Main Feature Description
DSO1000B Series HandHeld Oscilloscope User Manual 9
two different frequencies. Mainly it uses a specific frequency to switch between two
analog channels CH1 and CH2 so that the channels will generate swap trigger signals
through the trigger circuitry.
Trigger Mode: You can select the Auto or Normal mode to define how the oscilloscope acquires
data when it does not detect a trigger condition. Auto Mode performs the acquisition freely in
absence of valid trigger. It allows the generation of untriggered waveforms with the time base set
to 80ms/div or slower. Normal Mode updates the displayed waveforms only when the
oscilloscope detects a valid trigger condition. Before this update, the oscilloscope still displays the
old waveforms. This mode shall be used when you want to only view the effectively triggered
waveforms. In this mode, the oscilloscope displays waveforms only after the first trigger. To
perform a single sequence acquisition, push the SINGLE SEQ button.
Trigger Coupling: Trigger Coupling determines which part of the signal will be delivered to the
trigger circuit. This can help to obtain a stable display of the waveform. To use trigger coupling,
push the TRIG MENU button, select an Edge or Pulse trigger, and then select a Coupling option.
Trigger Position: The horizontal position control establishes the time between the trigger position
and the screen center.
Slope and Level: The Slope and Level controls help to define the trigger. The Slope option
determines whether the trigger point is on the rising or falling edge of a signal. To perform the
trigger slope control, press the TRIG MENU button, select an Edge trigger, and use the Slope
button to select rising or falling. The LEVEL button controls the trigger point is on which position of
the edge.
4.3 Data Acquisition
When you acquire an analog signal, the oscilloscope will convert it into a digital one. There are
two kinds of acquisition: Real-time acquisition and Equivalent acquisition. The real-time acquisition
has three modes: Normal, Peak Detect, and Average. The acquisition rate is affected by the
setting of time base.
Normal: In this acquisition mode, the oscilloscope samples the signal in evenly spaced intervals to
establish the waveform. This mode accurately represents signals in most time. However, it does
not acquire rapid variations in the analog signal that may occur between two samples, which can
result in aliasing and may cause narrow pulses to be missed. In such cases, you should use the
Peak Detect mode to acquire data.
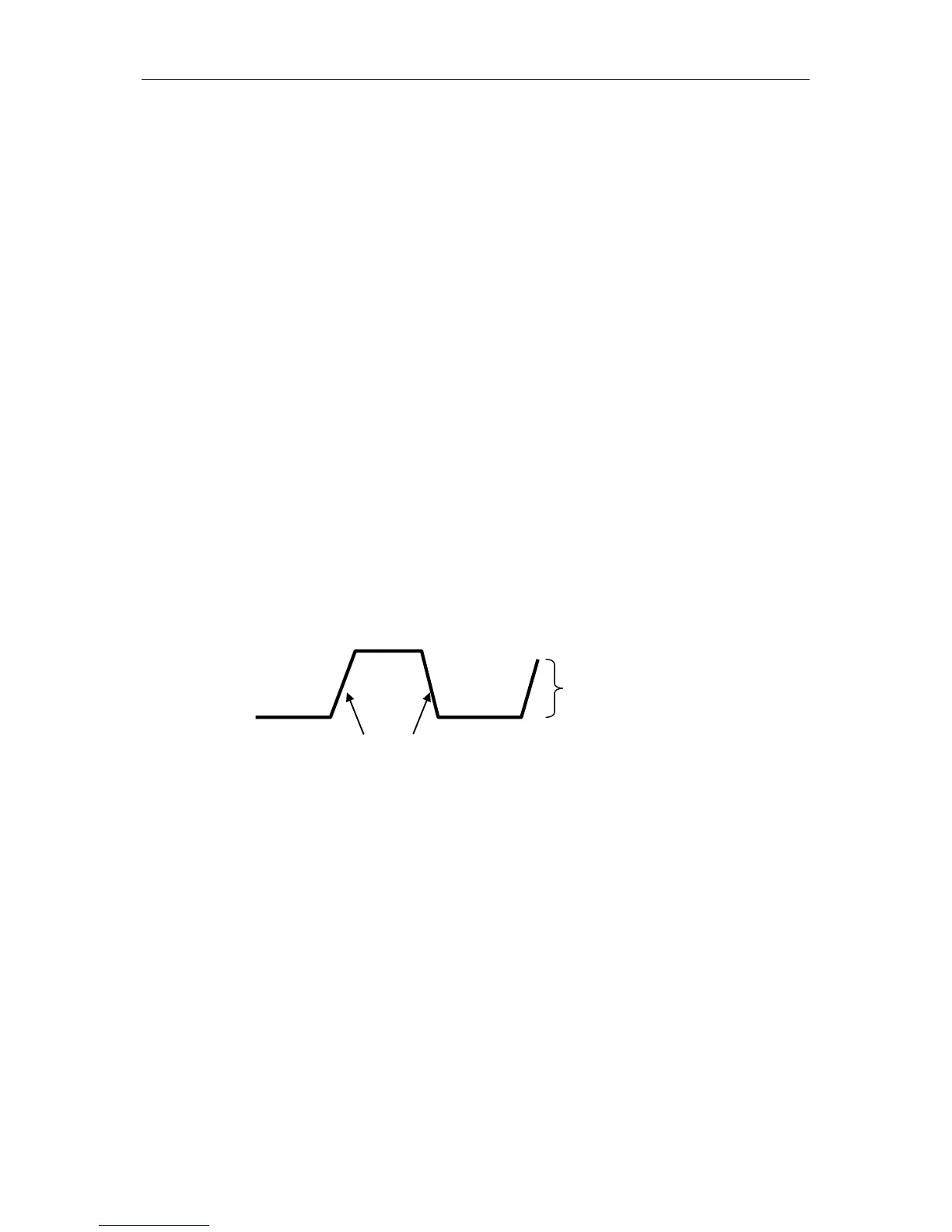
Peak Detect: In this acquisition mode, the oscilloscope gets the maximum and minimum values of

 Loading...
Loading...