[2] How to tune each parameter
(2-1) Tuning target of each parameter
There are many parameters, which influence the motor performance in SLV, 0-SLV & V2 control modes.
In some cases auto tuning is not fully sufficient to get the best motor performance because there are
various kinds of motors in the world. It is sometimes necessary to adjust by hand after the auto tuning.
Generally the performance of the motor can be determined from two criteria:
Ø Torque performance at low speed
Ø Speed response against target speed
Table 1 shows main parameters that influence the motor performance inSLV mode. The concept is the same
in 0-SLV and V2 modes as well.
Table 1. Explanation of parameters related to motor performance in SLV mode
Code Function Remarks
H001 Auto tuning mode This determines the method of auto tuning.
00 (NOR) : Auto tuning invalid
01 (NRT) : Auto tuning with motor at standstill
02 (AUT) : Auto tuning with motor rotation
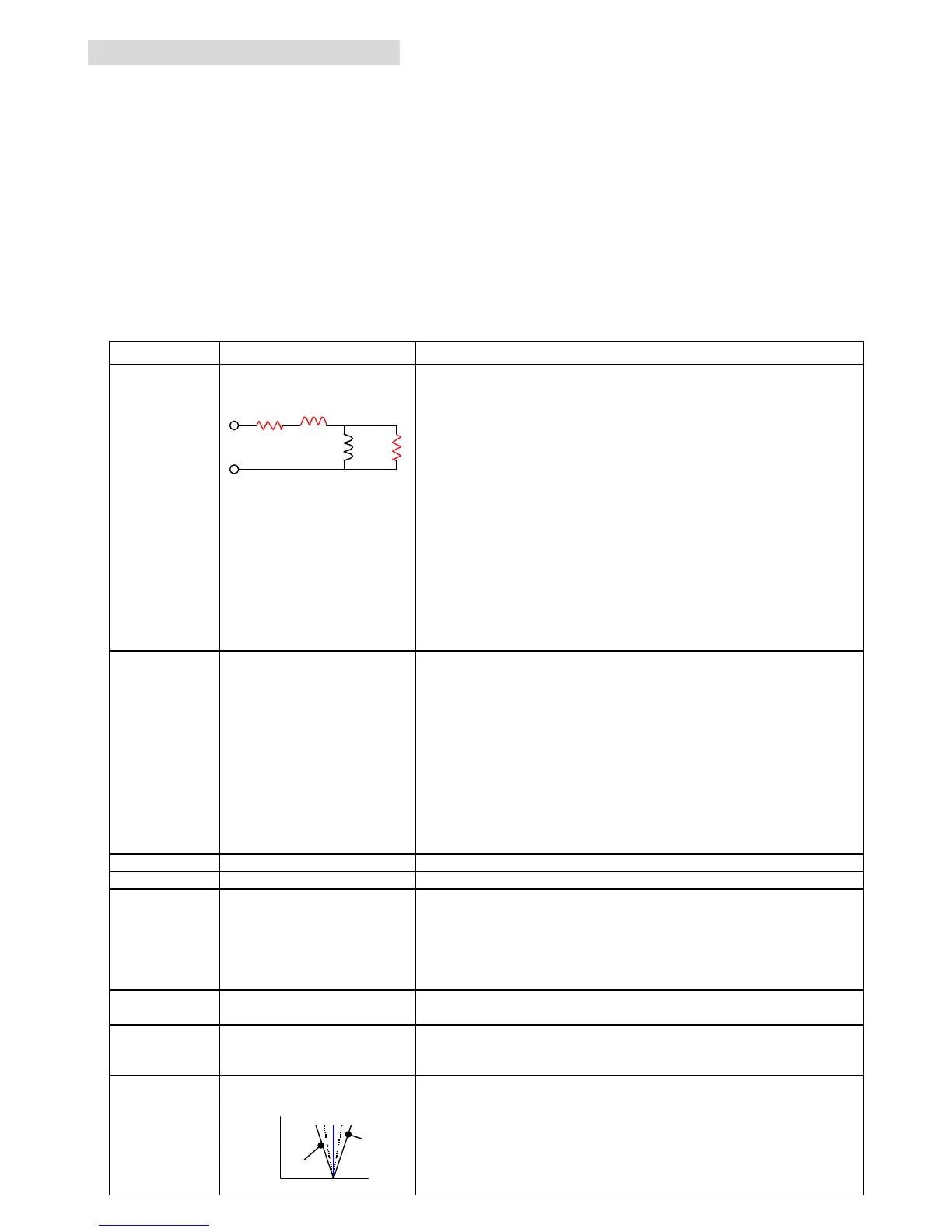
Auto tuning determines the following motor constants
automatically. (See left figure as well.)
Ÿ R1 (primary resistance)
Ÿ R2 (secondary resistance)
Ÿ L (leakage inductance)
Ÿ I
o
(magnetizing current at base frequency)
Ÿ J (total load inertia)
Normally better motor performance can be obtained by auto tuning
with motor rotation with an actual load on the motor. But if the
system does not allow rotating the motor, like a lift application for
example, auto tuning with motor at standstill can be used.
H002 Motor constant selection This determines which set of motor parameters is used by the drive.
00 : Motor parameters for a Hitachi standard motor
(Uses [H020] ~ [H024] )
01 : Use auto tuning data
(Uses [H030] ~ [H034] )
02 : Use auto tuning data with On-line auto tuning
On-line auto tuning occurs every time the inverter stops. It
measures R1 and R2, the main values that may change
due to a motor temperature change. The tuning period is roughly
5 seconds maximum, and if the RUN command is given during
the tuning routine, the inverter will start and tuning is aborted.
H003 Motor kW This sets the motor kW, not a kW of an inverter.
H004 Motor poles
H005
Speed response factor K
Controls the speed response
Ÿ
Large K à Quick response (Too high a value can cause instability.)
Ÿ Small K à Slow but stable response
Value is also dependent on Proportional gain (P-gain : [H050])
and Integration gain (I-gain : [H051]). ( K = f(Kp, Ki) ).
H006 Motor stability control factor This should be adjusted in case of motor instability.
Increase / decrease depends on the situation.
H020 / H030 Primary resistance of the
motor R1 [Ω]
Influences mainly the torque at low speed.
Ÿ Large R1 à Higher torque (Too high R1 à Over magnetizing)
Ÿ Small R1 à Smaller torque
H021 / H031 Secondary resistance of the
motor R2 [Ω]
Influence mainly on the speed change ratio (= slip compensation)
Ÿ Large R2 à Increase speed change ratio
(= Actual speed becomes faster than a target speed.)
Ÿ Small R2 à Decrease speed change ratio
(= Actual speed becomes slower than a target speed.)
R1 L
LM
R2

 Loading...
Loading...











