T
glTexEnv
Chapter 18
428
Description
A texture environment specifies how texture values are interpreted when a fragment is
textured. target must be GL_TEXTURE_ENV. pname can be either
GL_TEXTURE_ENV_MODE, GL_TEXTURE_ENV_COLOR or
GL_TEXTURE_LIGHTING_MODE_hp (if the extension GL_hp_texture_lighting is
supported).
If pname is GL_TEXTURE_ENV_MODE, then params is (or points to) the symbolic
name of a texture function. Four texture functions may be specified: GL_MODULATE,
GL_DECAL, GL_BLEND, and GL_REPLACE. If pname is
GL_TEXTURE_LIGHTING_MODE_hp, two possible values for param may be specified:
either GL_TEXTURE_PRE_SPECULAR_hp or GL_TEXTURE_POST_SPECULAR_hp.
A texture function acts on the fragment to be textured using the texture image value
that applies to the fragment (see glTexParameter) and produces an RGBA color for that
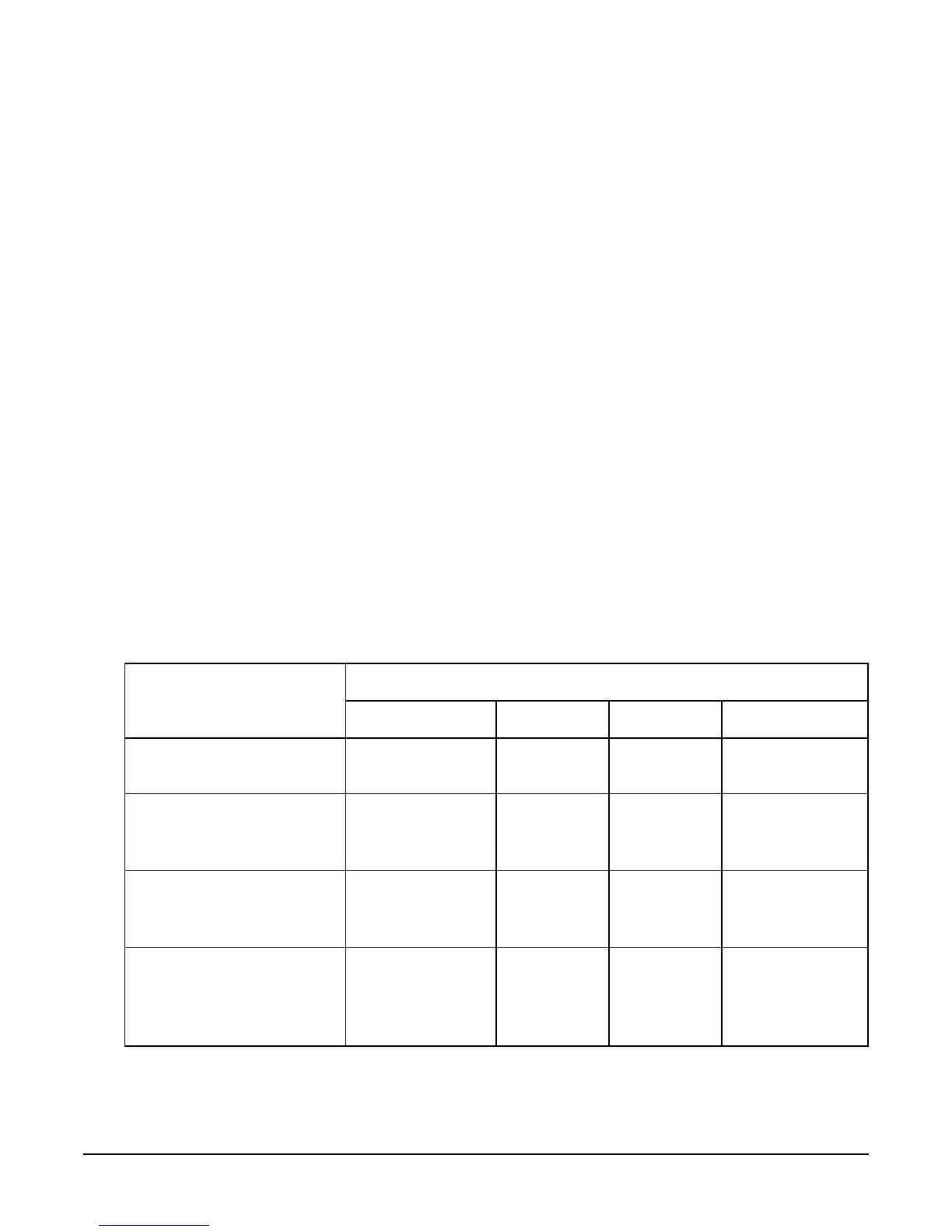
fragment. The following table shows how the RGBA color is produced for each of the
three texture functions that can be chosen. C is a triple of color values (RGB) and A is
the associated alpha value. RGBA values extracted from a texture image are in the
range [0, 1]. The subscript f refers to the incoming fragment, the subscript t to the
texture image, the subscript c to the texture environment color, and subscript v indicates
a value produced by the texture function.
A texture image can have up to four components pertexture element (see glTexImage1D,
glTexImage2D, glCopyTexImage1D, and glCopyTexImage2D). In a one-component
image, L
t
indicates that single component. A two-component image uses L
t
and A
t
. A
three-component image has only a color value, C
t
. A four-component image has both a
color value C
t
and an alpha value A
t
.
Base Internal Format
Texture Functions
GL_MODULATE GL_DECAL GL_BLEND GL_REPLACE
GL_ALPHA C
v
= C
f
A
v
= A
f
A
t
(undefined) C
v
= C
f
A
v
= A
f
C
v
= C
f
A
v
= A
t
GL_LUMINANCE
1
C
v
= L
t
C
f
A
v
= A
f
(undefined) C
v
= (1 - L
t
)
C
f
+ L
t
C
c
A
v
= A
f
C
v
= L
t
A
v
= A
f
GL_LUMINANCE_ALPHA
2
C
v
= L
t
C
f
A
v
= A
t
A
f
(undefined) C
v
= (1 - L
t
)
C
f
+ L
t
C
c
A
v
= A
t
A
f
C
v
= L
t
A
v
= A
t
GL_INTENSITY C
v
= C
f
I
t
A
v
= A
f
I
t
(undefined) C
v
= (1 - I
t
)
C
f
+ I
t
C
c
A
v
= (1 - I
t
)
A
f
+ I
t
A
c
C
v
= I
t
A
v
= I
t

 Loading...
Loading...




















