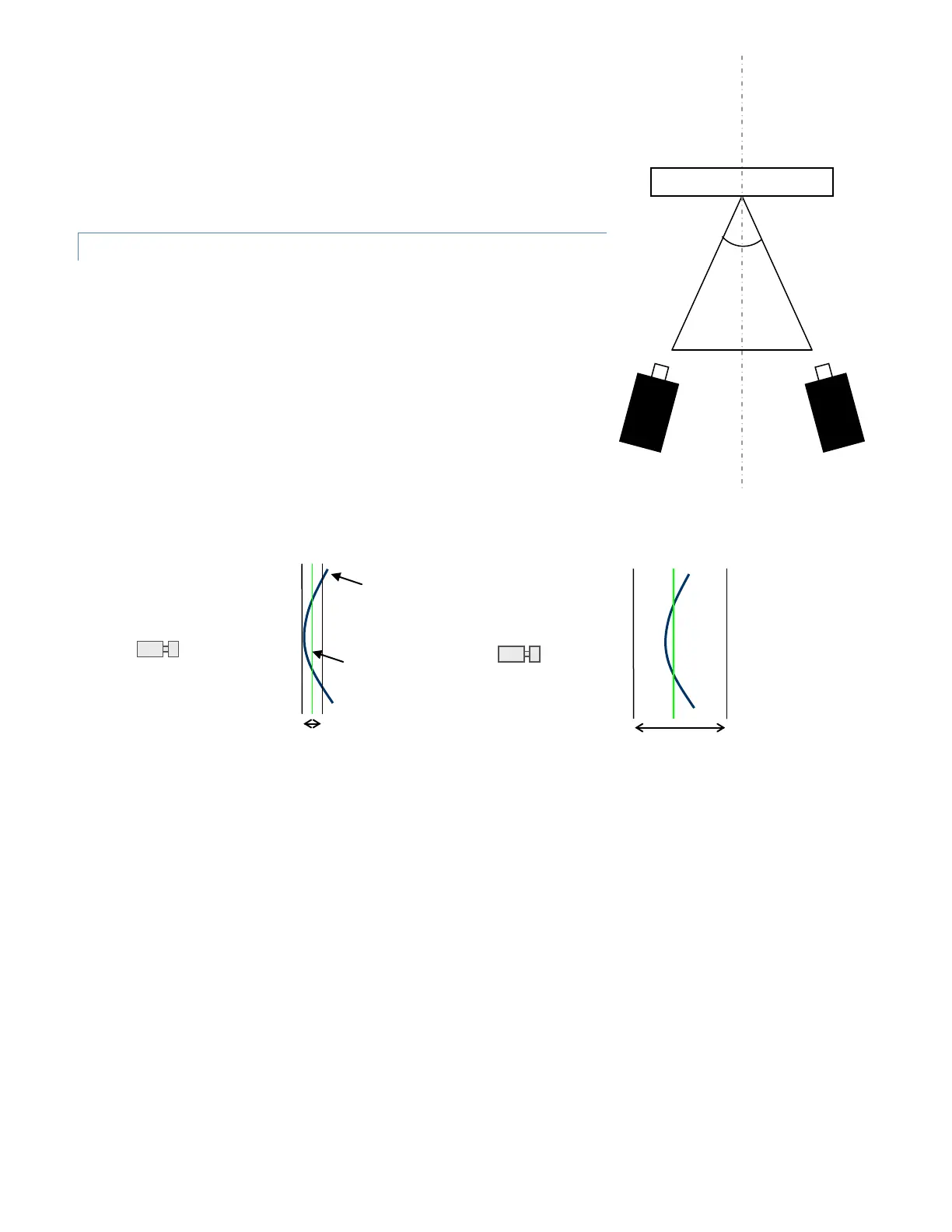
Once a lens and approximate distance is selected, the cameras can be pointed.
The cameras should be positioned somewhat symmetrically about the specimen;
this will keep the magnification level consistent. The exact angle included
between the cameras is not critical but selecting a correct stereo angle will give
best results: the angle should be at least 25º for short lenses (8mm, 12mm), at
least 20º for medium lenses (35mm), and at least 15º for longer lenses (70mm).
The angle should be kept below approximately 60º.
ADJUSTING FOCUS
When the cameras have been positioned, the next step will be to set focus. Use
the focus control on your lenses to achieve a sharp focus on the entire specimen.
Usually, it will be necessary to zoom in on the image to check fine focus; slight
defocus will not be visible with the image zoomed out to fit on screen. While
zoomed in, look closely at both the far and near edge of the specimen to ensure
that the entire surface is in focus, before proceeding.
Tip: to aid in focusing, open the lens’s aperture all the way. This will reduce the
depth of field and make any focus issues very obvious. Then return the aperture
to the appropriate setting for the test. (You will need to temporarily reduce the
exposure time to compensate – see following section.)
Focusing with large aperture – small DOF After closing aperture – focal plane is well centered
Focal plane
Camera
 Loading...
Loading...