ALESIS FUSION
ANALOG SYNTHESIS TUTORIAL
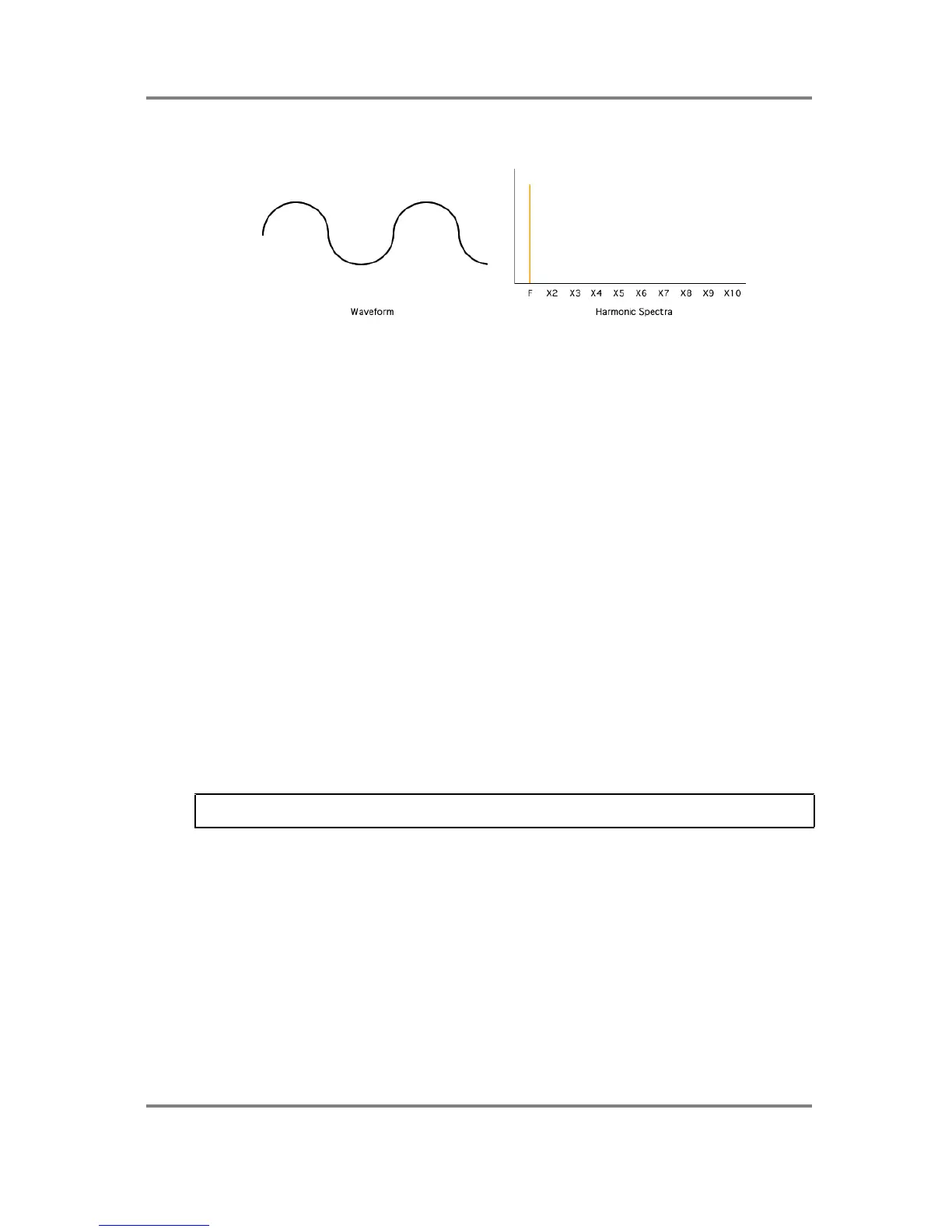
Sine wave
The sine wave is the simplest waveform known and has only a fundamental with no harmonics
at all. As such, it is a very ‘unnatural’ sounding waveform (there is no sound in nature
or musical
instrument that doesn’t contain
any
harmonics) and therefore is
very good for creating pure
sounds. It
is also very good for creating ‘sci-fi’ sounds because the early electronic music
pioneers
of the 50s and 60s only had very simple sine wave oscillators to play with. The
humble
sine wave is also very useful for reinforcing the fundamental of other waveforms and
comes into its own as a ‘sub-bass’ reinforcing the fundamental of a bass sound an
octave down
where it’s not so much heard as ‘felt’. This is not a new technique - church organists have
been
using it for centuries!!!
Noise generators
So far, we have only looked at pitched waveforms. There
are also sounds (such as drums and
sound effects... wind, surf,
etc.) that have unpitched elements. These are created on an
analog synthesiser using a noise generator.
Noise is made
up of every frequency in the audio spectrum sounding at once. The most
commonly known is white noise, so called
because, like white light, it has an even distribution
of frequencies across the spectrum. However, there are also other types of noise such as pink
noise where the frequencies are balanced across the musical octaves.
The technicalities
are largely irrelevant - all you need to know is that white noise is bright and
‘hissy’
and suitable for wind and breath sounds whilst pink noise has more ‘rumble’ and is
useful for thunder and surf sound effects.
Fusion also offers a
red noise option which is even more biased towards the low frequencies
and is seriously menacing and ‘rumbly’.
NOTE:
Noise has no pitch parameter and is not possible to ‘play’ noise in
the conventional
sense of the word - in other words, you can’t pick out a tune using noise!!!
Sound generators
Page 6

 Loading...
Loading...




