19
EVD-2 • 5401042 • REV L • 03/05
DETERMINING THE MAXIMUM LINEAR DISTANCE ON A SAFE
A rule of thumb for estimating the maximum linear distance from the recommended
detector location to any point on the protected surface is:
Example: h = 62" w = 55" d = 29"
1. Compute X1 = h + w 1. X1 = 62"+ 55" (X1 = 117")
2. Compute X2 = 2d + w 2. X2 = (2 x 29") + 55" (X2 = 113")
3. Find X = minimum ( X1, X2 ) 3. X = 113"
4. Compute J = w + d 4. J = 55" + 29" (J = 84")
5. Find D = maximum ( X, J ) 5. D = 113"
Where: h = Safe Height
w = Safe Width
d = Safe Depth
D = Maximum Linear Distance
This rule of thumb is valid for most available safe sizes. However, if any one dimension
is very large or very small when compared to the other two dimensions, the safe may not
follow this rule. In those cases, contact Potter’s technical support for assistance. Table 6
lists some common safe dimensions and their maximum linear distances when detectors
are installed in recommended locations.
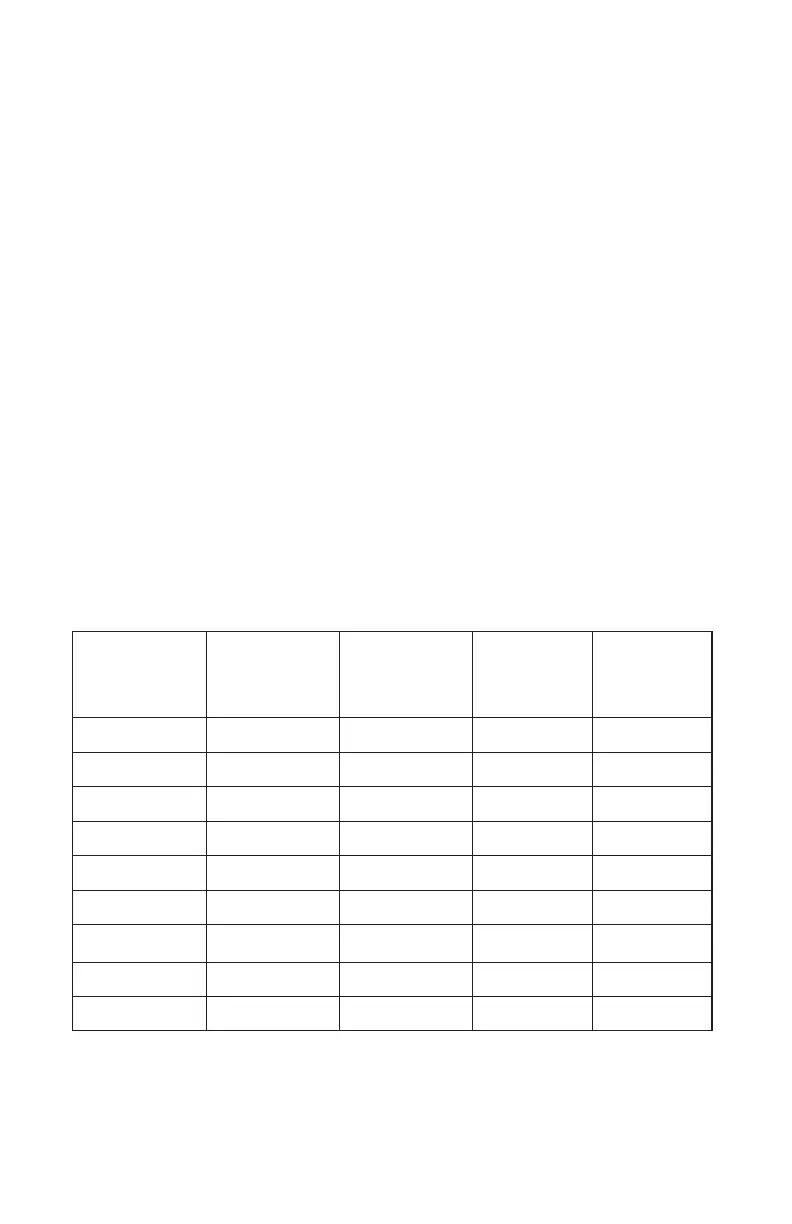
Table 6. Typical Safe Exterior Dimensions and Maximum Linear Distances
thgieH
)sehcnI(
htdiW
)sehcnI(
htpeD
)sehcnI(
emuloV
).tf.uc(
raeniLmumixaM
ecnatsiD
)sehcnI(
00.5200.1200.1283.600.
64
00.2300.5200.5275.1100.75
00.2400.1300.9258.1200.37
00.2500.1300.9250.7200.38
00.2600.1300.9262.2300.98
00.2600.5500.9232.
7500.311
00.4600.1300.9203.3300.98
00.2700.5300.9292.2400.39
00.9700.3400.3378.4600.901

 Loading...
Loading...