138 SI-Ethernet User Guide
Issue: 1
7.4 Non-cyclic data access
Unidrive M supports the use of non-cyclic data access by user programs.
By simply enabling non-cyclic data (Non-cyclic mode enabled (S.02.035)) and
specifying a base parameter (Non-cyclic base parameter (S.02.036)), a user program
can be used to read or write a parameter either locally in the host drive or option
module, or in another drive or option module on the network.
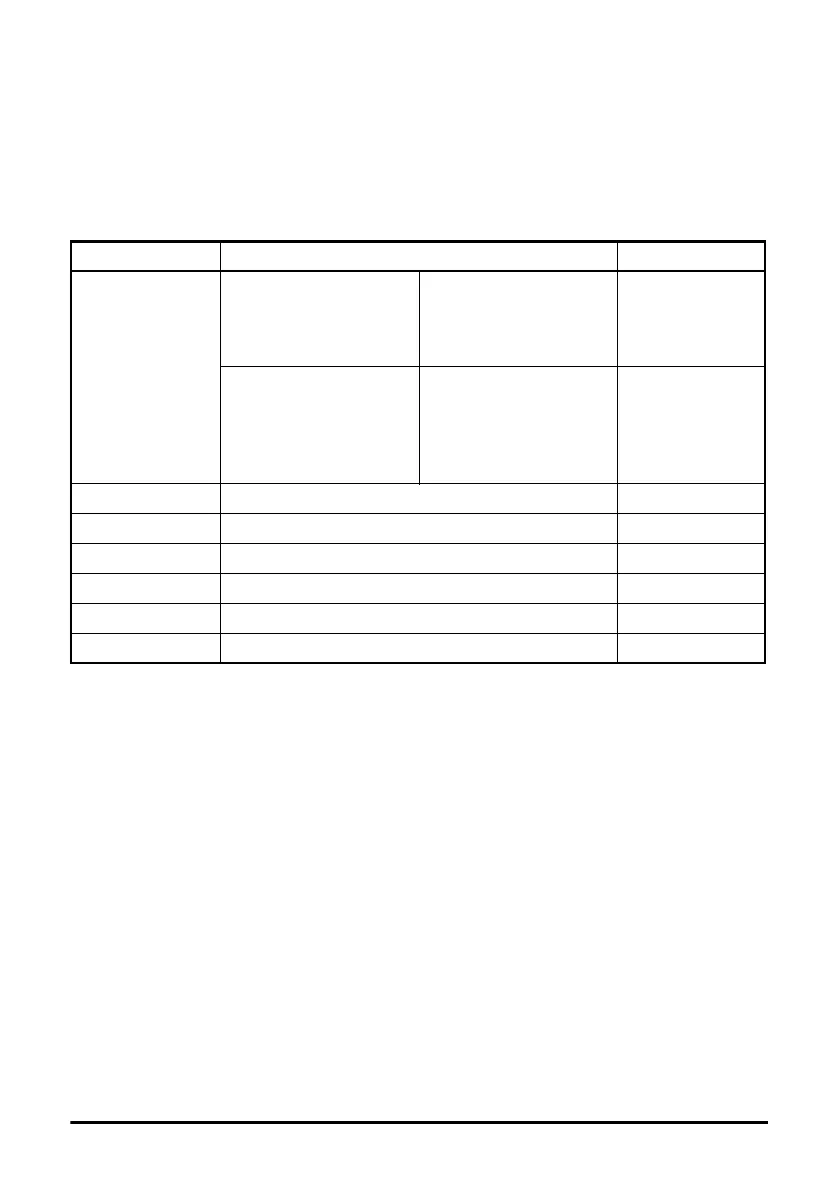
Table 7.7 Non-cyclic data parameter functions
The base address specifies the first parameter in a group of seven consecutive
parameters that will be used to read from or write to a parameter in the drive or option
module at the specified IP address by a user program.
The non-cyclic data access feature operates on a “state machine” principle, this means
that the commands must be sent in the correct sequence otherwise the parameter
access will fail.
The following diagram illustrates the operation of the non-cyclic parameter access state
machine.
Parameter Function Bits
Base address
(S.02.036)
Command
0 = No command
1 = Check / Abort
2 = Read one parameter
3 = Write one parameter
0 to 7 (LSB)
Status
0 = Idle
1 = Ready
2 = Processing
3 = OK
4 = Error
8 to 15 (MSB)
Base address + 1 Destination IP address wwwxxx 0 to 15
Base address + 2 Destination IP address yyyzzz 0 to 15
Base address + 3 Parameter address SMM 0 to 15
Base address + 4 Parameter address PPP 0 to 15
Base address + 5 Parameter value LSW or error code 0 to 15
Base address + 6 Parameter value MSW 0 to 15

 Loading...
Loading...











