Overview of BIOS Features
73
3.9 BIOS Security Features
The BIOS includes security features that restrict access to the BIOS Setup program
and who can boot the computer. A supervisor password and a user password can be
set for the BIOS Setup program and for booting the computer, with the following
restrictions:
• The supervisor password gives unrestricted access to view and change all the Setup
options in the BIOS Setup program. This is the supervisor mode.
• The user password gives restricted access to view and change Setup options in the
BIOS Setup program. This is the user mode.
• If only the supervisor password is set, pressing the <Enter> key at the password
prompt of the BIOS Setup program allows the user restricted access to Setup.
• If both the supervisor and user passwords are set, users can enter either the
supervisor password or the user password to access Setup. Users have access to
Setup respective to which password is entered.
• Setting the user password restricts who can boot the computer. The password
prompt will be displayed before the computer is booted. If only the supervisor
password is set, the computer boots without asking for a password. If both
passwords are set, the user can enter either password to boot the computer.
• For enhanced security, use different passwords for the supervisor and user
passwords.
• Valid password characters are A-Z, a-z, and 0-9. Passwords may be up to
16 characters in length.
Table 37 shows the effects of setting the supervisor password and user password. This
table is for reference only and is not displayed on the screen.
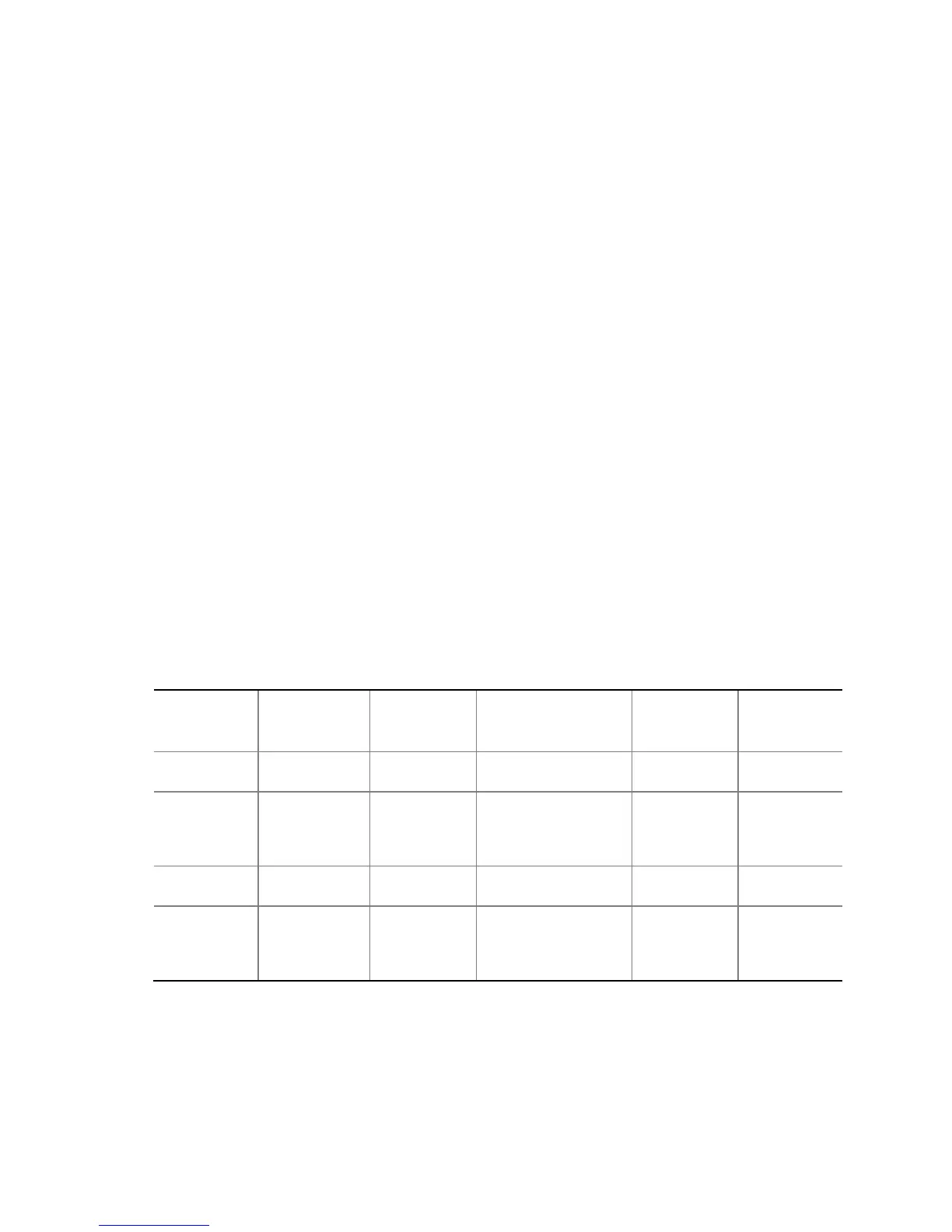
Table 37. Supervisor and User Password Functions
Password
Set
Supervisor
Mode
User Mode
Setup Options
Password
to Enter
Setup
Password
During
Boot
Neither Can change all
options
(Note)
Can change all
options
(Note)
None None None
Supervisor
only
Can change all
options
Can change a
limited
number of
options
Supervisor Password Supervisor None
User only N/A Can change all
options
Enter Password
Clear User Password
User User
Supervisor
and user set
Can change all
options
Can change a
limited
number of
options
Supervisor Password
Enter Password
Supervisor or
user
Supervisor or
user
Note: If no password is set, any user can change all Setup options.
 Loading...
Loading...