I
,
,t_
L
X[I. TROUBLESHOOTING
GUIDE
FOR
LOCKOUT
CONDITIONS
If the heat
pump
goes
into lockout
on a
high
or low
pressure
switch, the cause
of the
lockout
can be narrowed down by
knowing the
operating mode and which
pressure
switch the
unit
locked
out on. The following table will help track down the
problem
once this
information
is known. NOTE: A lockout
condition is a result of the heat
pump
shutting itself off to
protect
itself. Never
bypass the lockout circuit. Serious damage
can be caused by the system operating without lockout
protection.
L
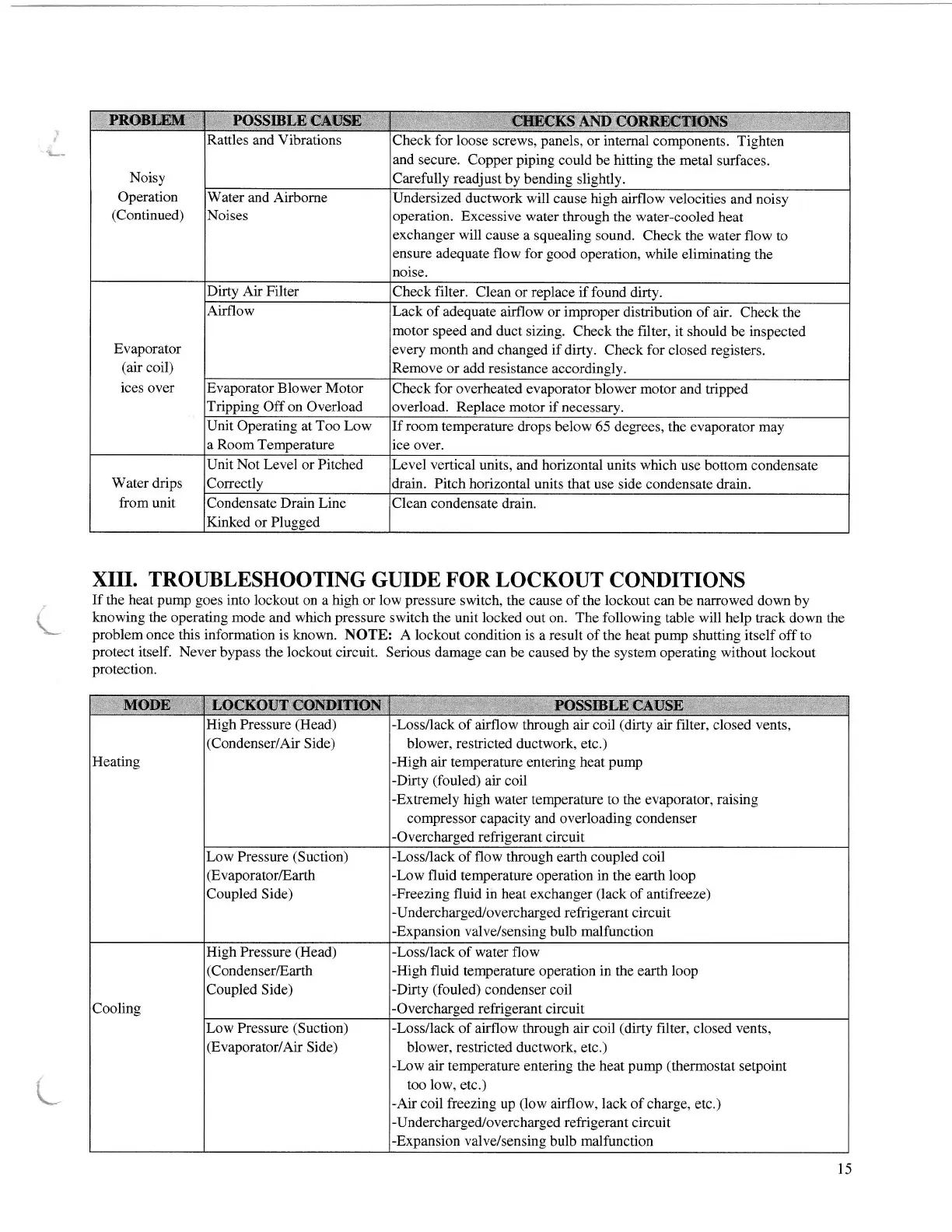
Rattles and Vibrations
Check for loose
screws,
panels,
or internal
components. Tighten
and secure. Copper
piping
could be hitting
the metal surfaces.
Carefully readjust
by
bending slightly.
Noisy
Operation
(Continued)
Water and Airborne
Noises
Undersized
ductwork will
cause high airflow velocities
and noisy
operation.
Excessive
water through the water-cooled
heat
exchanger will cause
a squealing sound.
Check the water flow
to
ensure
adequate flow for
good
operation, while
eliminating the
noise.
Dirty Air Filter
Check
filter.
Clean
or
replace
if found dirty
Airflow
Lack of adequate
airflow or improper
distribution of air.
Check the
motor
speed and
duct sizing. Check the filter, it should
be inspected
every month
and changed if dirty. Check for
closed registers.
Remove or add resistance
accordingly.
Evaporator B lower Motor
Tripping
Off on Overload
Check for overheated
evaporator blower motor
and tripped
overload. Replace
motor if necessary.
Evaporator
(air
coil)
ices
over
Unit Operating
at
Too Low
a Room Temperature
If room temperature
drops below 65 degrees, the
evaporator may
lce over
Unit Not Level or Pitched
Correctly
Level vertical
units, and horizontal
units which use bottom condensate
drain. Pitch horizontal
units that use side condensate drain.
Water drips
from unit
Condensate Drain Line
Kinked or Plugged
Clean condensate drain.
High Pressure
(Head)
(Condenser/Air
Side)
-Lossflack
ofairflow through air coil
(dfuty
air filter, closed vents,
blower, restricted
ductwork, etc.)
-High
air temperature entering heat
pump
-Dirty
(fouled)
air coil
-Extremely
high water temperature to the
evaporator,
raising
compressor capacity and overloading condenser
-Overcharged
refrigerant circuit
Heating
Low Pressure
(Suction)
(Evaporator/Earth
Coupled Side)
-Loss/lack
of
flow
through earth coupled coil
-Low fluid
temperature operation in the earth
loop
-Freezing
fluid in heat exchanger
(lack
of antifreeze)
-Undercharged/overcharged
refrigerant circuit
-Expansion
valve/sensing bulb malfunction
High Pressure
(Head)
(Condenser/Earth
Coupled
Side)
-Loss/lack of water flow
-High
fluid temperature operation in the earth loop
-Dirty
(fouled)
condenser coil
-Overcharged refrigerant
circuit
Cooling
Low Pressure
(Suction)
(Evaporator/Air
Side)
-Loss/lack
of airflow through air coil
(dirty
filter, closed vents,
blower, restricted
ductwork, etc.)
-Low
air temperature
entering the
heat
pump (thermostat
setpoint
too
low,
etc.)
-Air
coil
freezing
up
(low
airflow,
lack
of charge, etc.)
-Undercharged/overcharged refrigerant
circuit
-Expansion valve/sensing
bulb malfunction
l5
PR€3IjM{
POSSI3LACA{'SE
{ffiiCXS AN}
CORAffiTISNS
MODT
LOCKOUT COI{DITIO}\I POSSIBLECAUSE
 Loading...
Loading...

