8
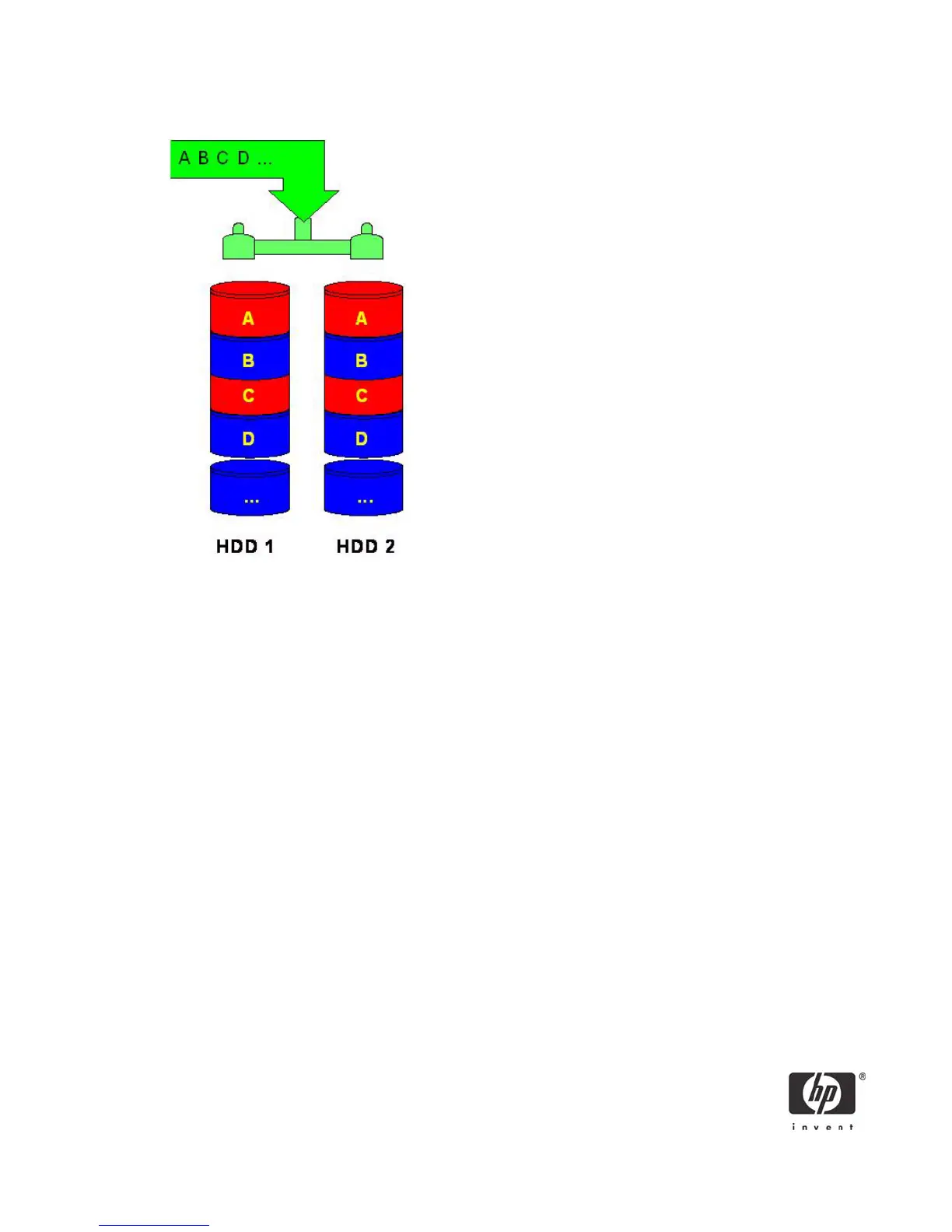
Figure 3 Reliability: RAID 1 - Mirroring
RAID 5 with three hard drives
RAID 5 has been used in servers for many years and is one of the most common types of RAID. RAID 5
uses striping with parity data in distributed blocks across all member disks. Therefore, the mass storage
controller can simultaneously write new information to two hard drives and parity information to the third
hard drive, so if one hard drive fails, the RAID controller can rebuild all the information after the volume
degradation occurred. Hence, RAID 5 with three hard drives has similar performance to RAID 0 with two
hard drives, and the reliability of RAID 1 with a minimum of three hard drives.

 Loading...
Loading...















