Switch Meshing
Switch Meshing Fundamentals
Host
(Both links
use the
same
MAC
address.)
Switch
4000M
LAN
Untagged VLAN 1
Tagged VLAN 20
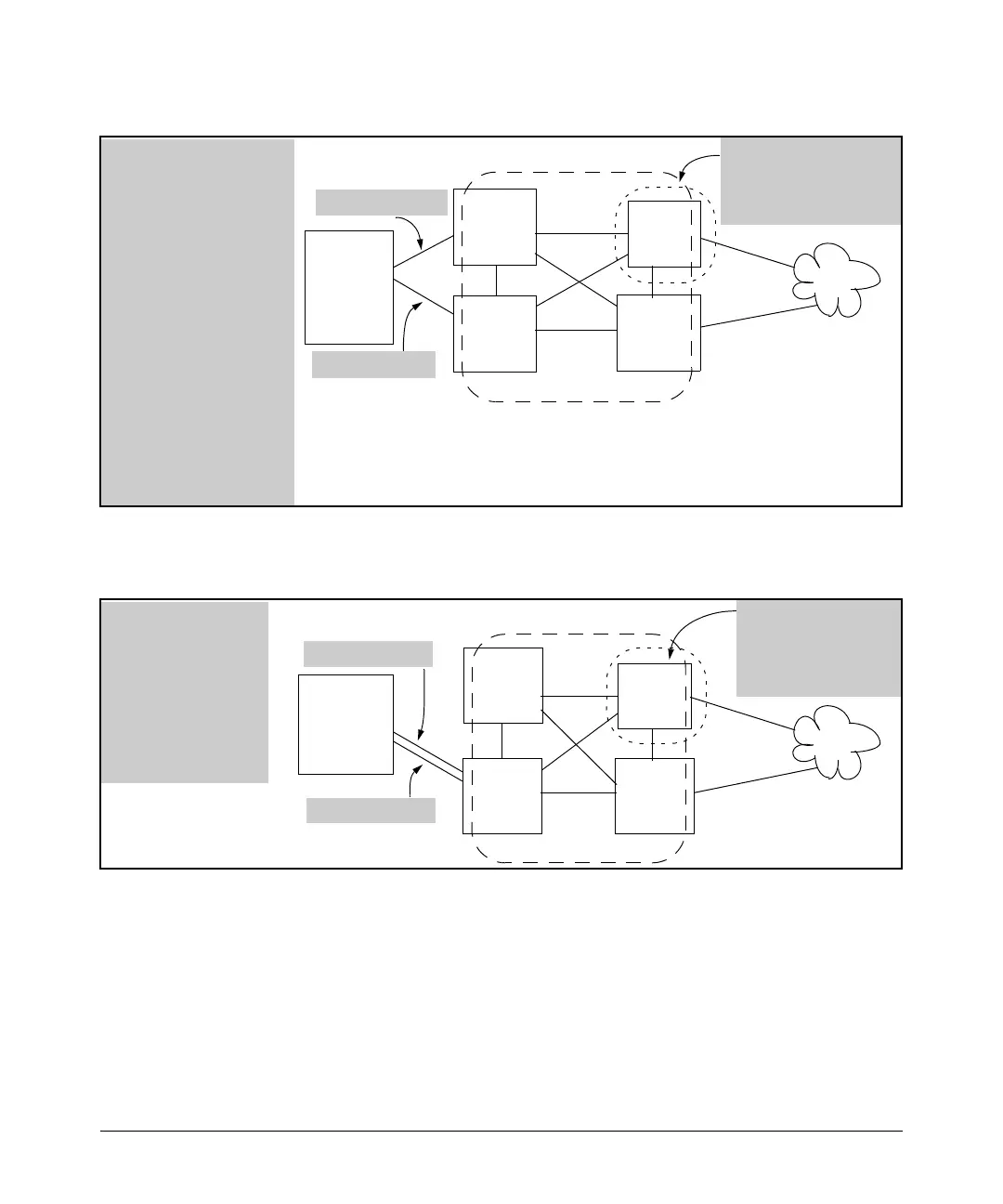
Scenario 1: In a heteroge-
nous mesh, creating the
mesh with only one 5300xl,
3400cl, or 6400cl switch
connected to the host (on
VLAN 1, for example), and
then connecting a second
5300xl, 3400cl, or 6400cl
switch to the host
(regardless of the VLAN
used) results in connectivity
issues with the host.
Scenario 2: Adding the
Switch 4000M after bringing
up the mesh with two later
switches (5300xl, 3400xl, or
6400cl) already connected to
the host as shown here (with
or without separate VLANs)
blocks the Switch 4000M
from the mesh.
The Switch 4000M is not
supported in topologies
allowing the same MAC
address on multiple
switches.
Mesh Domain
3400cl,
6400cl, or
5300xl
Switch
3400cl,
6400cl, or
5300xl
Switch
3400cl,
6400cl, or
5300xl
Switch
Figure 7-5. Example of an Unsupported Heterogeneous Topology Where Duplicate MAC Addresses Come
Through Different Switches (Regardless of the VLANs Used)
Host
(Both links
use the
same MAC
address.)
5300xl,
6400cl,
or 3400cl
Switch
Switch
4000M
LAN
Tagged VLAN 20
Creating the mesh with
only one Series 5300xl,
3400cl, or 6400cl switch
connected to the host,
and using tagged
VLANs for multiple
connections between
the host and the meshed
switch allows normal
meshing operation.
The Switch 4000M is
not supported in
topologies allowing the
same MAC address on
multiple switches.
Mesh Domain
Untagged VLAN 1
5300xl,
6400cl,
or 3400cl
Switch
5300xl,
6400cl,
or 3400cl
Switch
Figure 7-6. Example of a Supported Heterogeneous Topology Where Duplicate MAC Addresses Come
Through Different VLANs on the Same Switch
Note that in figures 7-5 and 7-6, if all switches are 3400cl, 6400cl, or 5300xl
devices, then you can use either topology.
Also, if you have two separate switch meshes with the topology shown in
figure
7-7, you cannot join them into a single mesh.
7-9

 Loading...
Loading...











