(
(~
('"
Chapter 4. Primitive (Built-In) Functions
APL
functions
are
of
two
types: user-defined and
those
that
are built
into
the
APL
language. User-defined functions are discussed
in
Chapter 6. Built-in functions,
called primitive functions, are
denoted
by a symbol and
operate
on
the
data
you
supply
to
them.
The value
or
values
you
supply are called arguments. Primitive functions
that
use
two
arguments, such
as
A";-
B,
are said
to
be dyadic;
functions
that
use
one
argument
are said
to
be monadic, such
as";-
B,
which yields
the
reciprocal
of
B.
Arguments can
be single
data
items (scalars), strings
of
data
(vectors), tables
of
data
(matrices),
or
multiple tables
of
data
(N-rank arrays). Arguments can also be expressions
or
user-
defined
functions
that
result
in
a scalar, vector, matrix,
or
N-rank array.
There are
two
types
of
primitive functions: scalar functions and mixed functions.
There
are also
operators
that
operate
on
the
primitive functions. Examples
of
the
functions
and
operators
are provided
throughout
this
chapter
for easy reference and
are set
up
as
they
would appear
on
the
display.
PRIMITIVE SCALAR FUNCTIONS
Scalar functions
operate
on
scalar arguments and arrays.
They
are
extended
to
arrays
element
by element.
The
shape and rank (see
Chapter
3)
of
the
result de-
pend
on
the
shape and rank
of
the
arguments.
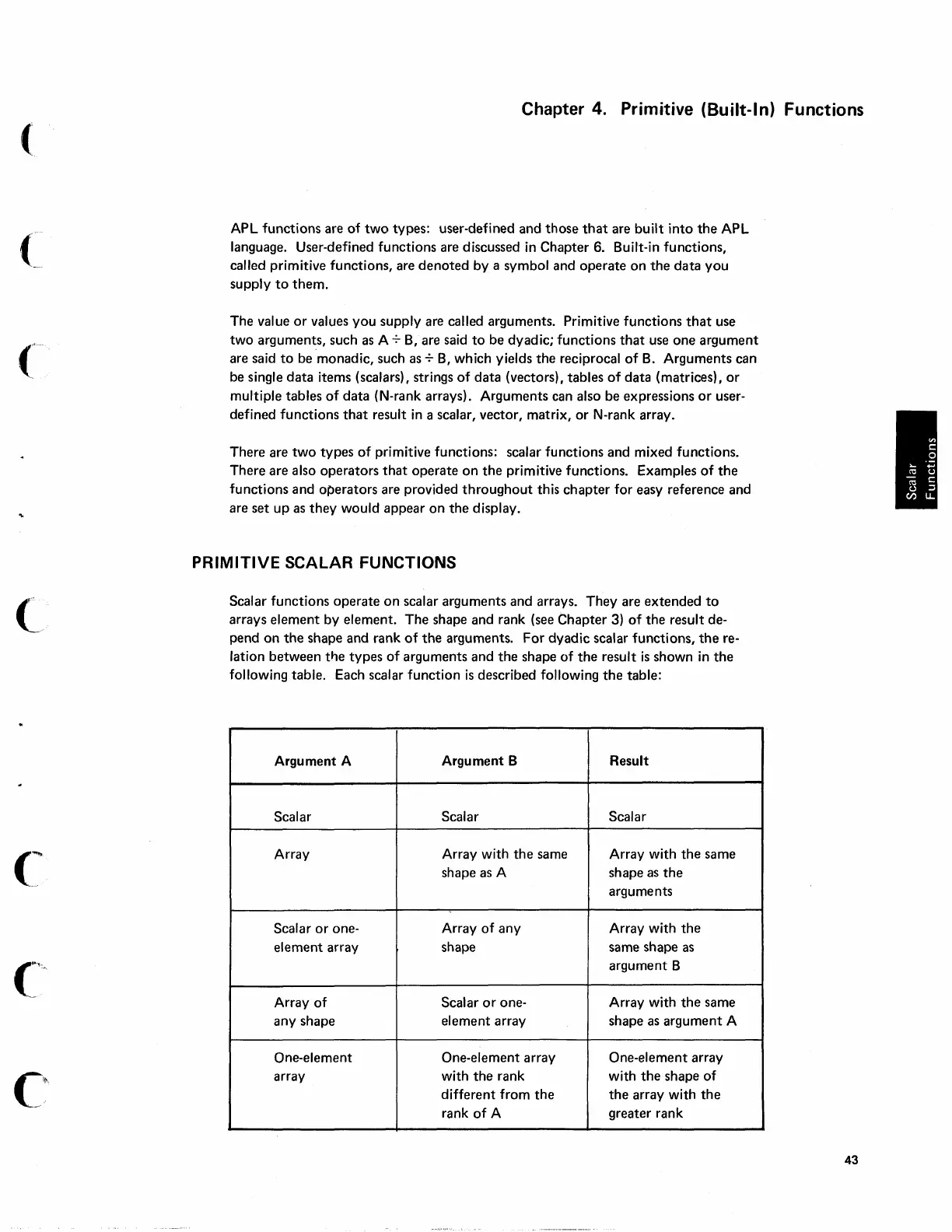
For
dyadic
scalar functions,
the
re-
lation
between
tile
types
of
arguments
and
the
shape
of
the
result
is
shown
in
the
following table. Each scalar
function
is
described following
the
table:
Argument A
Argument B
Result
Scalar Scalar Scalar
Array Array with
the
same Array with
the
same
shape as A shape
as
the
arguments
Scalar
or
one-
Array
of
any
Array with
the
element
array shape same shape as
argument B
Array
of
Scalar
or
one-
Array with
the
same
any
shape element array shape
as
argument
A
One-element One-element array
One-element array
array with
the
rank with
the
shape
of
different
from
the
the
array with
the
rank
of
A
greater rank
43

 Loading...
Loading...
















