6.2.2 Variable types and operations
Declaring variable types
With C programs, you have to declare the type of data that will be assigned to each
variable before you can use the variable. The following statement, for example, tells
the computer that the variable “x” will be used for the storage of integers:
int x;
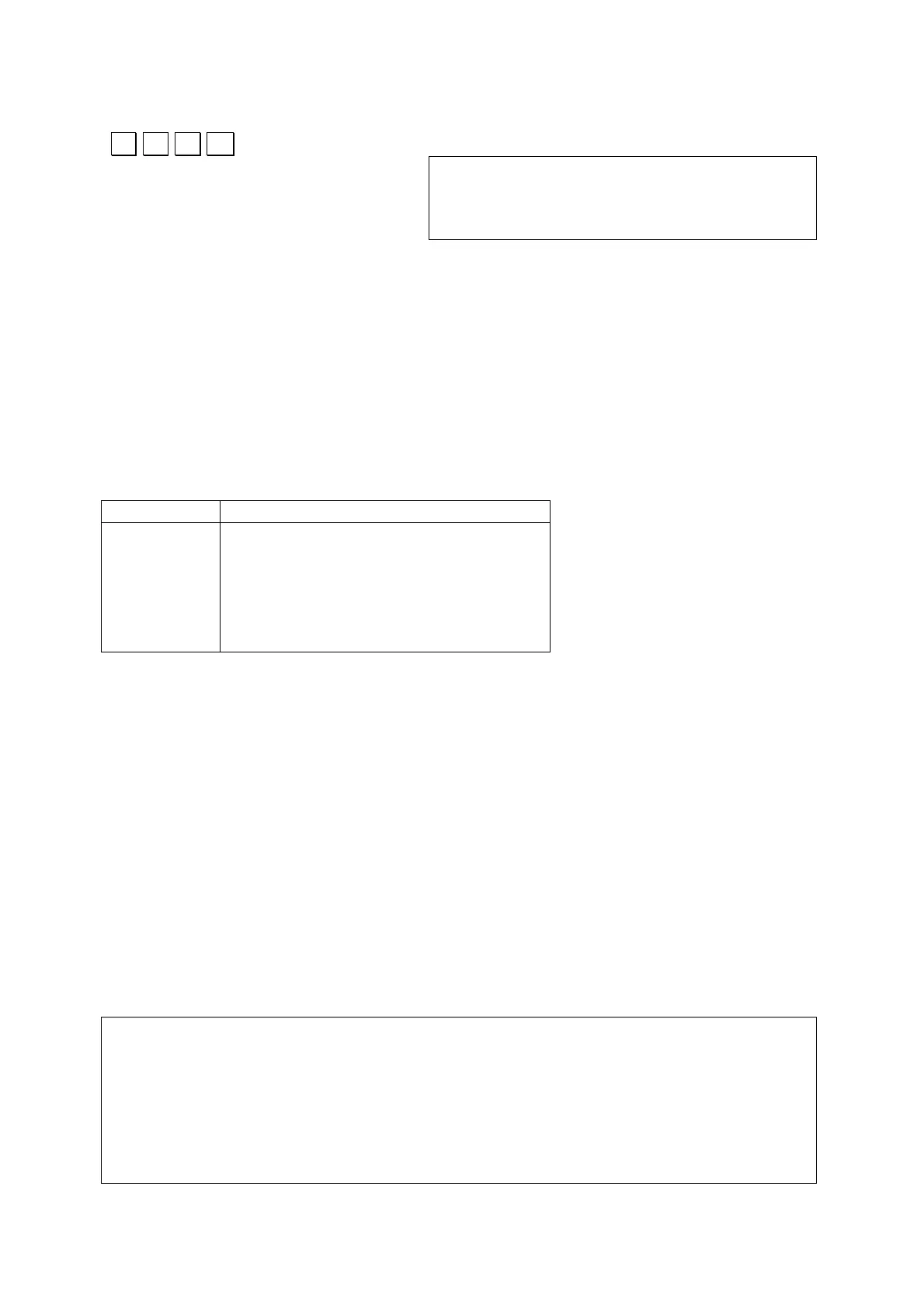
The following table shows the other declarations that can be made for variables.
Besides these, you can also include the declaration “unsigned” in front of any of the
integer declaration (except long) to indicate that the integer is unsigned (no
positive/negative sign)
*Note: the “int” declaration is hardware dependent, despite the fact it is the default
type in many cases, and the fastest for arithmetics. On the pocket computer, which
uses a 16-bit microprocessor, it refers to a 16-bit integer. But on other processors, it
may refer to 24-bit or 32-bit integers. For best portability, it is recommended to use
the “short” declaration instead, when possible.
Assigning values to variables
To see how to declare variables and also how to assign values, let’s write a program
that performs various operations using the values 49 and 12.
Enter the editor and input the following program.
/* Arithmetic Operations 1 */
main(){
short a,b,c,d,e;
a=49+12;printf(“%d “,a);
b=49-12;printf(“%d “,b);
c=49*12;printf(“%d “,c);
d=49/12;printf(“%d “,d);
e=49%12;printf(“%d¥n“,e);
 Loading...
Loading...