20
AGR 070A through 100A Product Manual AGR-3
Sound Power Levels
Acoustical consultants may require sound power octave band data to perform a detailed acoustical
analysis. The tables that follow present sound power levels per ARI Standard 370, “Sound Rating
of Large Outdoor Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Equipment”. These standards were developed
to establish uniform methods of determining the sound power radiated by large outdoor and indoor
equipment. The aforementioned methods are based on providing sound power levels by octave
band and the overall ‘A’ weighted value. Measurements are taken over a prescribed area around the
unit and the data is mathematically calculated to give the sound power, dB.
Sound Reduction due to Distance from the Unit
The distance between a source of sound and the location of the sound measurement plays an
important role in minimizing sound problems. The equation below can be used to calculate the
sound pressure level
at any distance if the
sound power
is known. Results for typical distances are
tabulated in Table 14. Another way of determining the effect of distance is to work from sound
pressure only. “Q”, the directionality factor, is a dimensionless number that compensates for the
type of sound reflection from the source. For example, a unit sitting on a flat roof or ground with
no other reflective surfaces or attenuation due to grass, snow, etc., between source and receiver:
Q=2.
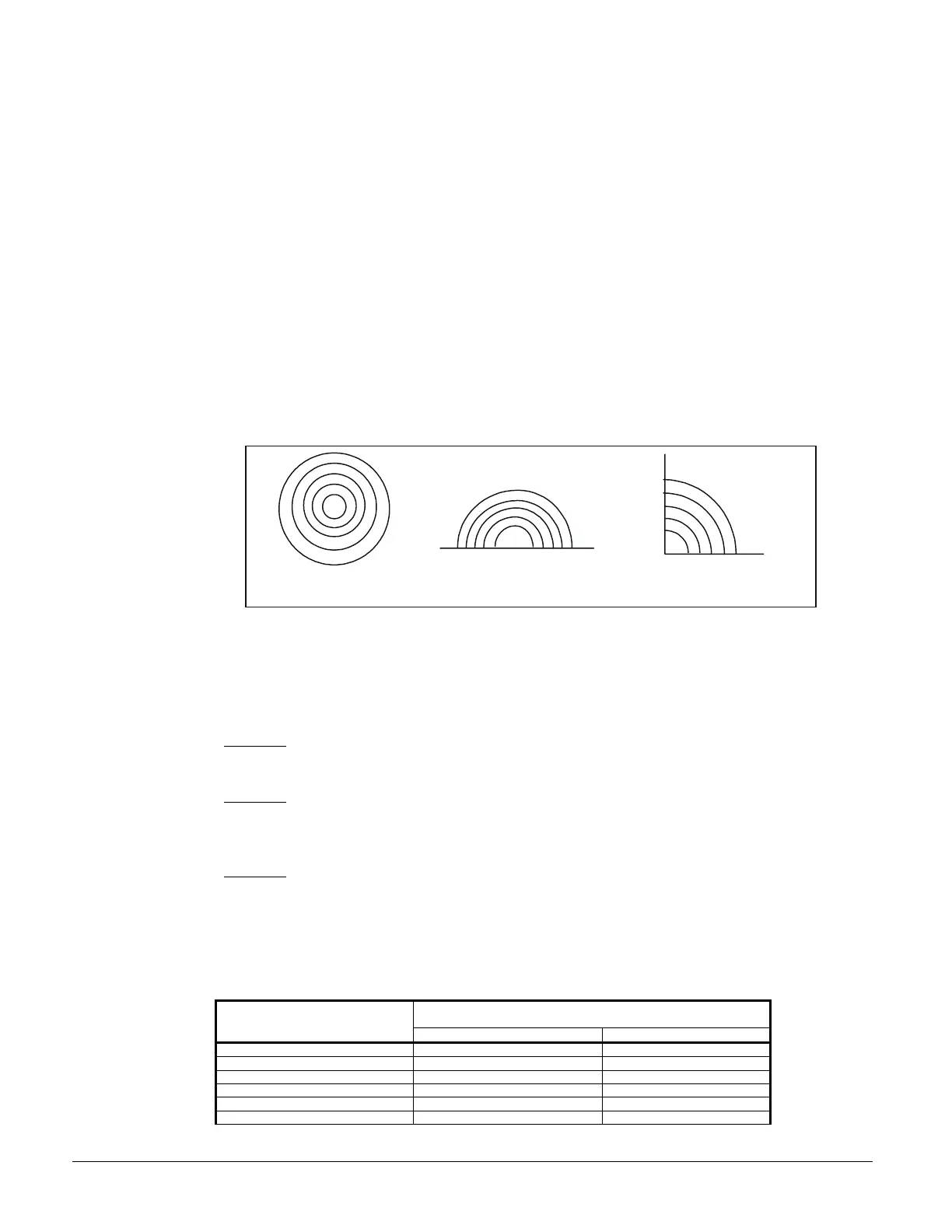
Figure 6, "Q" Definition, Plan View, Unit Located in Center
Uniform Spherical Radiation
Q=1 no reflecting surface
Uniform Hemispherical Radiation
Q=2 single reflecting surface
Uniform Radiation over ¼ of sphere
Q=4 two reflecting surfaces
Sound pressure can be calculated at any distance from the unit if the sound power is known.
Lp=Lw-(20 log r) + (10 log Q) - .5
Lp = sound pressure r = distance from unit in feet
Lw = sound power Q = directionality factor
With Q=1, Unit suspended in space (theoretical condition), the equation simplifies to:
Lp = Lw – (20)(log r) –0.5
With Q=2, for a unit sitting on a flat roof or ground with no adjacent vertical wall as a reflective
surface, the equation simplifies to:
Lp = Lw – (20)(log r) + 2.5
With Q=4 for a unit sitting on a flat roof or ground with one adjacent vertical wall as a reflective
surface, the equation simplifies to:
Lp = Lw – (20)(log r) + 5.5
The equations are reduced to table form in Table 14 for various distances and the two most usual
cases of “Q” type of location.
Table 14, dB Conversion of Sound Power to Pressure for Distance
DB Reduction from Sound Power at the Source to Sound
Pressure at Referenced Distance
Distance from Sound Source
ft. (m)
Q=2 Q=4
30 (9) 27.1 24.0
50 (15) 31.6 28.5
75 (23) 35.1 32.0
100 (30) 37.6 34.5
150 (46) 41.1 38.0
200 (61) 43.6 40.5
 Loading...
Loading...











