14
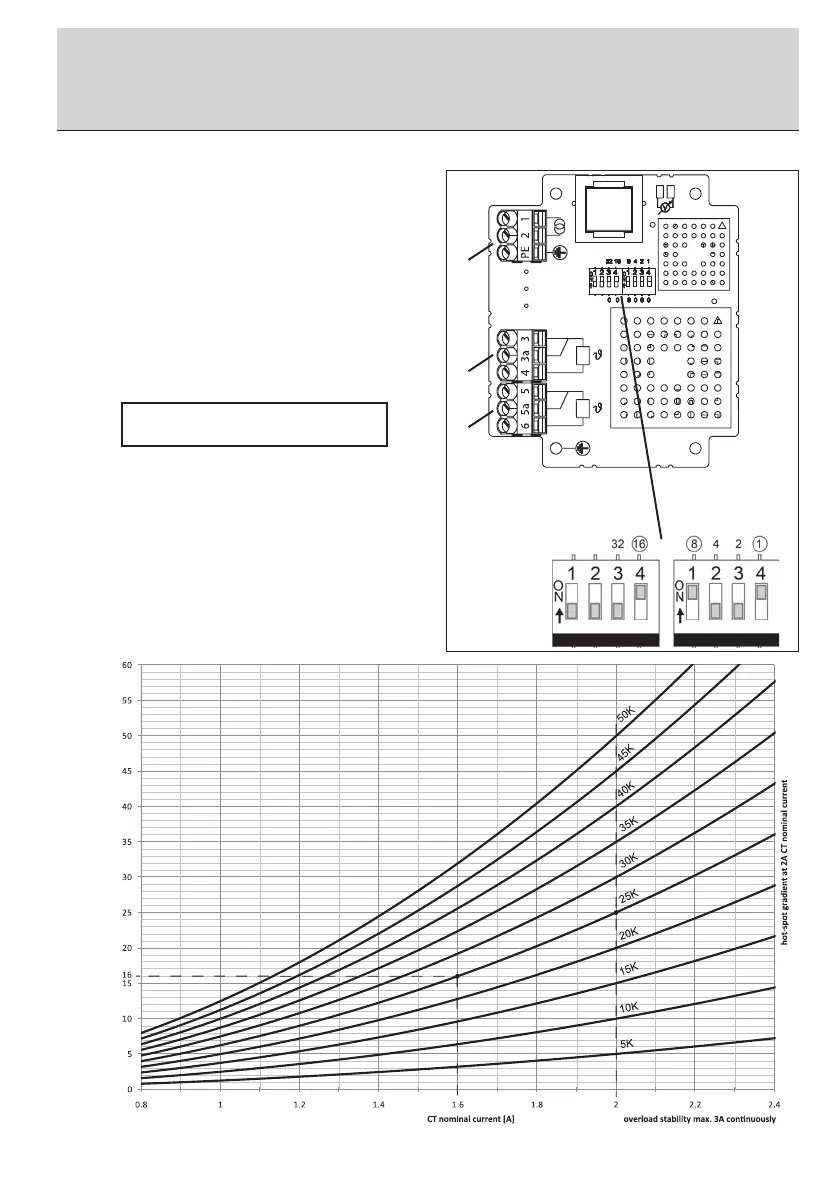
the position of switches S1 and S2 for the desired gradients in
the table in the appendix (chap. 12.2 - hot-spot gradient table
for 2 A CT nominal current) and set these accordingly (see
figure 3). The hot-spot gradient can be set from 4 K to 50 K in
increments of 1 K.
For example, the switch setting shown in figure 3, item 4 must
be set for a hot-spot gradient of 25 K.
7.2 Setting for 2 A CT nominal current ≠ 2 A
If the CT nominal current is greater or smaller than 2 A, the
hot-spot gradient to be set must be calculated with the
following formula:
Hg[K] = Hg
nominal
* 4 A
2
/ CT
nominal
2
e.g.) Hg
nominal
= 16 K
CT
nominal
= 1.6 A
Hg[K] = 16 K * 4 A
2
/ (1.6 A)
2
= 25 K at 2 A CT nominal
current
See chap. 13.2 (hot-spot gradient table for 2 A CT nominal
current) for the switch positions to be set for the DIP switches
(figure 3, item 4).
S2S1
4
Fig. 3
1
2
3
nominal hot-spot gradient [K]
Example: A 16 K hot-spot gradient at a nominal
current of 1.6 A CT corresponds to
25 K at 2 A.
A switch setting results as shown in
figure 3 (chap. 13.2 – hot-spot gradient
table for 2 A CT nominal current).
Fig. 4
7 Setting the hot-spot gradient
 Loading...
Loading...