1.1 Coordinate Systems
1-1
HW0481924
1 Relative Job
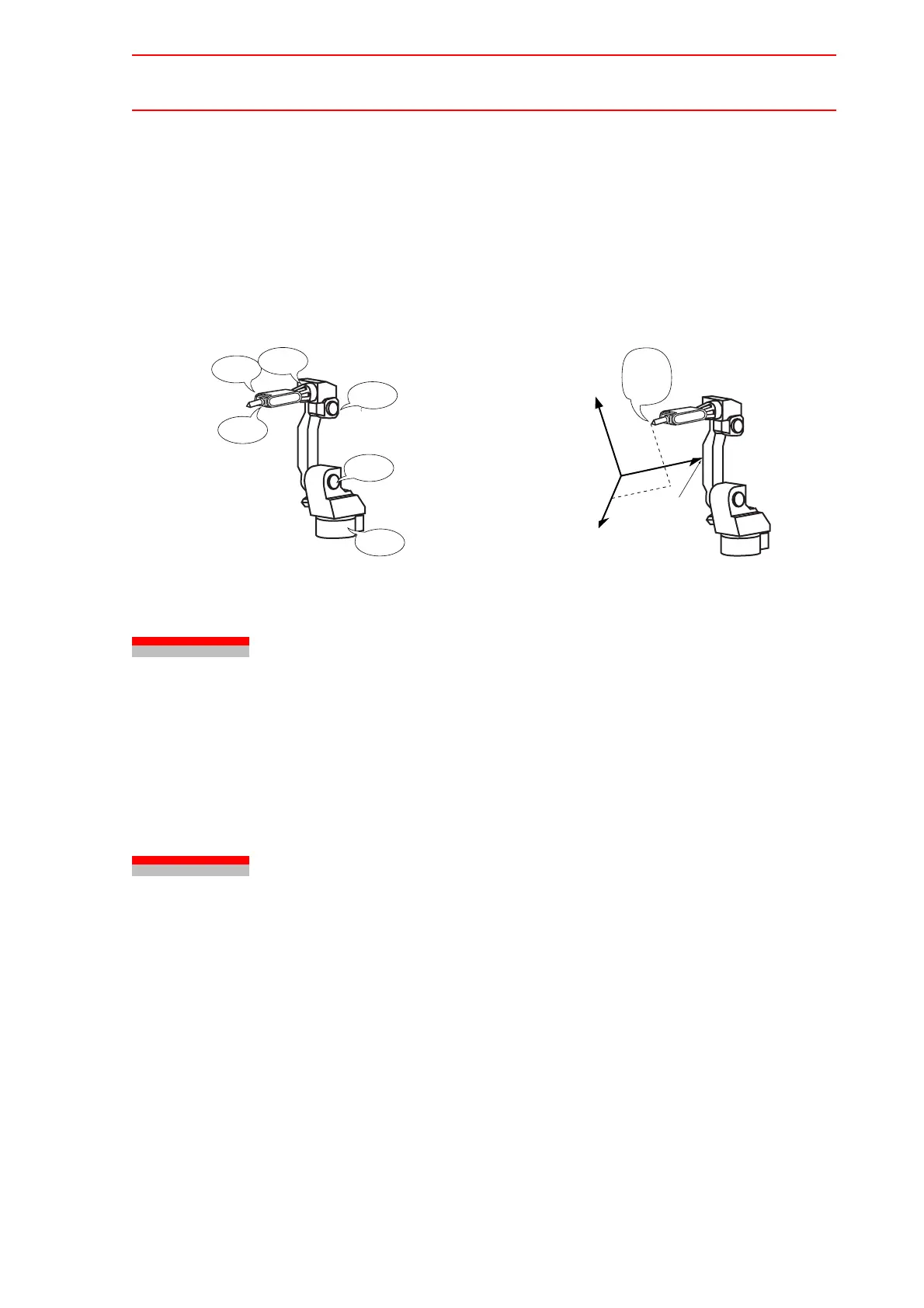
In a standard job, each position is defined by a set of pulse numbers, which represent the
amount of revolutions of the S, L, U, R, B, and T axes.
In a relative job, however, each position is represented with a set of three values (X, Y, Z) in a
specified coordinate system.
1.1 Coordinate Systems
In a relative job, any of the following three types of coordinate systems can be used:
• Base coordinate system
• Robot coordinate system
• User coordinate system (24 systems available)
1.2 Relative Job Shift Functions
In a relative job that uses a user coordinate system, changing the definition points to re-deter-
mine the coordinate system also changes the coordinates used for the robot operations
accordingly.
Also when the operating coordinate system number is changed, the coordinates used for
operations are also changed accordingly.
Pulse Type Position Data of Standard Job XYZ-type Position Data of Relative Job
B=xxxx
R=xxxx
U=xxxx
T=xxxx
L=xxxx
S=xxxx
Z-coordinate
X-coordinate
Y-coordinate
X=xxxx
Y=xxxx
Z=xxxx

 Loading...
Loading...