224 Cisco LAN Switching Configuration Handbook
■ Low (1)
■ Medium (2)
■ High (3)
Traffic in the AF classes can be dropped, with the most likelihood of dropping in the
Low category and the least in the High category. In other words, service level AF class 4
with drop precedence 3 is delivered before AF class 4 with drop precedence 1, which is
delivered before AF class 3 with drop precedence 3, and so on.
Class 5 is also called the Expedited Forwarding (EF) class, offering premium service and
the least likelihood of packet drops. The Default class selector (DSCP 000 000) offers
only best-effort forwarding.
Class 6, Internetwork Control, and Class 7, Network Control, are both set aside for net-
work control traffic. This includes the Spanning Tree Protocol and routing protocols, traf-
fic that is not user-generated but usually considered high-priority.
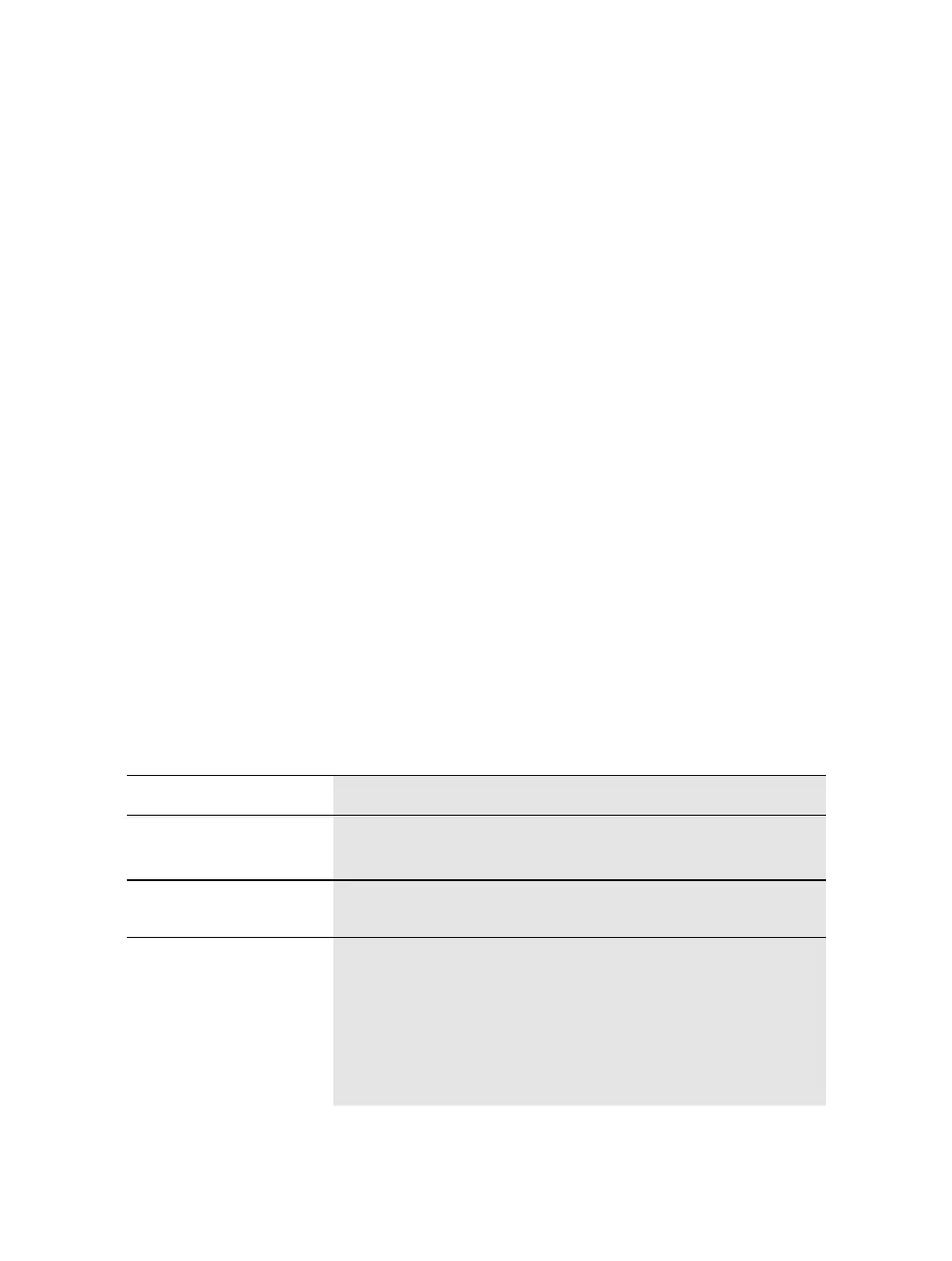
Table 13-1 shows how the IP precedence names and bits have been mapped to DSCP val-
ues. DSCP is broken down by per-hop behavior (PHB), class selector, and drop prece-
dence. Many times, DSCP values are referred to by the codepoint name (AF23, for exam-
ple), which are also listed in the table. The DSCP bits are shown along with their decimal
equivalent. In many DSCP-related commands, you need to enter a decimal DSCP value,
even though it is difficult to relate the decimal numbers with the corresponding DSCP
service levels and PHBs. Use this table as a convenient cross-reference.
Table 13-1 Mapping of IP Precedence and DSCP Fields
IP Precedence (3 Bits) DSCP (6 Bits)
Name Value Bits
Per-Hop
Behavior
Class
Selector
Drop
Precedence
Codepoint
Name
DSCP Bits
(Decimal)
Routine 0 000 Default — — Default 000 000 (0)
Priority 1 001 AF 1 1: Low AF11 001 010 (10)
2: Medium AF12 001 100 (12)
3: High AF13 001 110 (14)
 Loading...
Loading...











