Instructions for Use | Therapy Modes and Controls
Mixed Modes 24
SIMV-PC: Synchronous Intermittent Mandatory Ventilation- Pressure Control
DESCRIPTION:
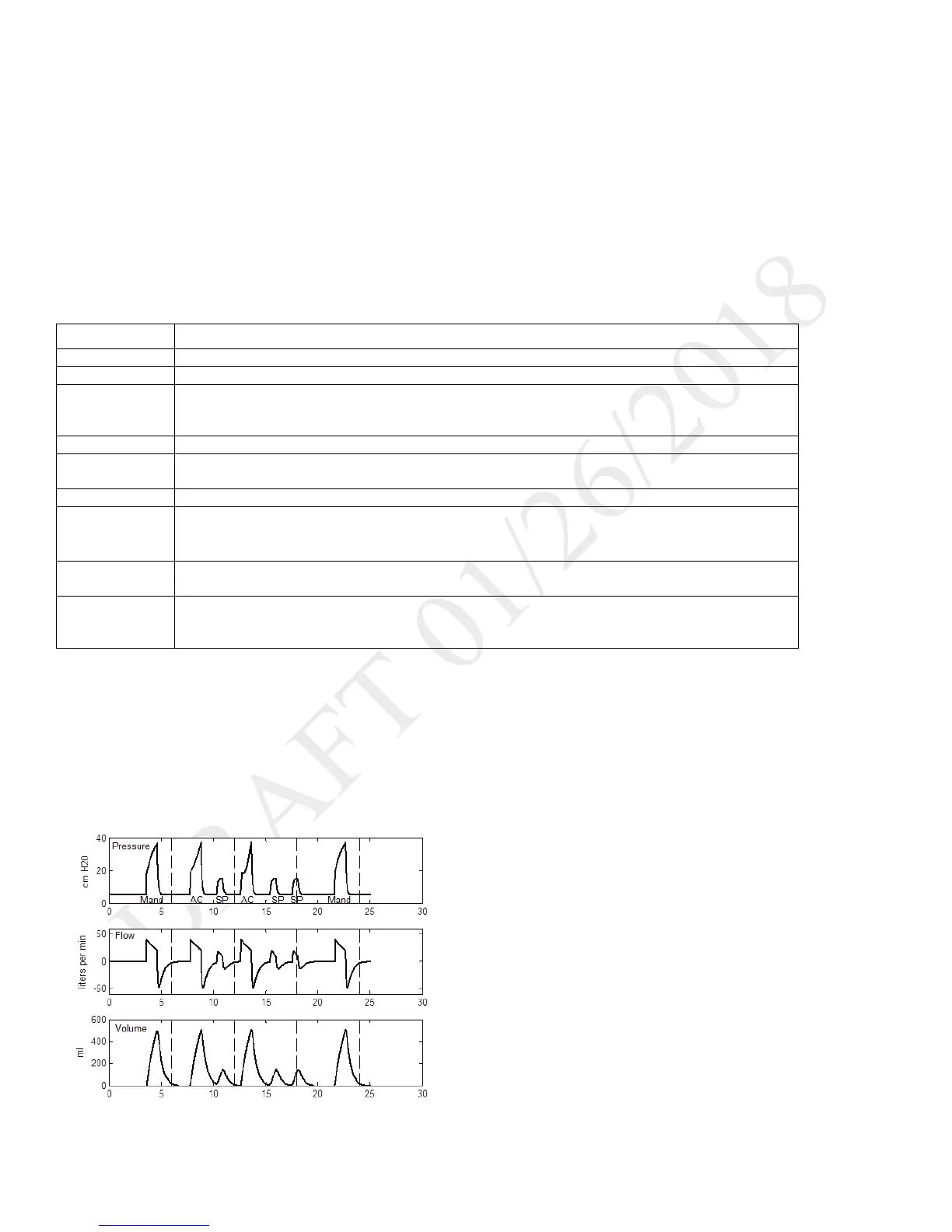
SIMV-PC mode is a pressure control mode that provides a mixture of mandatory and spontaneous breaths. SIMV-PC mode guarantees one
mandatory breath in each cycle. Spontaneous breaths can be delivered with pressure support. The breath rate determines the length of the cycle.
The first phase of the cycle is reserved for synchronizing a mandatory breath with patient effort. If the patient triggers a breath during this phase of
the cycle, the ventilator delivers a synchronized mandatory breath. If a patient does not trigger a breath during the mandatory phase of the cycle,
then the ventilator delivers a mandatory breath. Breaths triggered by the patient after the mandatory breath in the cycle are spontaneous breaths.
This process is repeated at the start of every cycle.
SETTINGS:
Defines the applied pressure for all breaths
Target pressure that the device delivers during the inspiratory phase of a spontaneous breath
Positive end expiratory pressure
Positive pressure maintained in the patient circuit during exhalation: must be less than or equal to the
For a mandatory breath, length of the inspiratory phase
Time required for the ventilator to change from the expiratory pressure setting to the inspiratory pressure
setting when the breath is triggered.
Minimum rate of mandatory breaths per minute
• Sensitive Auto-Trak (passive circuits only)
• Flow Trigger (Passive, Active PAP, Active Flow, or Dual Limb circuits)
This control is available when the trigger type is Flow Trigger. The flow trigger initiates when the patient’s
inspiratory effort creates a flow equal to or greater than the flow trigger sensitivity setting.
Sensitivity
This control is available when the trigger type is Flow Trigger
As flow begins to decrease during inspiration, if the patient flow is less than the flow cycle set point, the
device cycles to expiration.
SETTABLE ALARMS:
• Circuit disconnect
• High tidal volume
• Low tidal volume
• High minute ventilation
• Low minute ventilation
• High respiratory rate
• Low respiratory rate
ILLUSTRATION
 Loading...
Loading...