26
4. Building the
Booms & Gaffs
The jumbo jib and fore booms have
metal fittings at their forward ends. The
main boom and fore and main gaff have
laser-cut jaws. Form a curve at the gaff
jaw’s throat (Figure 6-6).
Installation: Rigging in hand is easier
than when spars are on the model, so
don’t install the booms and gaffs until the
sails are laced or other rigging applied.
Reminder: Finish detailing and painting
the spars before setting them aside. Once
rigging commences, they must be ready
to mount.
General Rigging &
Sailmaking Information
Newcomers to the nautical world
should learn the following rigging
nomenclature. Old salts can skip this
part and grab a mug of grog. Because
Bluenose has no square sails, many terms
don’t apply, but may come in handy on
your next project.
Each edge and corner of a sail has a
name. On a for
e-and-aft sail, the top is
the
head, bottom the foot, aft side the
leech, and forward side the luff. The for-
ward lower corner is the
tack, aft lower
corner the
clew, forwar
d upper corner
the
throat, and aft upper corner the peak.
A triangular sail is similar, except the
upper corner is called the head. It has
no thr
oat or peak.
Cringles, sewed into corners of sails or
elsewhere, are metal thimbles to which
lines are attached. They are named per
their location; for example, clew cringle.
Gr
ommets
ar
e either buttonhole-stitched
round holes in the sail or brass grom-
mets. They are used to pass a line
thr
ough the sail. Sails ar
e
bent to their
yard, stay, gaff, or boom.
Standing rigging: Fixed lines supporting
masts and spars. Standing rigging is
generally wormed, parceled, and served
with a light line. It also is tarr
ed; hence,
its black or dark brown appearance.
Shr
ouds
: T
ransverse lines supporting
masts.
Deadeyes are wood and have
thr
ee holes for r
eeving the
lanyard.
Lanyards are lines used to tighten
shrouds. On modern ships, metal
turn-
buckles
have replaced deadeyes. A heart
or bullseye is similar to a deadeye,
except it has one hole and is used on
more permanent installations.
Chain plates: Iron bars or rods on the
hull for holding deadeyes. T
opmast
shrouds have no chain plates. Instead,
futtock shrouds (lines or metal bars) run
from the deadeye or bullseye to the
mast band. If the futtock shr
ouds extend
just to the lower shr
ouds, they generally
tie to a wooden or metal rod called a
futtock stave. Catharpins, lines keeping
the futtock shrouds taut, brace in the
lower end of the futtock shrouds and
secure to the futtock staves.
Stays: Fore and aft lines supporting the
masts.
Backstays provide side and aft
support. They ar
e generally angled
slightly aft. A running or flying backstay
has a movable tackle on deck.
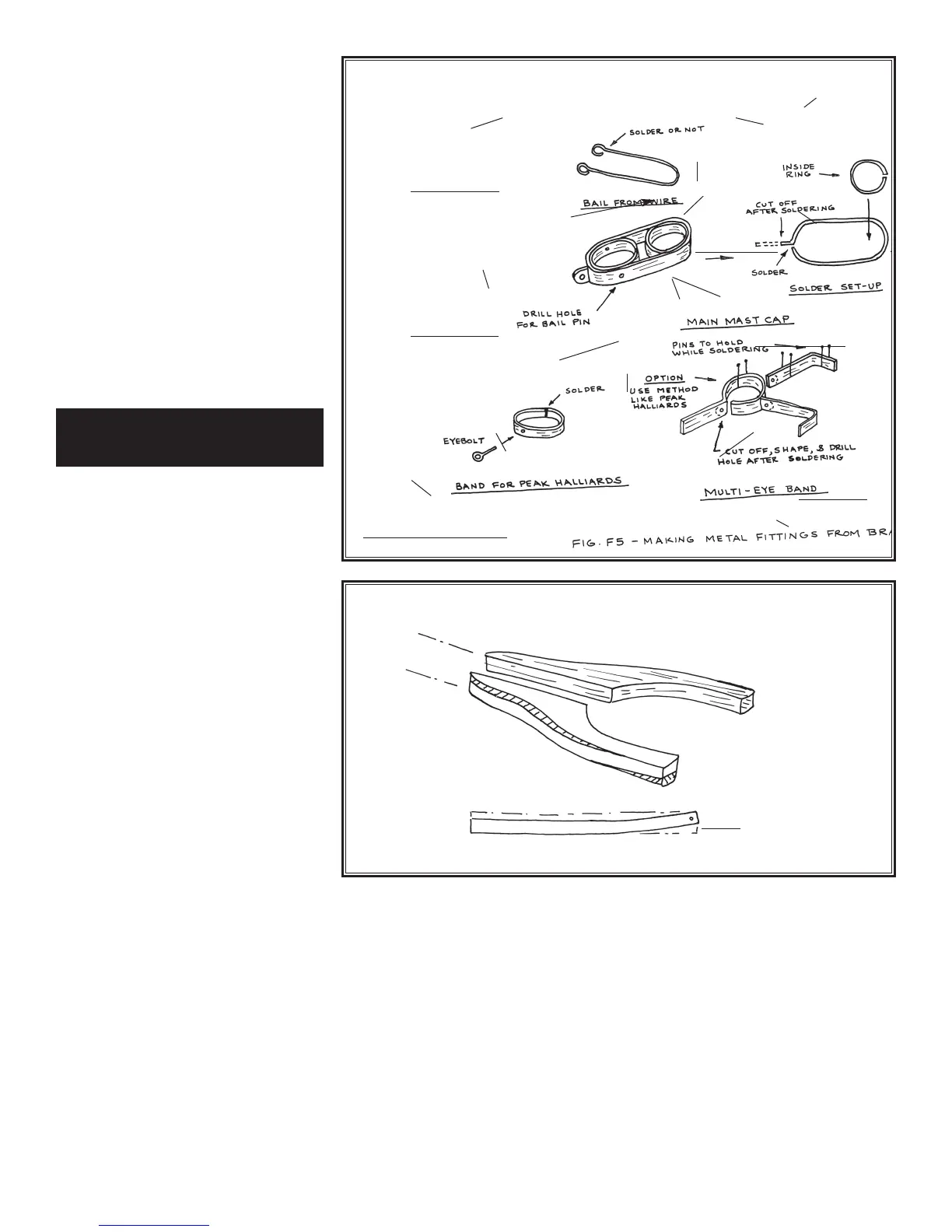
Fig. 6-5 Making Metal Fittings From Brass
Solder or Not
Pins to Hold
While Soldering
Option-Use Method Like
Peak Halliards
Cut Off, Shape & Drill
Hole After Soldering
Inside Ring
Outside
Ring
Solder Then Cut Off
Wire
Solder
Eyebolt
Cut Off After Soldering
Solder
Shape
Around a
Drill Bit
Could Also
Be Cut
From Brass
Tubing
Bail From Wire
Main Mast Cap
Multi-Eye Band
Sheet Band
Band For Peak Halliards
Solder Set-Up
Drill Hole For Bail Pin
Fig. 6-6 Gaff Jaws
Shape Laser-Cut
Jaw to Form Curve
Stage 7

 Loading...
Loading...