Saving tips
Your installation produces heat and hot water. This occurs via the control
settings you made.
Factors that affect the energy consumption are, for example, indoor tem-
perature, hot water consumption, the insulation level of the house and
whether the house has many large window surfaces. The position of the
house, e.g. wind exposure is also an affecting factor.
Also remember:
႑
Open the thermostat valves completely (except in the rooms that are to
be kept cooler for various reasons, e.g. bedrooms). The thermostats slow
the flow in the heating system, which the indoor module wants to
compensate with increased temperatures. It then works harder and
consumes more electrical energy.
႑
You can lower the temperature when away from the house by
scheduling "holiday setting" in menu 4.7. See page 51 for instructions.
႑
If you activate "Hot water Economy", less energy is used.
႑
You can influence the energy consumption by connecting the indoor
module to different supplements such as solar, gas or oil.
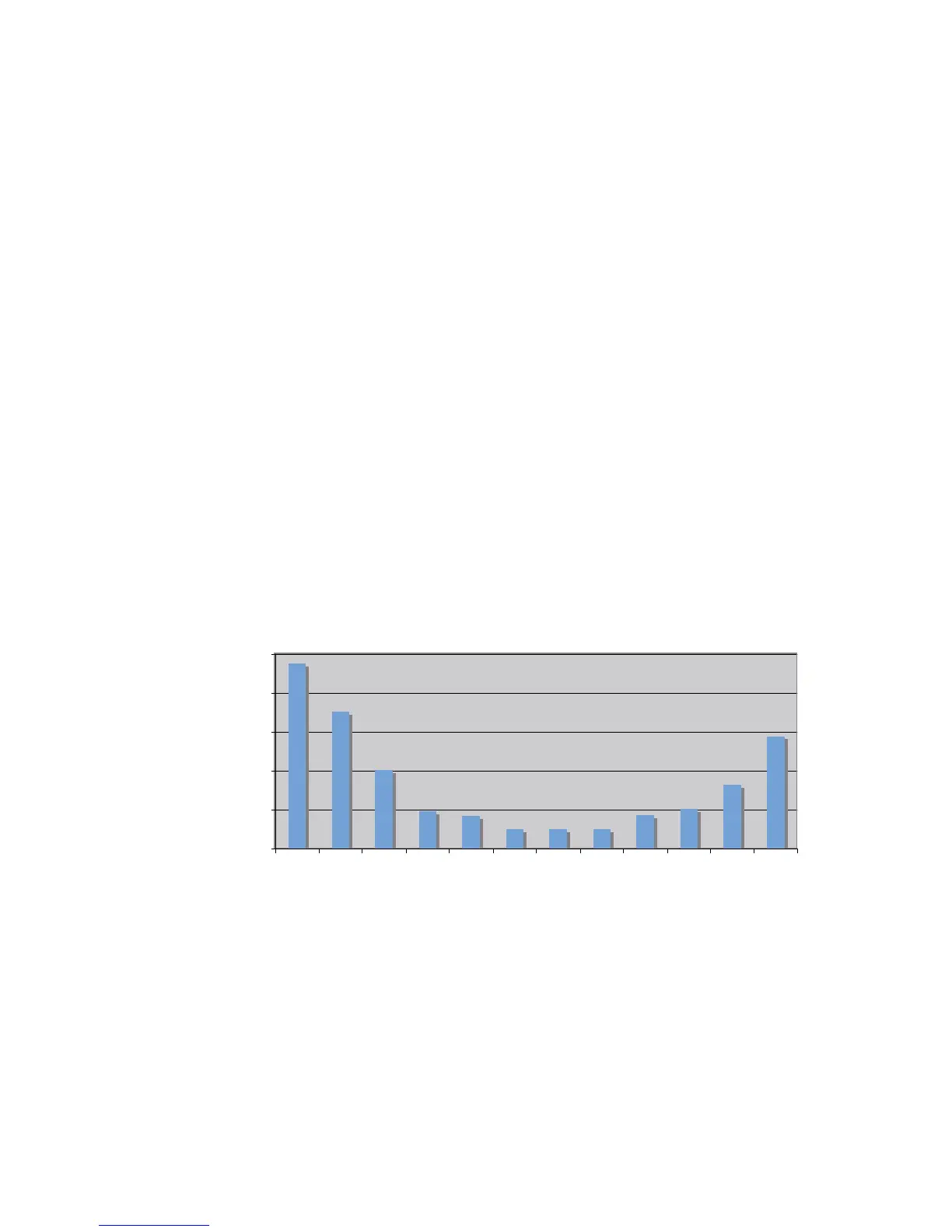
Power consumption
Energiförbrukning fördelat över året
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
jan feb mars april maj juni juli aug sep okt nov dec
Månad
990 V DSSUR[LPDWH
HQHUJ\ FRQVXPSWLRQ VSUHDG DFURVV WKH \HDU
0RQWK
-DQ )HE 0DU $SULO 0D\ -XQH -XO\ $XJ 6HS 2FW 1RY 'HF
RI DQQXDO
FRQVXPSWLRQ
Increasing the indoor temperature one degree increases the energy con-
sumption by approx. 5%.
Domestic electricity
In the past it has been calculated that an average Swedish household has
an approximate annual consumption of 5000 kWh domestic electri-
city/year. In today's society it is usually between 6000-12.000 kWh/year.
NIBE™ VVM 310Chapter 2 | The heating installation – the heart of the house22
 Loading...
Loading...