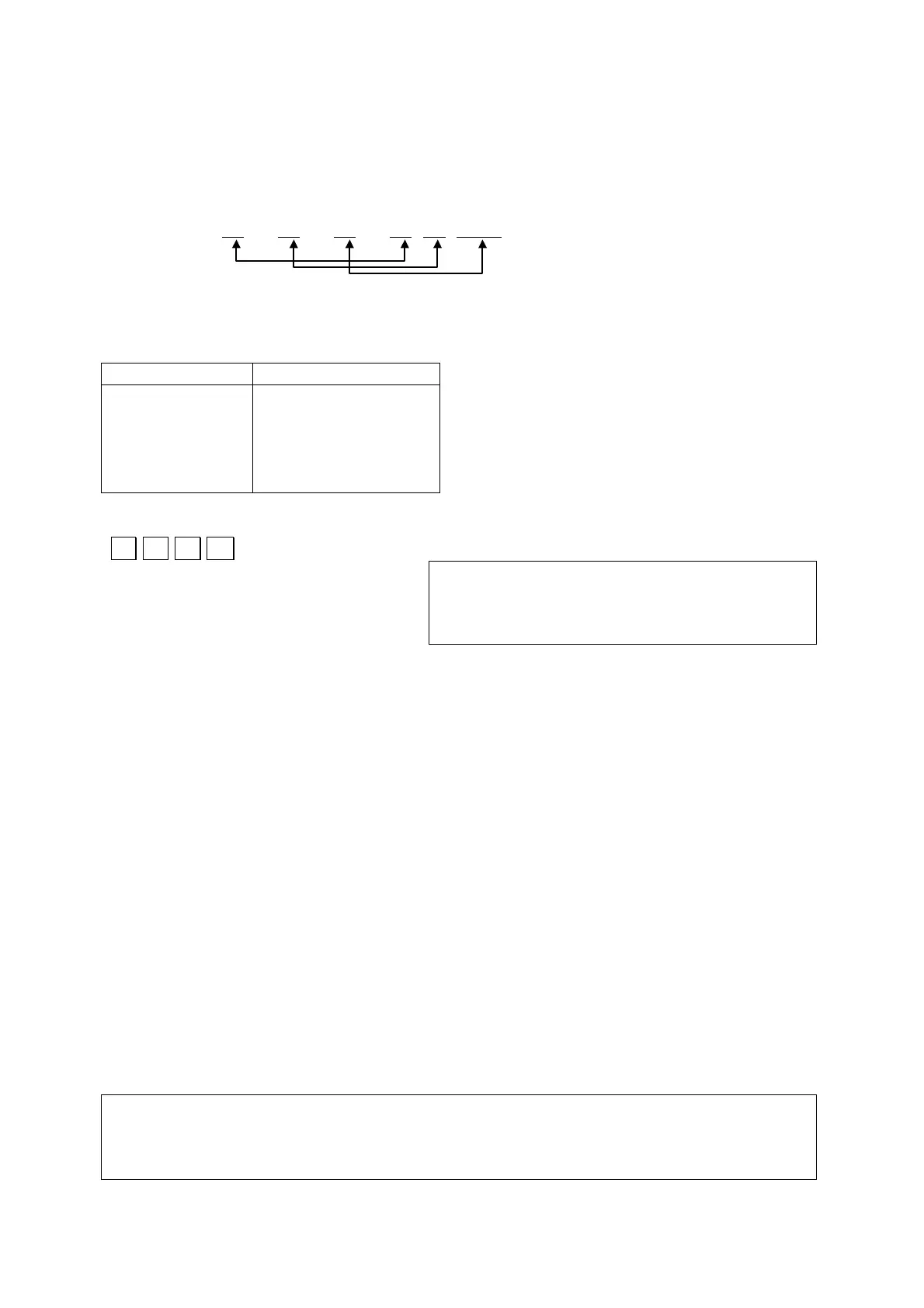
Note that there is a direct relationship with
• the 1
st
% construction and the 2
nd
argument
• the 2
nd
% construction and the 3
rd
argument
• the 3
rd
% construction and the 4
th
argument.
printf(“D=%d H=%x F=%f¥n”65,65,65.0);
You just have to be careful to ensure that the proper % construction is matched with
the proper value, or else you will get strange results. Here is a list of some other %
constructions in addition to those noted above.
Here we can see that the decimal equivalent of 65 is 65, the hexadecimal equivalent
is 41, and the floating-point equivalent is 65.000000.
Integer notation in C
In the previous program, the decimal value 65 was converted in accordance with
three corresponding % constructions. In some instances, however, you might want to
include the actual values as they are in printf() arguments, without conversion when
they are displayed. To do this, you have to specify the value as an integer constant.
With C, you can specify decimal, octal and hexadecimal values, as well as characters
as integer constant. Use the following formats to specify values or characters of
integer constants.
• 65 – displayed as decimal integer 65
• 0101 – displayed as octal value 101. Include 0 in the first digit of an octal value
to specify it as an integer constant.
• 0x41 – displayed as hexadecimal value 41. Include 0x in the first two digits of a
hexadecimal value to display it as an integer constant.
• ‘A’ – displayed as a single character. Include the character in single quotes.
If you go back to our last program and change the printf() arguments as noted below:
 Loading...
Loading...