142 Cisco LAN Switching Configuration Handbook
subnet) are well known and don’t require registration. You can find other well-known
multicast addresses listed in Appendix B, “Well-Known Protocol, Port, and other
Numbers.”
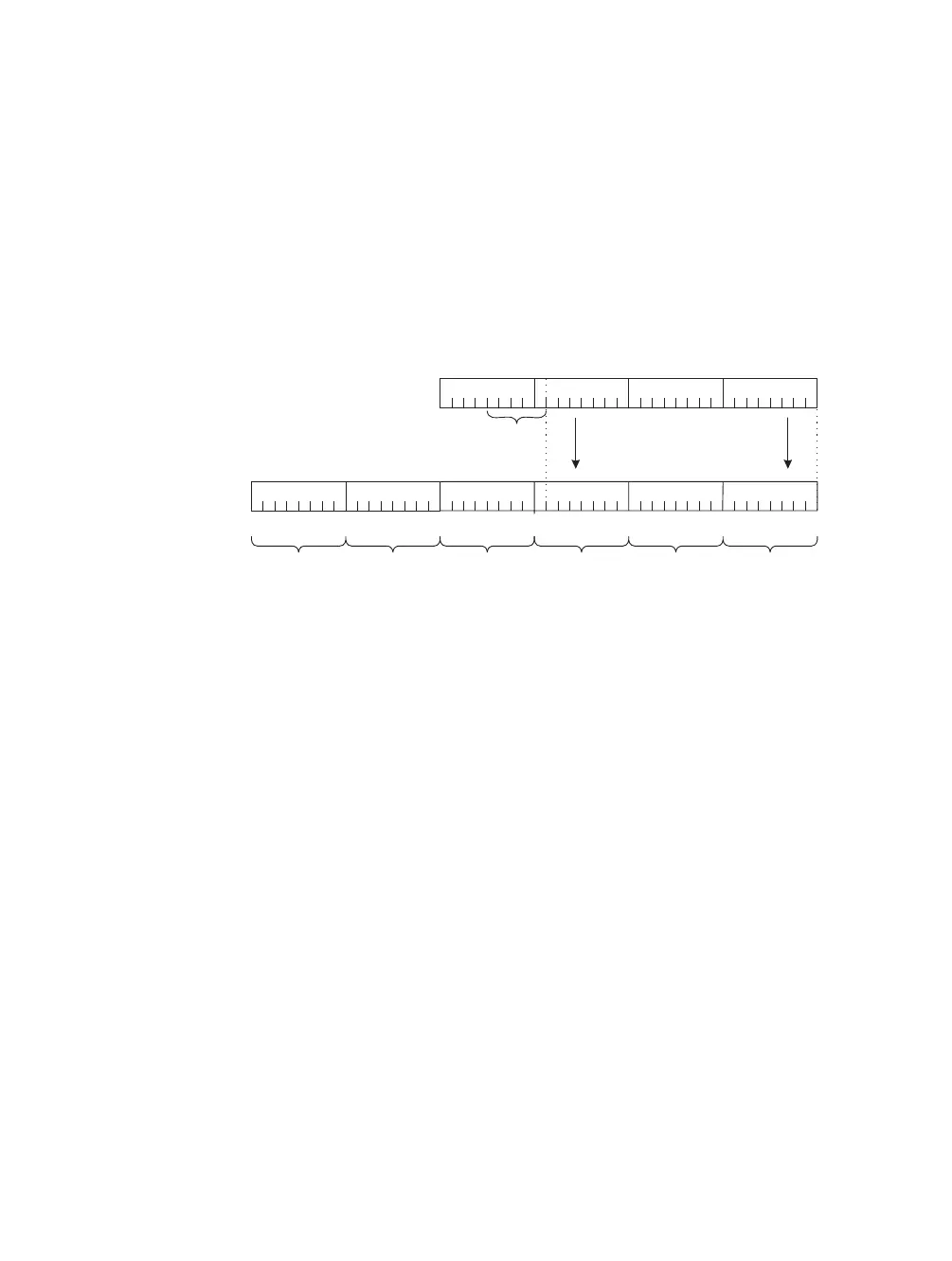
■ Multicast also uses Ethernet or MAC addresses beginning with 01-00-5e. (The least-
significant bit of the high-order byte is always 1.) The multicast IP addresses must be
translated into multicast MAC addresses in this fashion, following the structure
shown in Figure 9-1:
■ The 25 most-significant bits in the MAC address are always 01-00-5e.
■ The 23 lowest-significant bits are copied from the 23 lowest-significant bits of
the IP address.
■ The address translation is not unique; 5 bits of the IP address are not used,
therefore, 32 different IP addresses can all correspond to a single multicast
MAC address.
9-2: IGMP Snooping
■ Some Catalyst switches can be configured to intercept IGMP join requests as hosts
ask to join IP multicast groups.
■ IGMP join requests can occur as the following happens:
■ Hosts send unsolicited membership reports to join specific multicast groups.
■ Multicast routers acting as IGMP queriers send IGMP membership query mes-
sages to the all-hosts multicast group 224.0.0.1 every 60 seconds. Interested
hosts respond with membership reports to join specific multicast groups.
■ The switch keeps a record of the IP multicast group, its Layer 2 MAC address, and
the switch ports that connect to the requesting host and the multicast router.
1110
10000000 00000000
01 00 5e
224-239
010111100
.
x
.
y
.
z
23 Bits Transferred
to MAC Address
5 Bits
Unused
IP Multicast Address
Multicast MAC Address
xyz
Figure 9-1 Multicast Address Translation
 Loading...
Loading...











