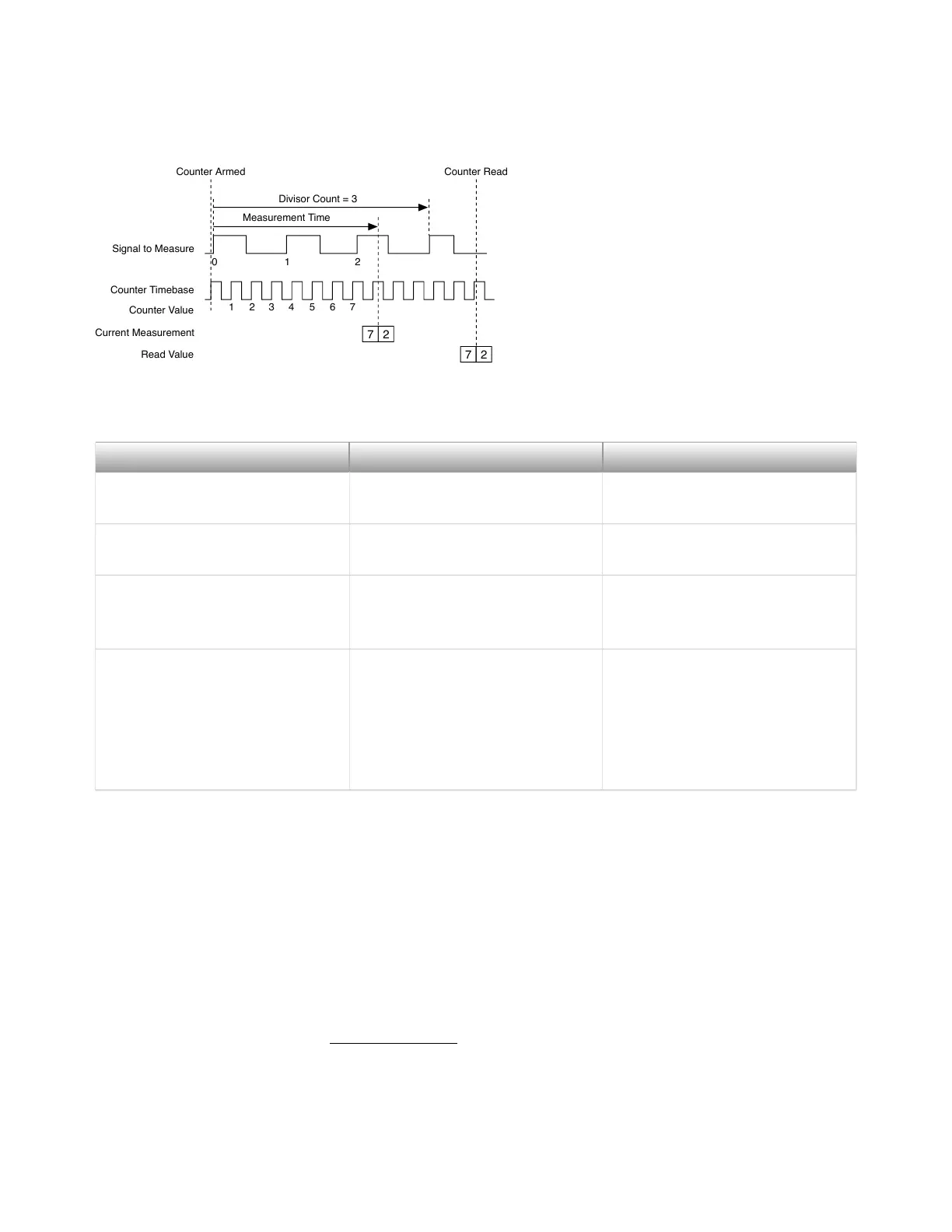
Figure 16. Measurement Time completes before Divisor
Signal to Measure
Counter Timebase
Counter Value
Current Measurement
Read Value
7 2
7 2
Counter Armed Counter Read
0 1 2
Divisor Count = 3
Measurement Time
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
The following table shows the summary of dierent frequency measurement
methods.
Divisor Measurement Time Counter Characteristic
1 0 (Disabled) Measure 1 period of the input
signal.
N 0 (Disabled) Measure N periods of the input
signal.
0 (Disabled) M Measures all the period of the
input signals that occur within
the M measurement time.
N M Returns the measurement of N
periods of the input signal or
the measurement that occurs
within the M measurement
time, whichever completes
first.
Trade-os—Dierent
frequency methods are used to trade-o between
measurement accuracy and measurement update rate for dierent input signal
frequencies. Increasing the divisor or measurement time improves the
measurement accuracy but also reduces the measurement rate.
Measurement Error—Measurement error is caused by the uncertainty in measuring
the frequency of the input signal due to the finite resolution of the counter timebase
clock.
You can calculate the maximum error using the following equation:
Measurement Error
( % ) =
f
x
(
N
periods
×
f
k
) -
f
x
× 100 %
ni.com
20
NI-9361 Getting Started
 Loading...
Loading...