6.1. BUS TOPOLOGY
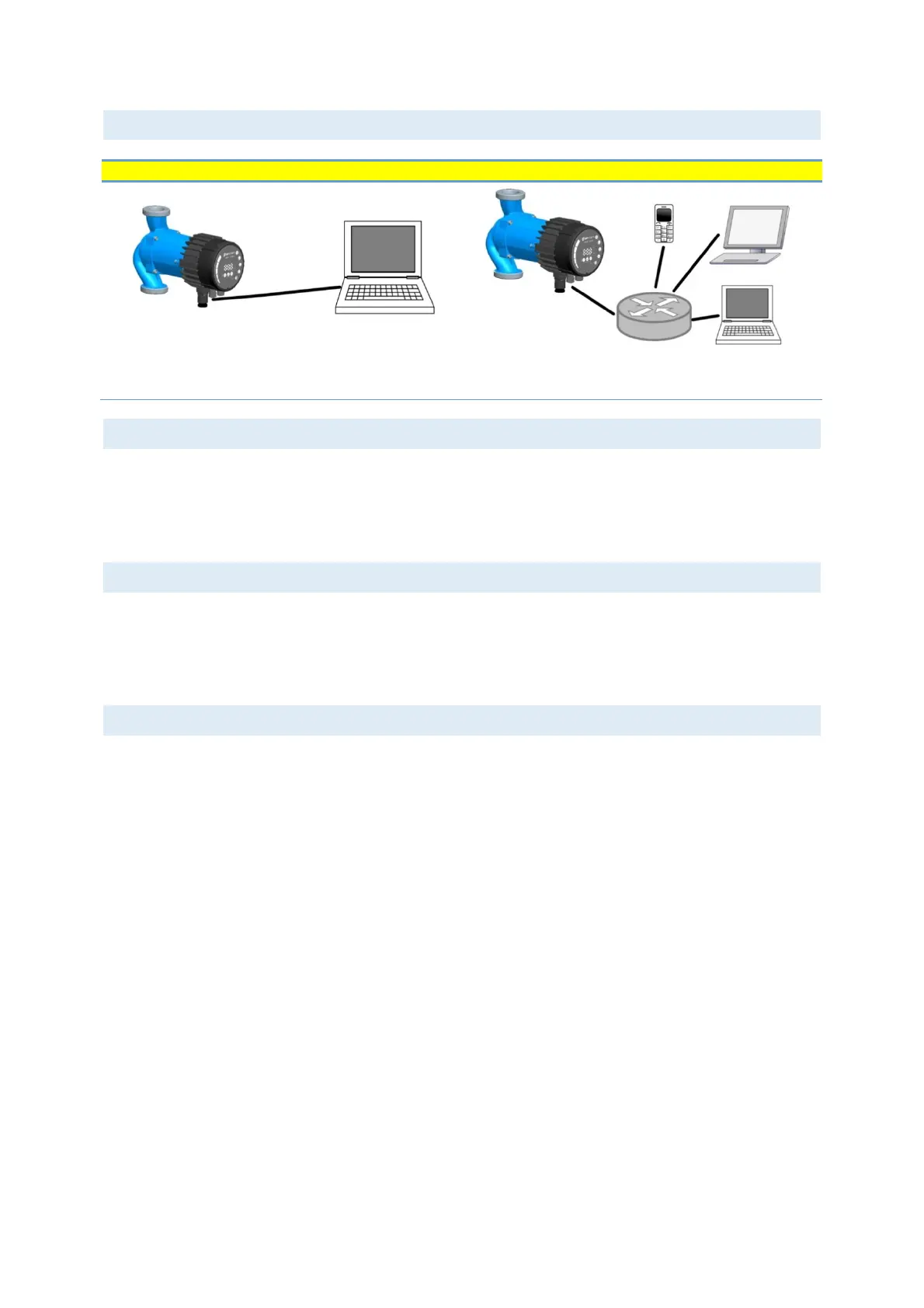
Ethernet connection topologies
Figure 4: connecting to a computer with a cross-over cable
Figure 5: connecting to a network via router
6.2. CONNECTING TO PUMP AD-HOC
When connecting directly with the computer, a cross-cable must be used to connect with the pump. The pump
can then be accessed by typing IP address “192.168.0.245” or “nmtpump” or “192.168.0.246” or “nmtpump2”
if it’s a left twin pump in to your web browsers address bar.
The computer must be set up to have a dynamic IP address.
6.3. CONNECTING TO PUMP VIA ROUTER
When connecting via a router, a patch cable must be used to connect with the pump. The pump can then be
accessed by typing IP address “192.168.0.245” or “nmtpump” or “192.168.0.246” or “nmtpump2” if it’s a left
twin pump in to your web browsers address bar.
The computer must be set up to have a dynamic IP address.
6.4. PUMP CONFIGURATION OVER ETHERNET
Pump configuration is possible via HTML pages that offer different options:
1. Overview (default page when you connect to the pump, web page OVERVIEW) displays pump operation
summary like:
• Operating mode,
• Power consumption,
• Head,
• Estimated flow,
• RPM
• Estimated efficiency,
• Priority set point,
• Mode switch position
• Input/output status
• Replay status
• Error code
• Twin pump status
• Night mode status
• Motor temperature
• Heat sink temperature,
• Number of restarts.

 Loading...
Loading...