Smart and efficient unit
The operational costs can be up to 75% less than that of an electric water heater, and can
be installed in locations which are unsuitable for solar hot water heating.
2.2 Characteristics
Easy to operate
Featuring an easy to use timer for both start and stop operations, with a controller to set the
desired water temperature.
Safe and environmentally friendly
Produces no harmful gases along with no open flame, making the unit safe to work with
when installing.
4
2. Specs
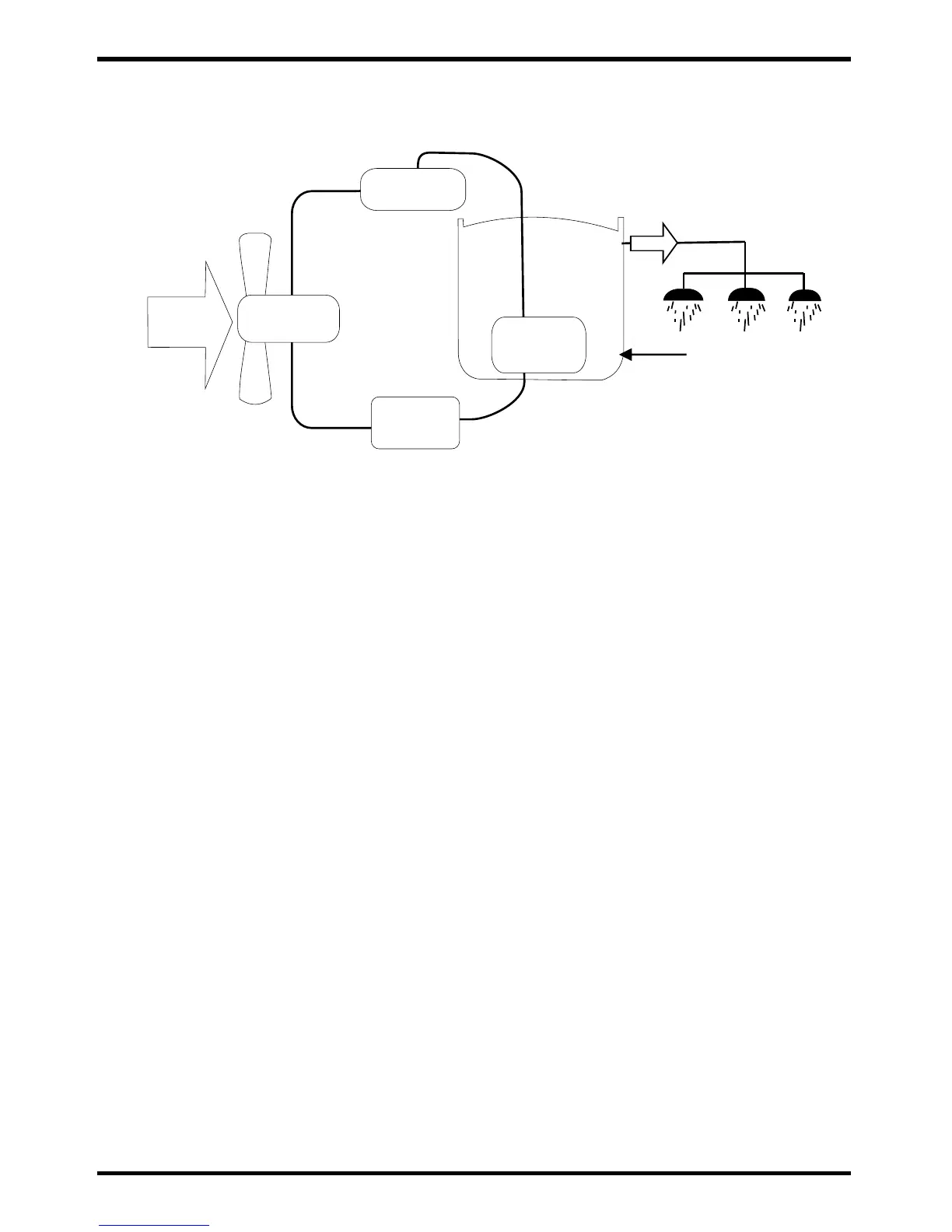
2.3 Operational Principle
4
Air from
outside
Hot water
Low temp.
Compressor
Compressor
Thermal
expansion
valve
Water supply
Tank
Picture 2
Air
exchanger
Water
exchanger
Heat Pump System Theory:
(1) Using a small power input to drive the compressor, the power used is Q1.
(2) While the unit is running, the power that comes ambient air is Q2 (from the refrigerant
transformation).
(3) The energy that the water gets from the unit is Q3.
(4) According to the law of conservation of energy:
﹛ Sum of input power = sum of output power Q1+Q2 = Q3
﹛ In standard working conditions, the power that heat pump gets from the environment is about
3.2 times the power input, Q2 = 3.2 x Q1
so: Q3 = Q1+Q2 = Q1+3.2Q1= 4.2Q1
Which means you can get 4.2Q1 from heat pump if you spend Q1 energy. Which means the
energy that you can get from heat pump after using 1 kW of electricity is equal to the energy that
you get from electrical element heater after using 4.2 kW of electricity. This makes the hot water
heat pump is one of the most energy efficient heating equipment available on the market today..
 Loading...
Loading...