3. Instruction Set
API
Mnemonic
Operands Function
71 D
HKY
Hexadecimal key input
Type
OP
Bit Devices Word devices Program Steps
X Y M S K H KnX
KnY
KnM
KnS
T C D E F
HKY: 9 steps
DHKY: 17 steps
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
Operands:
S: The start of input devices (occupies 4 consecutive devices) D
1
: The start of output devices
(occupies 4 consecutive devices) D
2
: Device for storing key input value D
3
: Key input status
(occupies 8 consecutive devices)
Explanations:
1. This instruction creates a 16-key keyboard by a multiplex of 4 consecutive external input
devices from S and 4 consecutive external output devices from D
1
. By matrix scan, the key input
value will be stored in D
2
. D
3
stores the condition of keys A~F and indicates the key input status
of both 0~9 and A~F..
2. M1029 = ON for a scan cycle every time when a key is pressed.
3. If several keys are pressed, only the first pressed key is valid.
4. D
2
maps to a decimal value, a 4-digit decimal value 0~9,999 (16-bit instruction) or an 8-digit
value 0~99,999,999 (32-bit instruction). If the entered number exceeds the available range, i.e.
4 digit in 16-bit and 8 digits in 32-bit instruction, the highest digit performs overflow
5. There is no limitation on the times of using this instruction in the program, but only one
instruction is allowed to be executed in the same scan time.
Program Example:
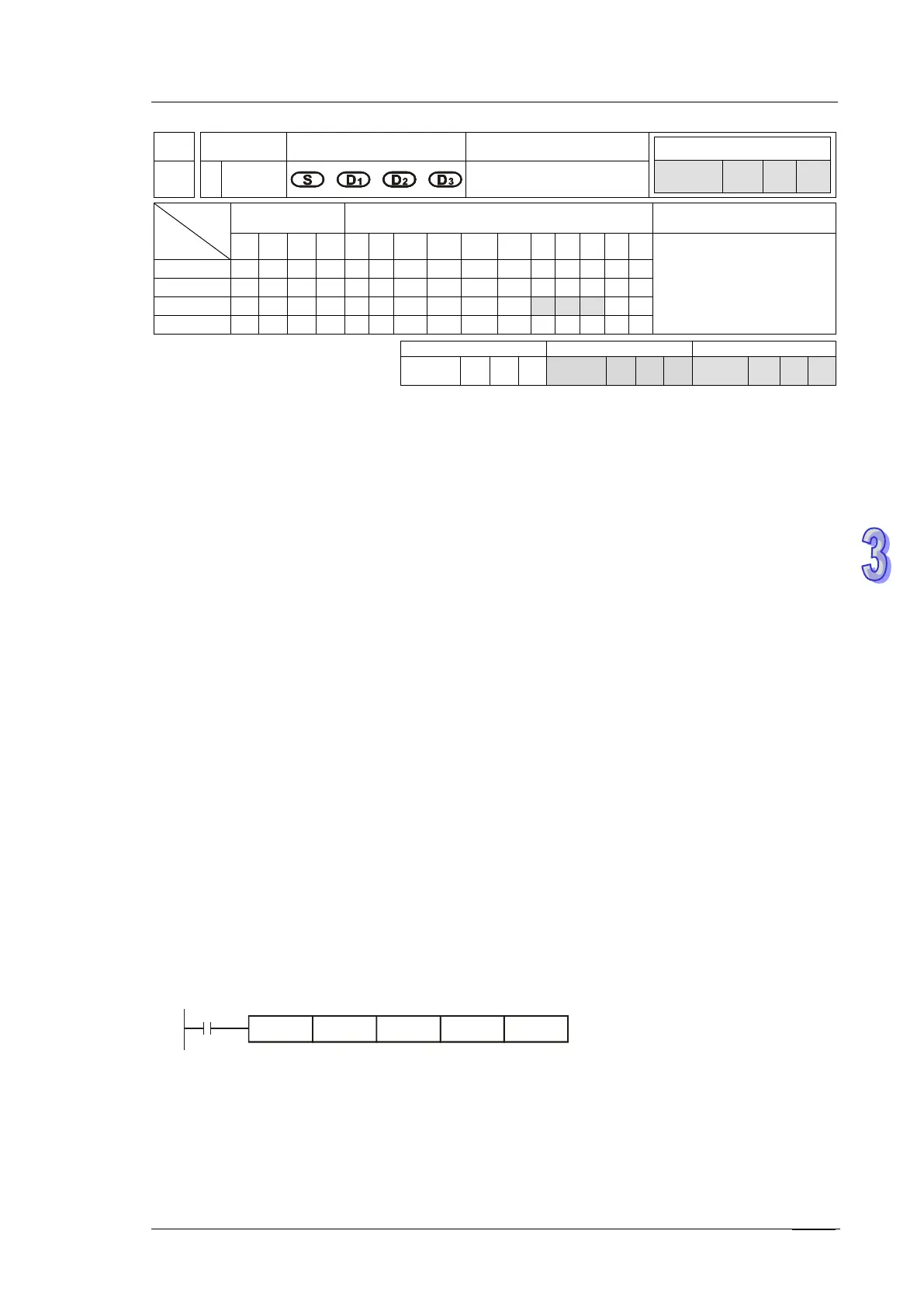
1. Designate 4 input points X20 ~ X23 and the other 4 output points Y20 ~ Y23 to construct a
16-key keyboard. When X4 = ON, the instruction will be executed and the keyed-in value will be
stored in D0 in BIN form. The key status will be stored in M10 ~ M19.
 Loading...
Loading...