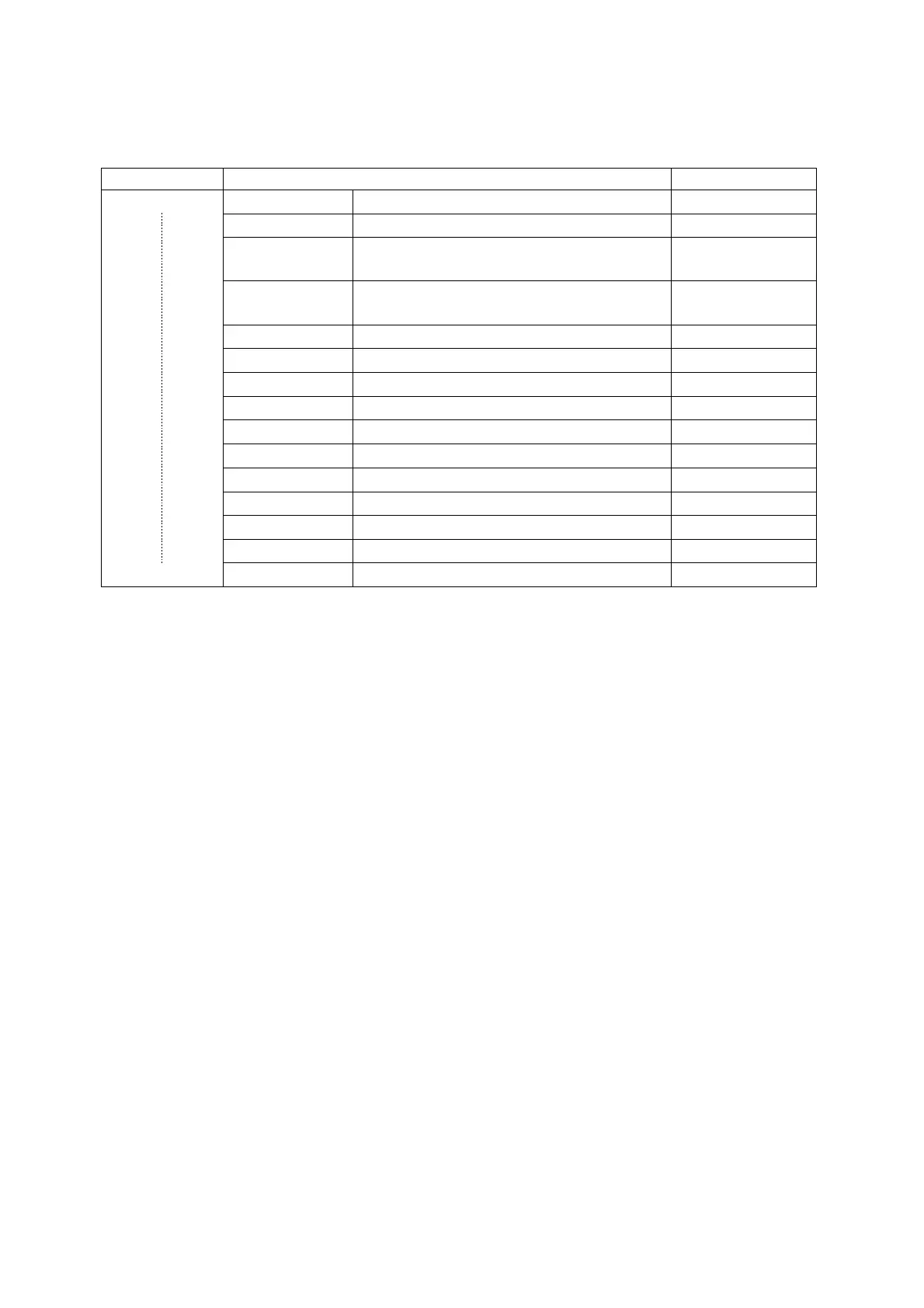
!, ~, ++, --, -, (type), *, &, sizeof
=, +=, -=, *=, /=, <<=, >>=, &=, ^=, |=
Note: Order of precedence is complicated. It is a good practice to use parenthesis
wherever the intention of the statement can be confusing for someone reading the
program, if not for the interpreter.
6.2.1 Cast operator
Data types are ranked as follows, with rank increasing from left to right:
Char < int < long < float < double …
In expressions with mixed data types, C will first convert all data to the same type as
that of the highest ranked data included in the expression, and then perform the
calculation. This is called implicit type conversion or type coercion.
This can become very complicated when unsigned types are involved. At the big
difference of BASIC that allows for one numeric type only, programming in C forces
to think carefully about minimum and maximum values that could occur, in order to
select the right data type and avoid unexpected results.
 Loading...
Loading...