D-Link EasySmart Switch User Manual
Figure 41 – L2 Feautres > IGMP Snooping setting
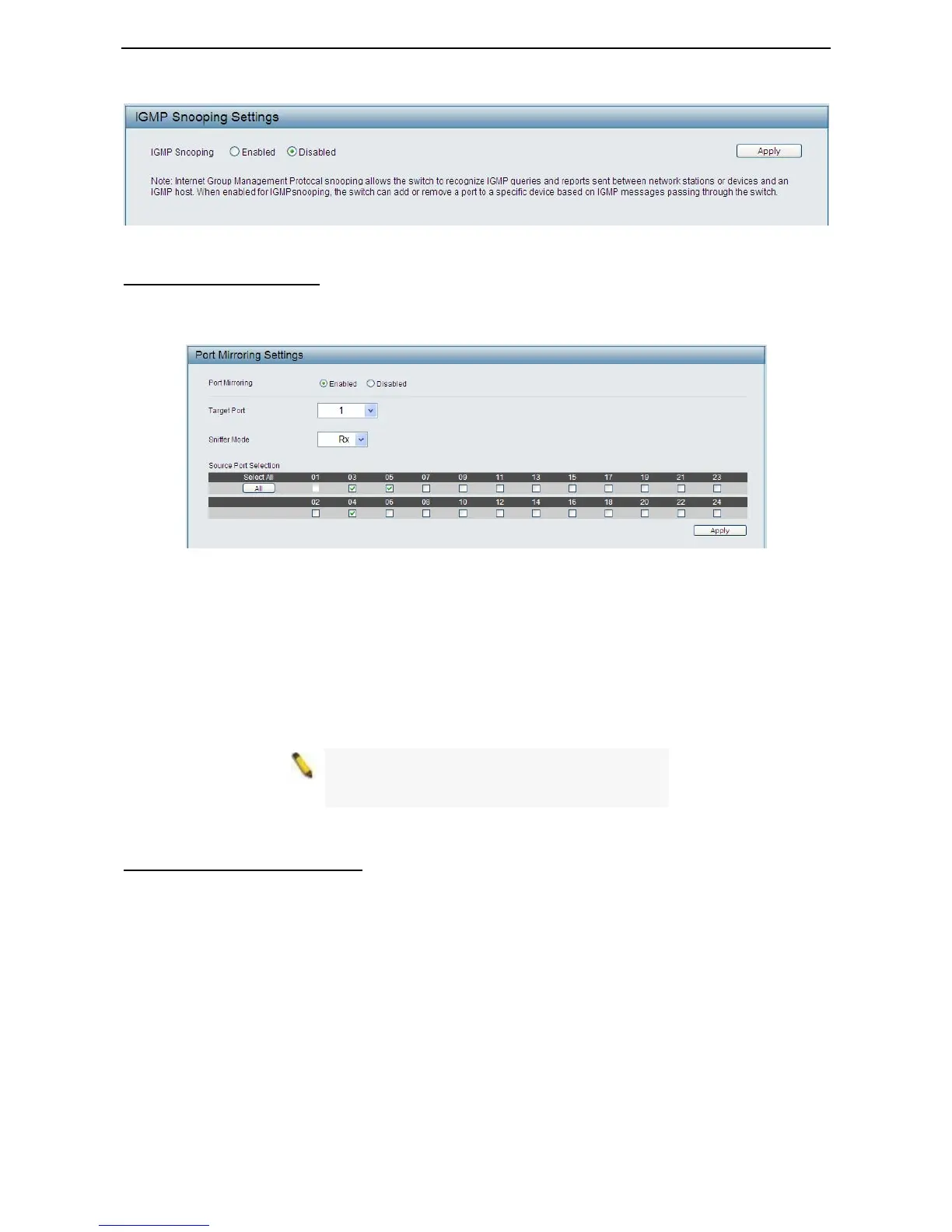
L2 Features > Port Mirroring
Port Mirroring is a method of monitoring network traffic that forwards a copy of each incoming and/or
outgoing packet from one port of the Switch to another port where the packet can be studied. This enables
network managers to better monitor network performances.
Figure 42 –L2 Features > Port Mirroring
Selection Sniffer Mode for the Source Ports are as follows:
TX (transmit) mode: Duplicates the data transmitted from the source port and forwards it to the Target Port.
Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
RX (receive) mode: Duplicates the data that received from the source port and forwards it to the Target Port.
Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
Both (transmit and receive) mode: Duplicate both the data transmitted from and data sent to the source
port, and forwards all the data to the assigned Target Port. Click “all” to include all ports into port mirroring.
NOTE: The target ports will stop mirroring packets
if there are unknown tags or destination packets
sent out by source ports.
L2 Features > Loopback Detection
The Loopback Detection function is used to detect the loop created by a specific port while Spanning Tree
Protocol (STP) is not enabled in the network, especially when the down links are hubs or unmanaged
switchs. The Switch will automatically shutdown the port and sends a log to the administrator. The Loopback
Detection port will be unlocked when the Loopback Detection Recover Time times out. The Loopback
Detection function can be implemented on a range of ports at a time. You may enable or disable this function
using the pull-down menu.
23

 Loading...
Loading...











