WATER FILL SAFETY SYSTEMS
These safety systems detect any possible malfunctions that might result from incorrect operation of the
hydraulic circuit or leakage from any of the components.
The electromechanical/hydraulic safety devices are always operative during the washing cycle and, in
some cases, even when the appliance is switched off.
These devices are fitted to dishwashers with both Electromechanical and Electronic control systems.
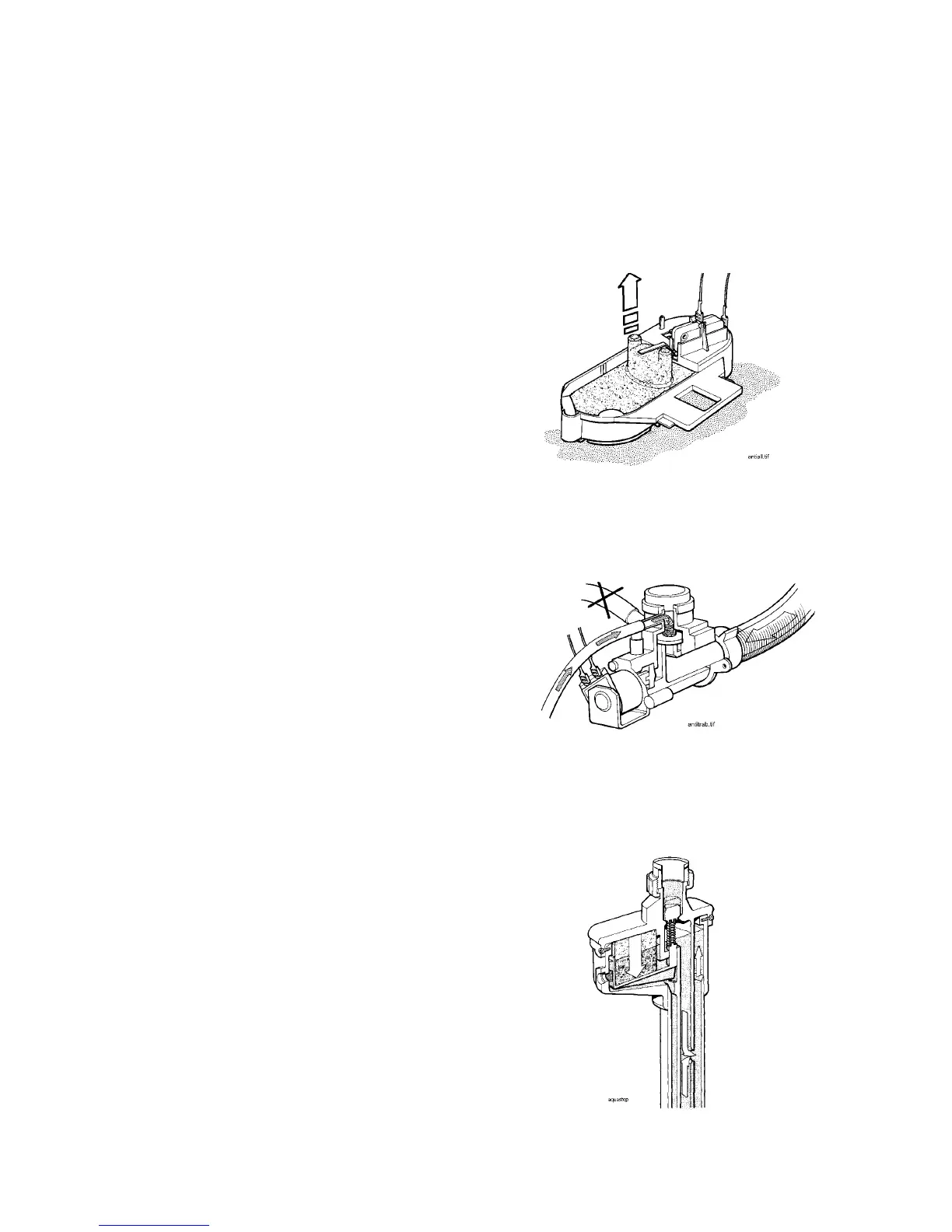
ANTI-FLOODING device
ANTI-OVERFLOW device
ACQUASTOP device
ANTI-FLOODING function
Electromechanical device connected in series to
the solenoid valve.
A floating sensor is housed in the bottom panel
of the machine. The sensor is connected to a
microswitch. When water is present in the
bottom of the tub, the float rises, actioning the
microswitch and disconnecting the solenoid
valve. As a result, the cycle is interrupted.
ANTI-OVERFLOW device
Mechanical device built into the solenoid valve
and connected with the IWMS.
As the level of water in the sump rises, the level
in the anti-overflow chamber of the IWMS, too,
rises, since the two sections are connected by a
tube.
When the water reaches the overflow level, it
flows through the siphon and descends to the
corresponding chamber in the IWMS. This
forces the internal air through the connector
tube, pressurizing the circuit, actioning the
safety device by moving the piston downwards
to block the flow of water.
ACQUASTOP device
Mechanical device built into the drain hose.
This assembly consists of a fill hose at the
extremity of which the device itself is fitted. This
forms an integral assembly, since the two
sections are joined by a hermetic seal which
guarantees perfect water-tightness.
If a leak should occur or if the fill hose should be
damaged, the water is recovered and ducted
through the outer sheath to the inside of the
device. This actions the system, as the sensor
which comes into contact with the water
expends, forcing the valve downwards to block
off the flow of water completely.
25
 Loading...
Loading...