Page 28
Details of Intake and Exhaust Piping Terminations for
Direct Vent Installations
NOTE - In Direct Vent installations, combustion air is taken
from outdoors and ue gases are discharged to outdoors.
NOTE - Flue gas may be slightly acidic and may adverse-
ly aect some building materials. If any vent termination
is used and the ue gases may impinge on the building
material, a corrosion-resistant shield (minimum 24 inches
square) should be used to protect the wall surface. If the
optional tee is used, the protective shield is recommend-
ed. The shield should be constructed using wood, plastic,
sheet metal or other suitable material. All seams, joints,
cracks, etc. in the aected area should be sealed using an
appropriate sealant. See gure 42.
Intake and exhaust pipes may be routed either horizon-
tally through an outside wall or vertically through the roof.
In attic or closet installations, vertical termination through
the roof is preferred. Figures 34 through 41 show typical
terminations.
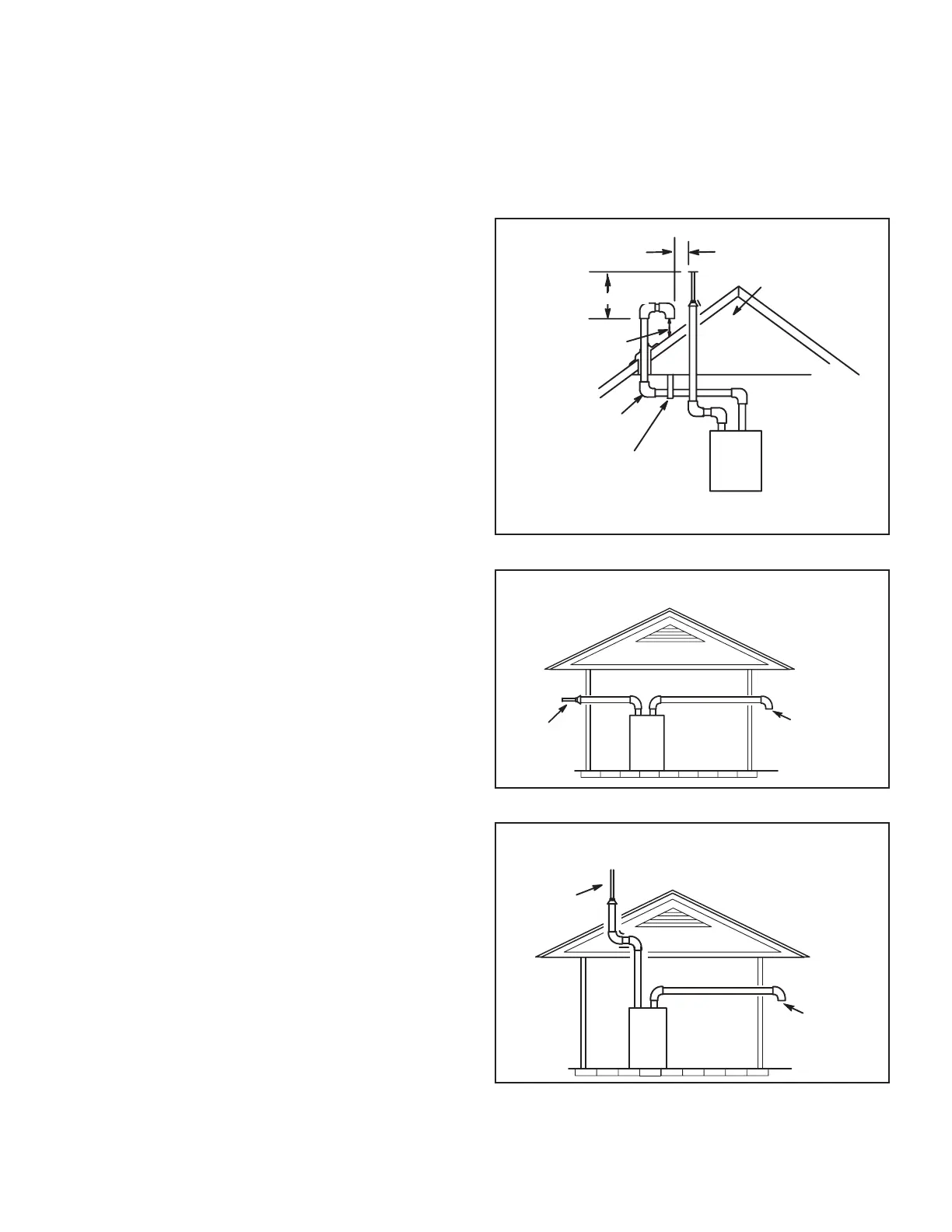
1 - Intake and exhaust terminations are not required
to be in the same pressure zone. You may exit the
intake on one side of the structure and the exhaust
on another side (gure 35). You may exit the
exhaust out the roof and the intake out the side of
the structure (gure 36).
2 - Intake and exhaust pipes should be placed as close
together as possible at termination end (refer to
illustrations). Maximum separation is 3” (76MM)
on roof terminations and 6” (152MM) on side wall
terminations.
NOTE - When venting in dierent pressure zones,
the maximum separation requirement of intake and
exhaust pipe DOES NOT apply.
3 - On roof terminations, the intake piping should
terminate straight down using two 90° elbows (See
gure 34).
4 - Exhaust piping must terminate straight out or up as
shown. A reducer may be required on the exhaust
piping at the point where it exits the structure to
improve the velocity of exhaust away from the intake
piping. See table 8.
NOTE - Care must be taken to avoid recirculation of
exhaust back into intake pipe.
5 - On eld-supplied terminations for side wall exit,
exhaust piping may extend a maximum of 12 inches
(305MM) for 2” PVC and 20 inches (508MM) for 3”
(76MM) PVC beyond the outside wall. Intake piping
should be as short as possible. See gure 42.
6 - On eld-supplied terminations, a minimum distance
between the end of the exhaust pipe and the end of
the intake pipe without a termination elbow is 8” and
a minimum distance of 6” with a termination elbow.
See gure 42.
7 - If intake and exhaust piping must be run up a side
wall to position above snow accumulation or other
obstructions, piping must be supported.
At least one bracket must be used within 6” from the
top of the elbow and then every 24” (610mm) as shown
in gure 42, to prevent any movement in any direction.
When exhaust and intake piping must be run up an
outside wall, the exhaust piping must be terminated
with pipe sized per table 8.The intake piping may be
equipped with a 90° elbow turndown. Using turndown
will add 5 feet (1.5m) to the equivalent length of the
pipe.
UNCONDITIONED
ATTIC SPACE
12” (305mm) ABOVE
AVERAGE SNOW
ACCUMULATION
3” (76mm) OR
2” (51mm) PVC
PROVIDE SUPPORT
FOR INTAKE AND
EXHAUST LINES
8” (203mm) MIN
Inches(mm)
DIRECT VENT ROOF TERMINATION KIT
FIGURE 34
Exhaust
Pipe
Furnace
Exiting Exhaust and Intake Vent
(different pressure zone)
Inlet Air
(Minimum 12 in.
305 MM) above
grade or snow
FIGURE 35
Roof T
erminated
Exhaust Pipe
Furnace
Exiting Exhaust and Intake Vent
(different pressure zone)
Inlet Air
(Minimum 12 in.
305 MM) above
grade or snow
FIGURE 36

 Loading...
Loading...











