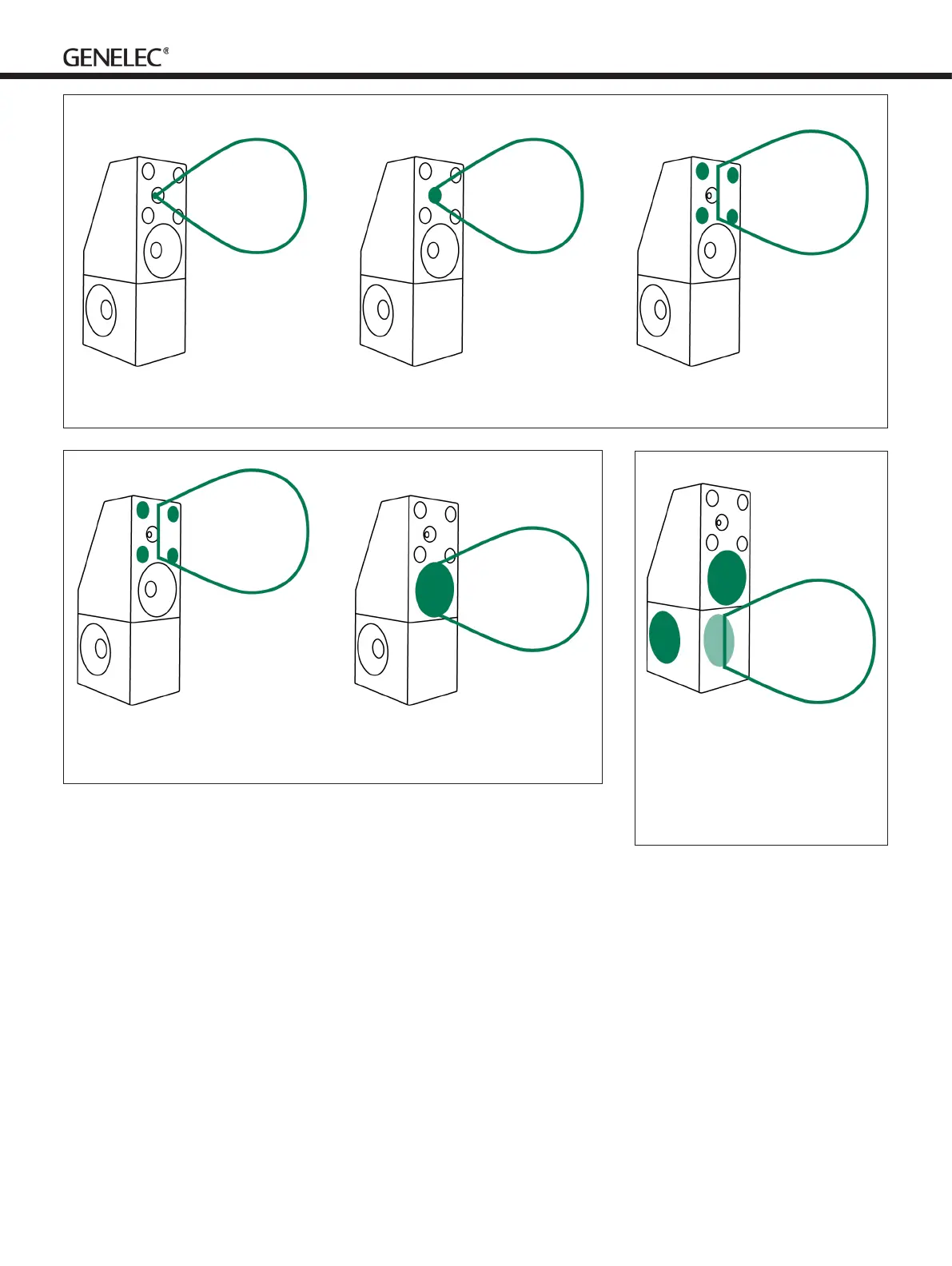
Figure 1. Principles of maintaining directivity; high frequencies in the tweeter (left), coaxial midrange driver range (middle) and low
midrange (right).
Figure 2. Principles of maintaining directivity; low midrange (left) matches to the
directivity of the 15-in woofer (right).
gets narrower. This means that in a typical
loudspeaker, the input-to-output latency is
the smallest close to the highest frequency,
progressively increases towards the bass
frequencies, and close to the low corner
frequency where the loudspeaker output
starts reducing the input-to-output delay is
usually the highest.
Genelec monitors use digital signal
processing to align the input-to-output delay.
This is done by applying a very small amount
of delay to higher frequencies to line them up
with lower frequencies. 8381A monitor oers
two values for this line-up, ‘low latency’
and ‘extended phase linearity’. These can
be selected in the GLM software. The ‘low
latency’ mode applies the minimum amount
of additional delay at higher frequencies
and can keep the latency constant down to
about 500 Hz. The ‘extended phase linearity’
setting applies just a little bit more delay
at higher frequencies and keeps the delay
constant down to about 200 Hz. As the delay
has a relationship to the rate of changes of
the system phase response, these settings
also have the eect that the phase change
for audio down to these frequencies
remains very small, and all audio output is
in phase across the important mid and high
frequencies, and this results in very accurate
reproduction of the waveforms at the monitor
output and therefore excellent reproduction
of the details in audio transients.
High-SPL Coaxial
The coaxial driver is installed in a directivity
control waveguide (DCW). The coaxial driver
uses a high linearity compression tweeter
with a 13 mm (.5 in) throat diameter and a
5-in conical midrange driver forming a part
of the complete Genelec Directivity Control
Waveguide™ (DCW™) design. The system
directivity is set by the driver size (diameter)
and the directivity control eect of the DCW
and enclosure front.
Quad Midrange System
The top enclosure offers an acoustic
point source design the high SPL tweeter-
midrange coaxial driver in a DCW is
supplemented with four 127 mm (5 in) dome
drivers. Combined, their acoustic output
appears to locate on the same acoustic
axis with the coaxial driver, and the quad
Figure 3. Room-adaptive woofer
system adjusts directivity accord-
ing to room acoustics so that the
frequency response is neutral at the
listening position.
 Loading...
Loading...