Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor DEVELOPER’S QUICK START GUIDE
5
NAcc – Native Acceleration – a mode or form of Intel® MKL in which the data being processed and the MKL
function processing the data reside on the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor.
Offload Compilers – The Intel® C/C++ Compiler and Intel® Fortran Compiler compilers, which can generate
binaries for both the host system and the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor. The offload compilers can generate
binaries that will run only on the host, only on the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor, or paired binaries that run on
both the host and the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor and communicate with each other.
Intel® MPSS – Intel® Manycore Platform Software Stack– the user- and system-level software that allows
programs to run on and communicate with the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor.
SCI - Symmetric Communications Interface – the mechanism for inter-node communication within a single
platform, where an node is a Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor or an Intel Xeon processor-based host processor
complex. In particular, SCI abstracts the details of communicating over the PCIe bus (and controlling related
Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor hardware) while providing an API that is symmetric between all types of nodes
System Configuration
The configuration assumed in this document is an Intel workstation containing two Intel® Xeon® processors,
one or two Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessors attached to a PCIe* x16 bus, and a GPU for graphics display.
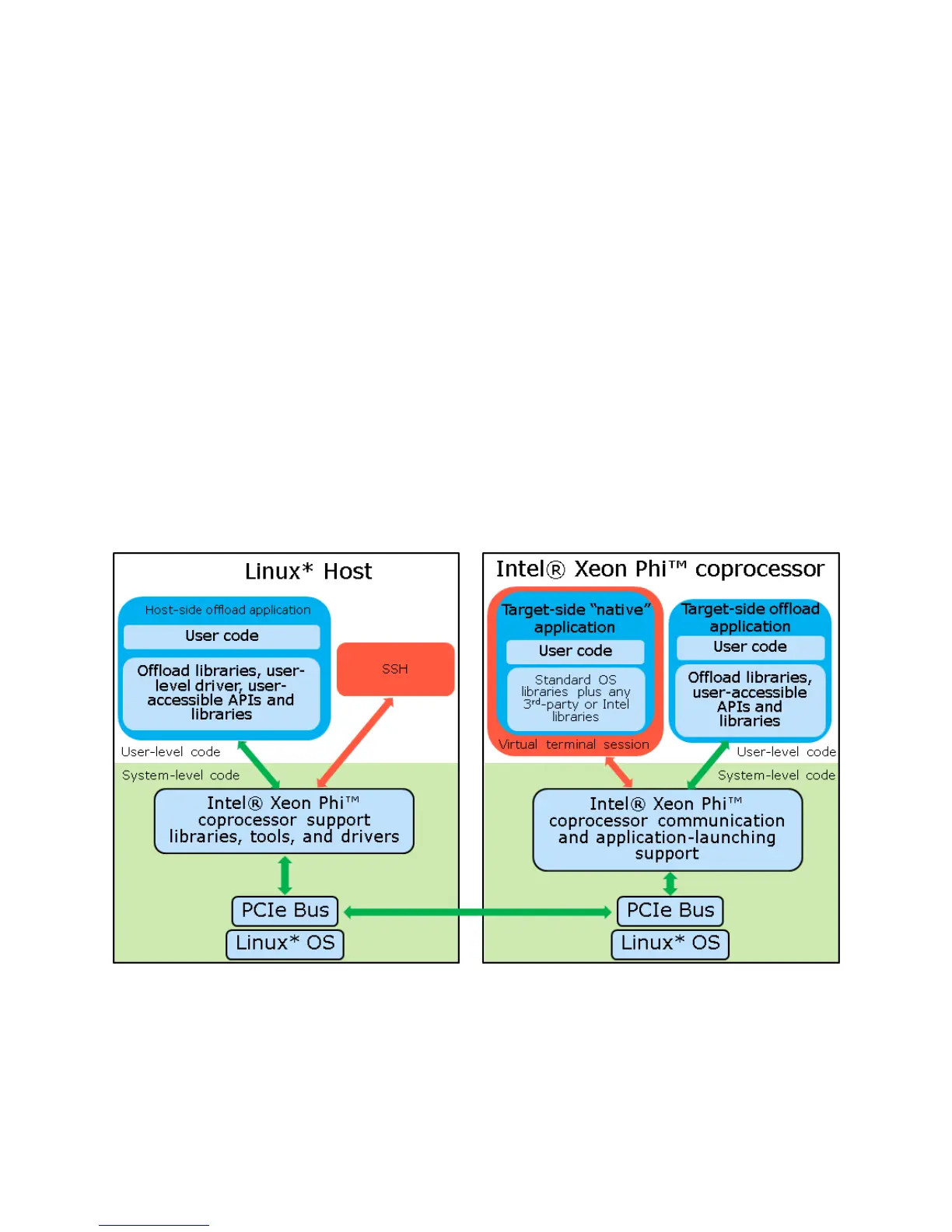
Intel® Xeon Phi™ Software
Figure 1: Software Stack
The Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor software stack consists of layered software architecture as noted below
and depicted in Figure 1.
Driver Stack:
The Linux software for the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor consists of a number of components:
 Loading...
Loading...











