15
4 Modbus protocol description
4.1 Master-Slave principle
Communication between a master (PC or notebook) and a slave (paperless
recorder) using the Modbus/J-bus takes place according to the master-slave
principle, in the form of data request/instruction - response.
The master controls the data exchange, the slaves only have a response
function. They are identified by their device address.
4.2 Transmission mode (RTU)
The transmission mode used is the RTU mode (Remote Terminal Unit). The
data is transmitted in the binary format (hexadecimal) with 8 or 16 bits for
integer values and 32 bits for float values.
Data format The data format describes the structure of a byte transmitted.
The paperless recorder can be operated either as a Modbus slave,
see Chapter 5.1 Modbus slave, Page 35, or as a Modbus master,
see Chapter 5.2 Modbus master, Page 38.
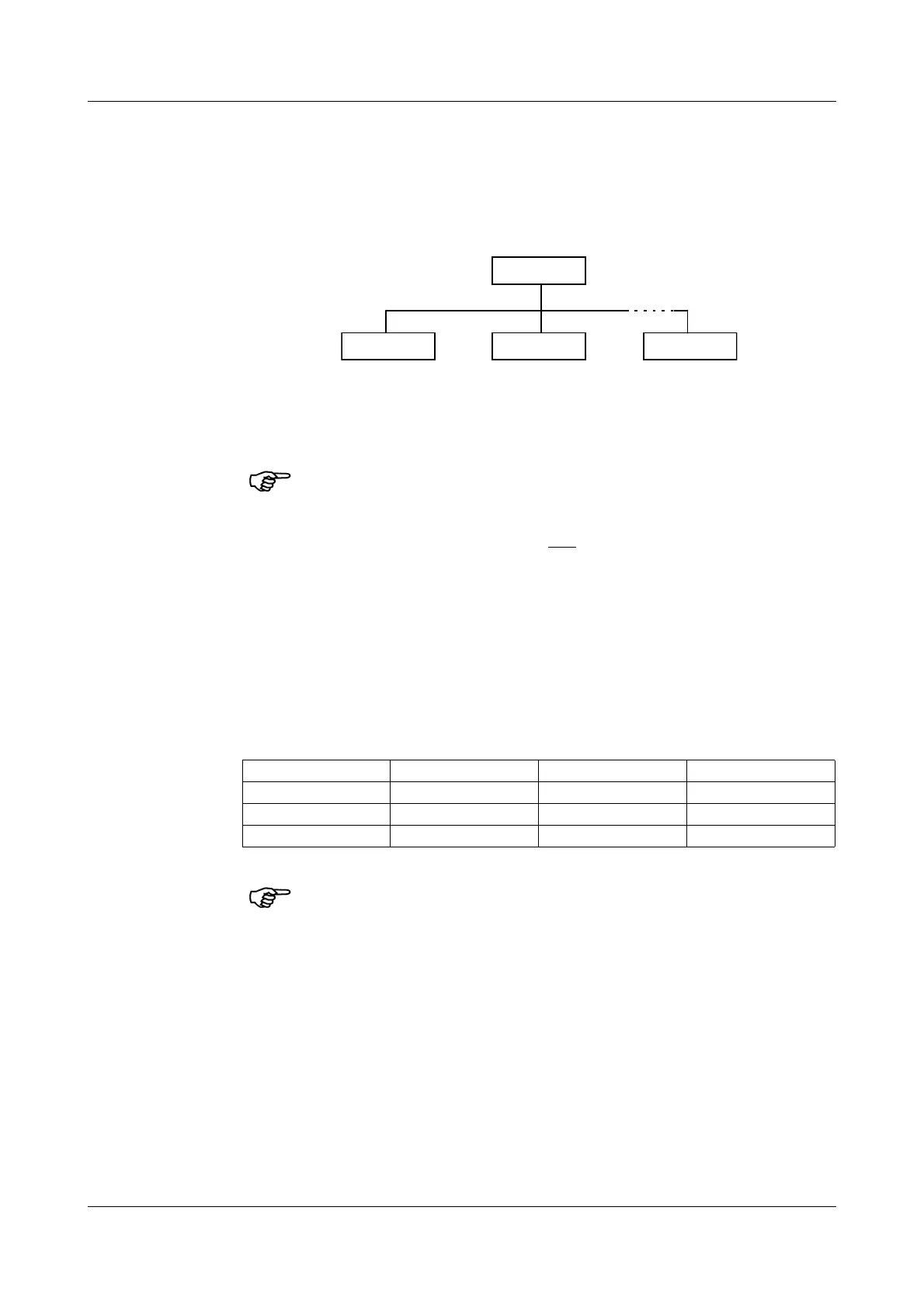
In a Modbus network, only one
device can be assigned with the
master function.
Master
Slave 1 Slave 2 Slave n
Data word Parity bit Stop bit Number of bits
8 bits no 1 9
8 bits even 1 10
8 bits odd 1 10
The data format to be used can be set, see Chapter 3.4
Configuration of the serial interfaces, Page 12.

 Loading...
Loading...