_ .
_
.:
If both rotary knobs are set to a band of
the same colour, the following ventila-
tion values are obtained:
Green band
for infants
(5-20 kg
body weight)
Blue band
for children
(20-40 kg
body weight)
Brown band
for adults
(as of 40 kg
body weight)
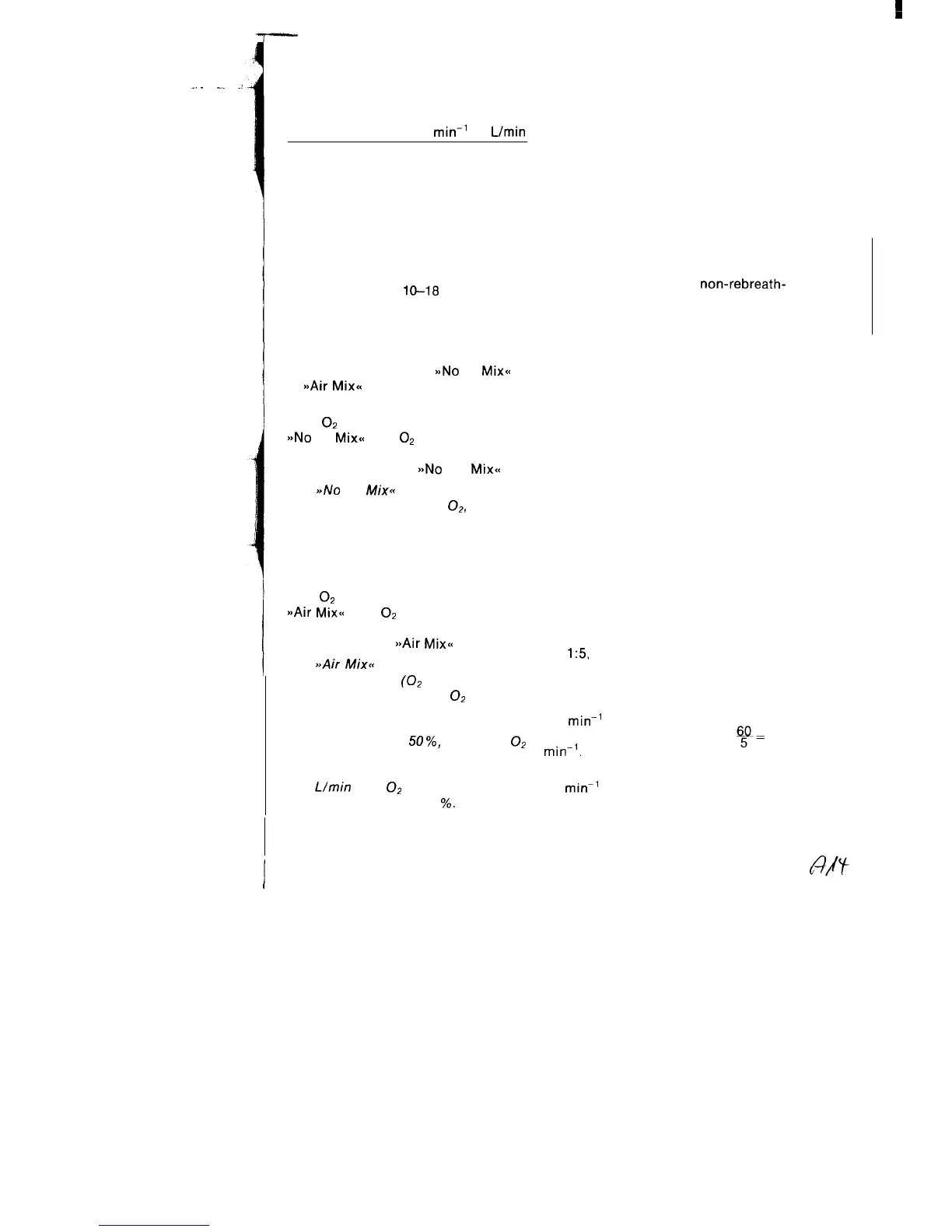
Ventilation MV
ratio
min-’
Llmin
28-35
l-3.5
18-28 3.5-7
lo-18
7-20
The switch is to be set to
a>No
Air
Mix<<
or
to
a,Air
Mix<<
depending on the patient’s
requirements:
High
O2
concentration required:
b>No
Air
Mixa
(and
O2
drive)
In the case of a toxic atmosphere (and
respiratory standstill):
DNO
Air
Mix<<
a>No
Air
Mix<<
setting:
The drive gas, e. g.
Op,
is routed
unblended to the patient. The
ventilation ratio and MV settings
remain unchanged irrespective of
the switch setting.
Low
O2
concentrations required:
BBAir
Mix<<
(with
02
drive)
or compressed-air drive
Small gas supply:
a>Air
Mix<<
a>Air
Mix=
setting:
The drive gas
(0,
or air) is blended
with ambient air. With
O2
drive and
an MV setting in excess of 7 Llmin
the percent by volume added is
approximately
50%,
i. e. the
O2
concentration is roughly 50 vol. %.
With an MV setting less than 7
Urnin
the
O2
concentration in-
creases up to 80 vol.
%.
Connect non-rebreathing valve to mask
or tube.
Make sure that airways are completely
free.
Check airway pressure gauge.
In normal circumstances the inspiratory
airway pressure values should be
approximately 20 mbar.
Atypical airway pressures
In the event of an excessively high
airway pressure reading, the MV
setting should first be checked as well
als the functioning of the
non-rebreath-
ing valve.
Ensure that airways are completely
free!
High airway pressure (50-70 mbar) in
conjunction with a buzzing noise (safety
valve in device blowing out) are an
indication of incorrectly positioned
airways or a kinked tube.
If the airway pressure reading is too
low, the MV setting must likewise be
checked.
The hose connections are also to be
tested for tightness and freedom from
leaks and the non-rebreathing valve is
to be checked for proper functioning.
Ventilation ratio for cardiopulmonary
resuscitation
Within the scope of cardiopulmonary
resuscitation of adults employing a ratio
of
1:5,
it must be ensured that a
ventilatory impulse is given after every
5th cardiac compression.
Given a cardiac massage frequency of
60
min-’
this means that ventilation
must be effected with a ratio of
min-‘.
y=
12
To facilitate setting, the ventilation ratio
12
min-’
on the Oxylog is provided with
a heart symbol.
I
12

 Loading...
Loading...