12
RESCUE GUIDE ‒ Technical information
TECHNICAL INFORMATION
CNG / CNG-PETROL VEHICLES (NATURAL POWER)
– Printed 692.68.340 – 1st Ed. 04/2015
Note
The pressure reducer must be positioned with the solenoid valve (1) facing upwards.
A maximum tilt of 15° from the vertical axis is permitted.
CNG shut-off solenoid valve
The CNG shut-off solenoid valve is normally closed.
This allows CNG to flow only when it is energized.
It is powered via the ignition key through a specific contactor and is connected directly to ground.
With the solenoid valve powered (ignition key set to MAR), CNG can flow towards the pressure reducer valve and then towards
the electro-injectors.
Inertial switch description
117678
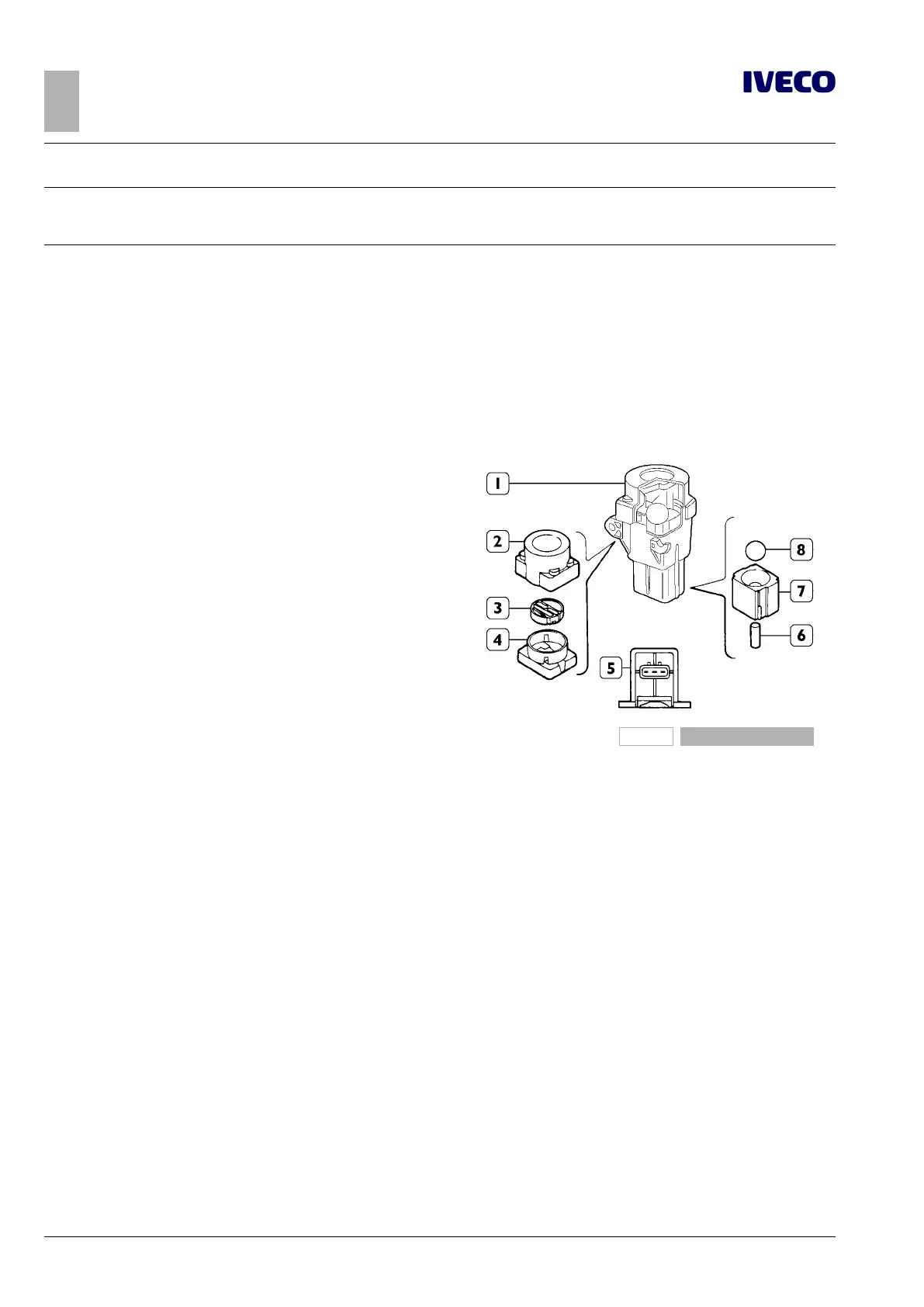
Figure 14
1 Inertial switch
2 Flexible cover
3 Switch
4 Switch seat
5 Connector
6 Permanent magnet
7 Permanent magnet
seat
8 Ball
This switch (1) trips in case of accident, cutting off the supply to the
solenoid valves both on the cylinders and on the pressure reducer,
consequently cutting off the gas supply.
A steel ball (8) fitted into a tapered housing is normally kept secured
by the attraction force of an adjacent magnet.
Under specific acceleration loads, the ball is released from the mag-
netic retainer (6) and gradually comes out of the tapered support
with an upward movement, according to the cone angle.
Above the ball (8) is a quick-connect mechanism that generates the
normally closed (N.C.) electric circuit.
The mechanism changes position when it is hit by the ball, from N.C.
(normally closed) circuit to N.O. (normally open) circuit, thus cutting
off the solenoid valve supply ground circuit.
In case of impact in any of the three orthogonal directions, the switch
will operate above the 12 g peak (acceleration values), equivalent to
an impact at 25 km/h.
The inertia switch (1) can be restored by pushing the button (3)
protected by a flexible cover (2) (that is also used to protect against
any foreign bodies).
The switch (1) is located in the engine compartment.

 Loading...
Loading...