24
SECTION 3 OPERATION
Continue practicing until uniform beads as shown in Figure 3.14 can be produced. A good method of practicing is to deposit
a series of beads, one next to the other until the plate is covered. The slag must be thoroughly removed between each pass.
Then deposit another series of beads at right angles to the first, thus holding up the plate to a greater thickness.
WEAVING
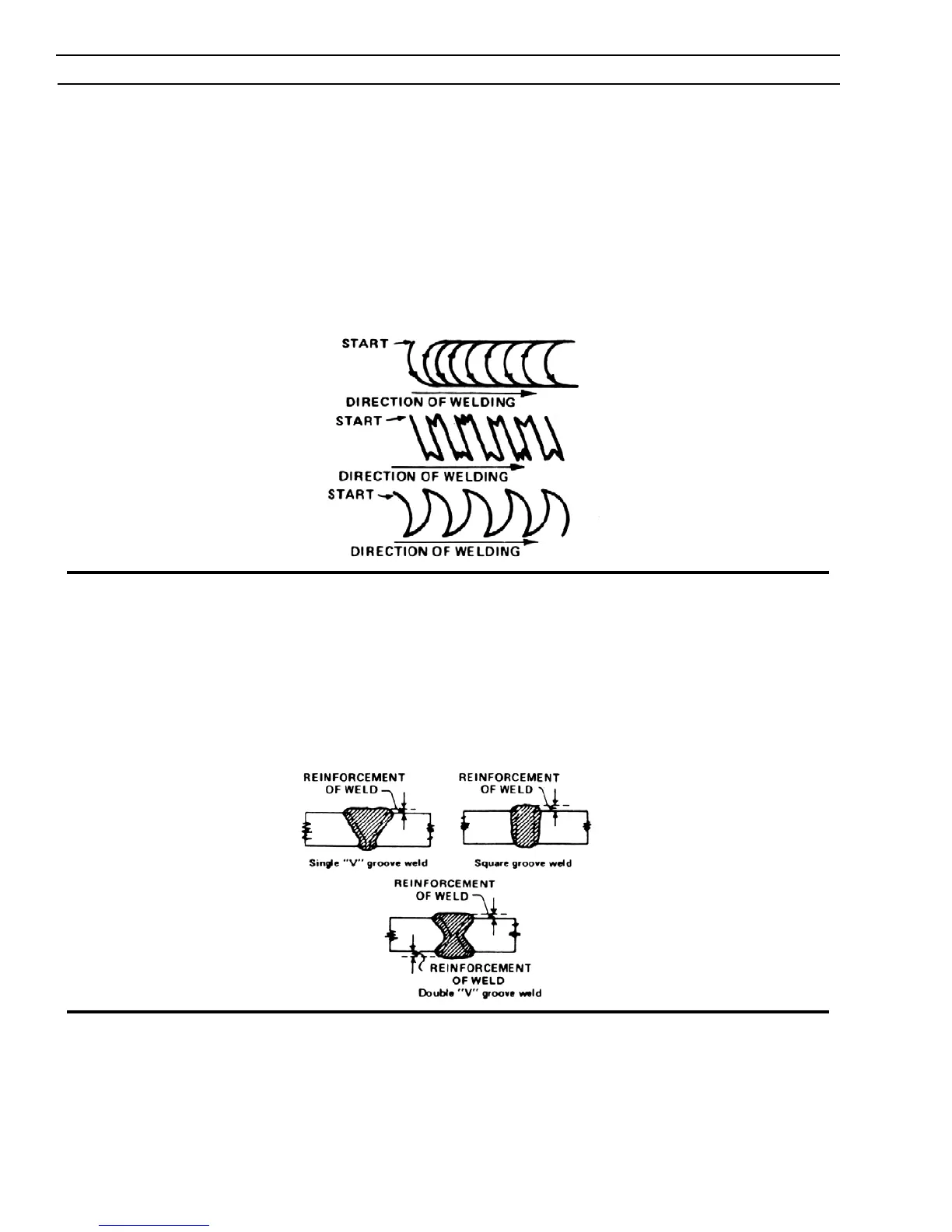
When it is necessary to cover a wider area in one pass of the electrode, a method known as weaving is employed. In this the
electrode is moved or oscillated from side to side in a set pattern. In order to be sure of uniform deposits, it is necessary to
use a definite pattern such as those illustrated in Figure 3.16. While weaving is helpful, particularly when building up metal,
it should be limited to weaves not exceeding 2-1/2 times the diameter of the electrode.
Figure 3.16 Weave Patterns
BUTT JOINTS
Up to this point the discussion has covered only the deposit of beads on flat plate. Such operations are helpful in building
up worn parts or applying hardfacing materials. The next step is learning to weld two pieces of metal together. For this
purpose, other types of welds are illustrated in Figure 3.17.
Figure 3.17 Butt Joints
 Loading...
Loading...