Normal
and
Inverse-Normal
Distributions
Normal distribution is frequently used to model the behavior of ran
dom variation about a mean. This model assumes that the sample
distribution is symmetric about the mean, M, with a standard devi
ation, S,
and
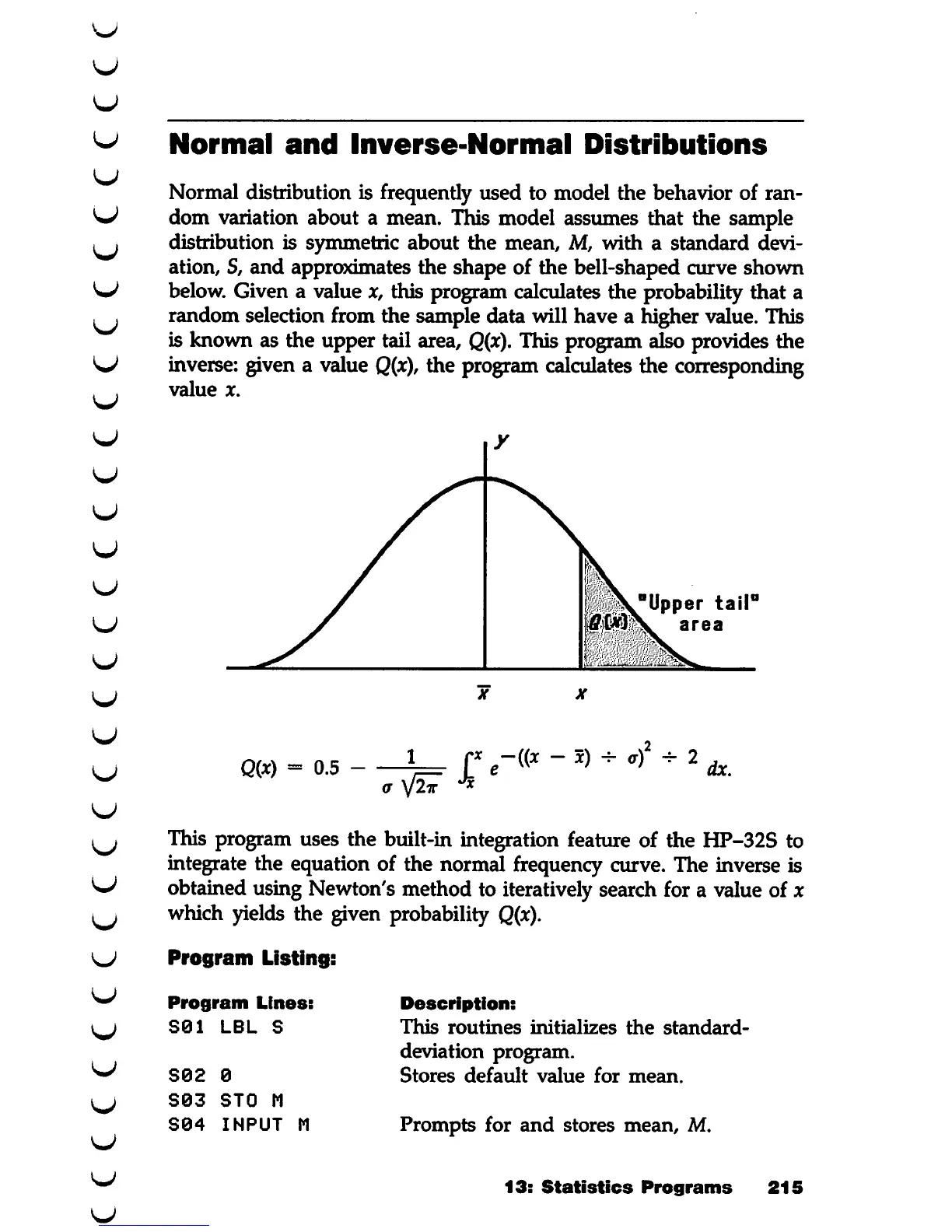
approximates the shape of the bell-shaped curve shown
below. Given a value x, this program calculates the probability that a
random selection from the sample data will have a higher value. This
is known as the upper tail area,
Q(x).
This program also provides the
inverse: given a value
Q(x),
the program calculates the corresponding
value
x.
Q(x) - 0.5 -
V27
X
' e"«* -
*>
+
•»
+ 2
ix.
This program uses the built-in integration feature of the HP-32S to
integrate the equation of the normal frequency curve. The inverse is
obtained using Newton's method to iteratively search for a value of x
which yields the given probability
Q(x).
Program
Listing:
Program
Lines:
501
LBL
S
502
0
503
STO
M
504
INPUT
M
Description:
This
routines
initializes
the
standard-
deviation program.
Stores
default
value
for
mean.
Prompts for
and
stores mean, M.
13:
Statistics
Programs
215

 Loading...
Loading...