42
ADDING SALT
I
f the conditioner/refiner uses all the salt before more is
added, hard water will result. EcoWater 3700/3702
series models have automatic salt level sensing. The
remote or your Wi-Fi account can also be used to moni-
tor salt. The conditioner/refiner salt status screen has
an optional display of the estimated number of days
until salt is depleted (“Out of salt in X days”). The con-
ditioner/refiner can also be programmed to display a
Low Salt Alarm a certain number of days before salt is
estimated to run out (See Page 31).
Be sure that the brinewell cover is on when adding salt.
NOTE: In humid areas it is best to keep the salt level
less than half full and add salt more often.
RECOMMENDED SALT: Cube, pellet, coarse solar,
etc., water conditioner salt is recommended. This type
of salt is high purity evaporated crystals, sometimes
formed and pressed into briquets. It has less than 1%
insoluble (not dissolvable in water) impurities. Clean,
high grade rock salts are acceptable, but may require
frequent brine tank cleaning to remove the “sludge”
residue (insolubles) collecting at the bottom of the tank.
POTASSIUM CHLORIDE: If you choose potassium
chloride (KCl) salt as a regenerant:
1) Make sure “Salt type” on the electronic control is set
to “KCl”, as shown on Page 31.
2) Place only one bag of potassium chloride (KCl) into
your conditioner/refiner at a time. The salt storage
tank should never contain more than 60 pounds of
KCl.
SALT NOT RECOMMENDED: Rock salt high in impuri-
ties, block, granulated, table, ice melting, or ice cream
making salts, etc., are not recommended.
SALT WITH IRON REMOVING ADDITIVE: Some salts
have an additive to help a water conditioner/refiner han-
dle iron in the water supply. Although this may help
keep the resin bed clean, it may also release corrosive
fumes that will weaken and shorten the life of some
EcoWater Systems conditioner/refiner electronic parts.
Iron Out salt is safe to use on two-tank models.
ECOWATER
S Y S T E M S
Service Information
BREAKING A SALT BRIDGE
S
ometimes a hard crust or salt “bridge” forms in the
brine tank. This is usually caused by high humidity or
the wrong kind of salt. When the salt bridges, an empty
space forms between the water and the salt. Then salt
will not dissolve in the water to make brine. Without
brine, the resin bed is not recharged and hard water will
result.
If the storage tank is full of salt, it is difficult to tell
whether there is a salt bridge. A bridge may be under-
neath loose salt. The following is the best way to check
for a salt bridge:
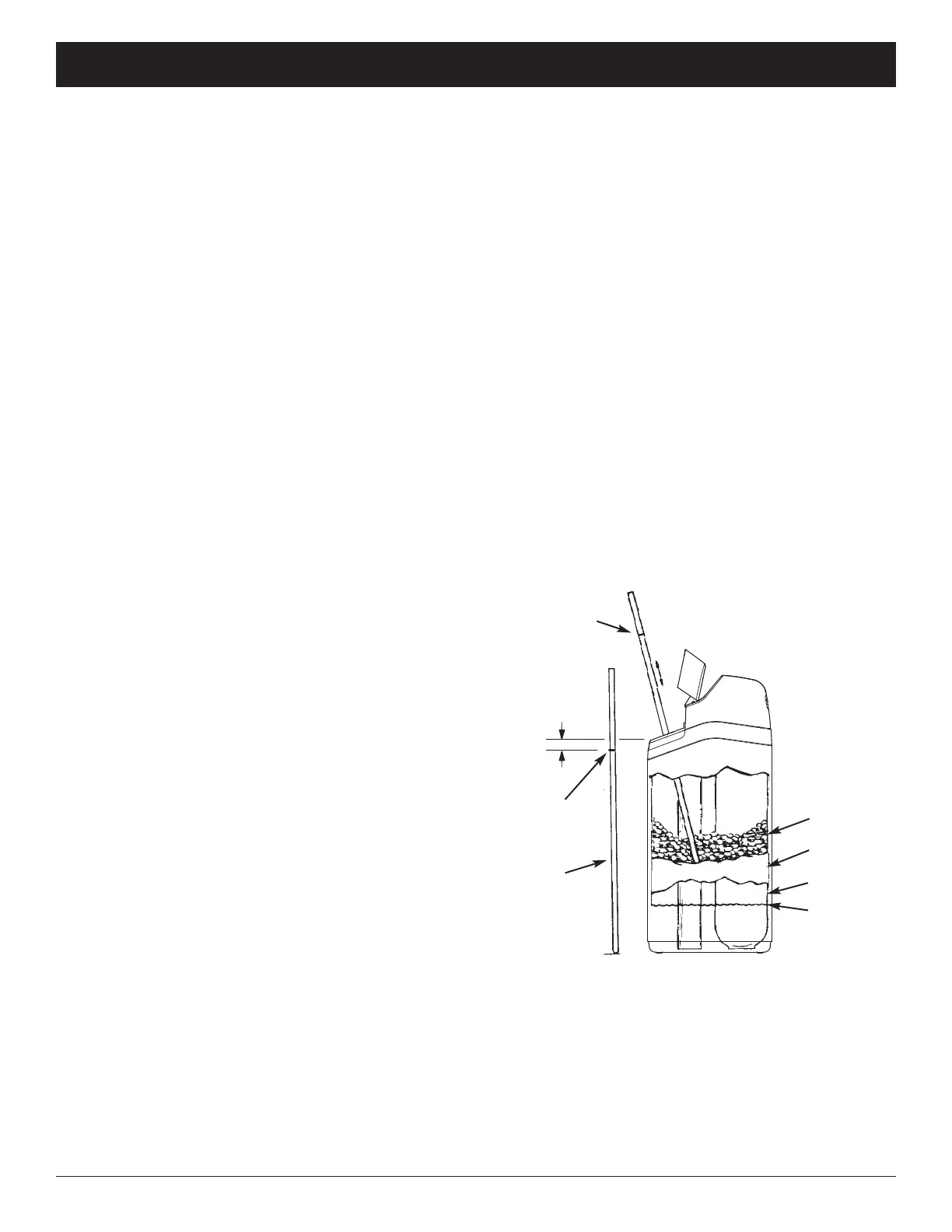
Salt should be loose all the way to the bottom of the
tank. Hold a broom handle, or like tool, up to the condi-
tioner/refiner, as shown in Figure 153. Make a pencil
mark on the handle 1” - 2” below the top of the rim.
Then, carefully push it straight down into the salt. If a
hard object is felt before the pencil mark is even with
the top, it is most likely a salt bridge. Carefully push
into the bridge in several places to break it. Do not try
to break the salt bridge by pounding on the outside
of the salt tank. You may damage the tank.
FIG. 153
1” - 2”
Pencil
Mark
Broom
Handle
Push tool into
salt bridge
to break
Water Level
Empty Space
Salt Bridge
Salt

 Loading...
Loading...