter slope / roll-off
Another (and final!) aspect to filters is their cutoff or ‘roll-off’ slope.
In the diagrams shown on previous pages, the filter roll-off above the CUTOFF
FREQUENCY is
at an angle - it is not abrupt and straight down. This is known as the ROLL-OFF
SLOPE and on
modern VA synths, it is possible to define this as an adjustable parameter.
On the
original analog synths, the roll-off was usually fixed (although some synths did offer a
switched option for an alternative). The most common filter slopes were:
12dB/Octave
Also known as a ‘2-pole’ filter. The roll-off is actually
quite gentle and gradually
attenuates/filters harmonics above or below the cutoff frequency
24dB/Octave
Also
known as a ‘4-pole’ filter, the roll-off is quite steep and attenuates/filters
harmonics above or below the cutoff frequency more dramatically.
Of the two, the 24dB/Octave filter was generally preferred as it has a ‘punchy’
sound and it was
common on many American-made synths from Moog and Sequential Circuits.
The
12dB/Octave filter, because of its gentler roll-off, allowed more harmonics above/below the
cutoff point to pass through and so was regarded
by many as a bit weak and ‘fizzy’. It was
common on many Japanese-made synths but was also adopted by US
manufacturer,
Oberheim (although they offered a switchable 4-pole
filter option in later models). Many
Japanese manufacturers followed suit.
Sound processors / modifiers
Page
15

 Loading...
Loading...




