9
ENGLISH
NOTES ABOUT
CONSTANT VOLTAGE SYSTEMS
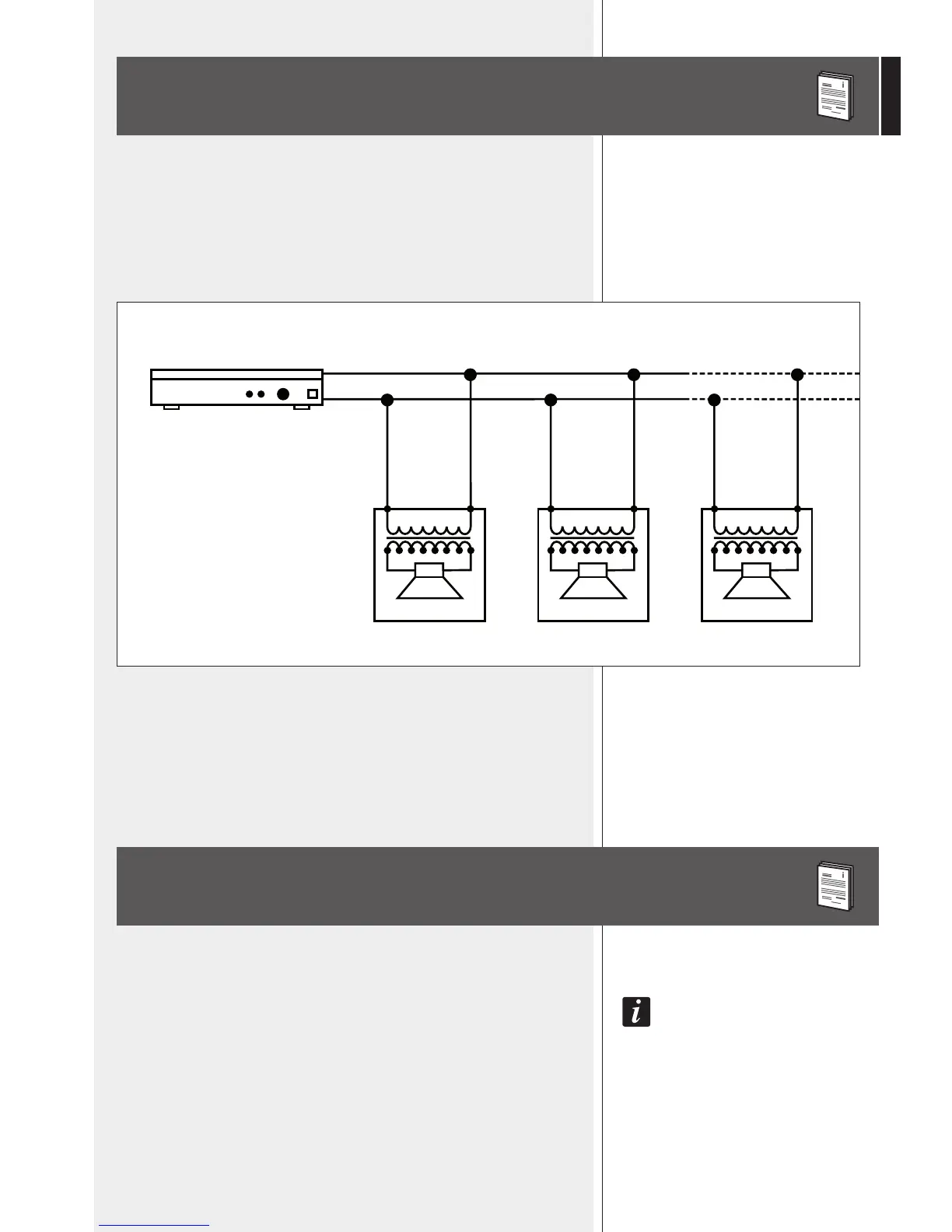
The loudspeaker input voltage (Vd) shall correspond to the amplifier output
voltage (Va).
The sum of nominal power values (Pd x n) of all loudspeakers connected to
the line shall not exceed the amplifier power (Pa).
Make sure all loudspeakers are connected in phase to ensure a correct
sound reproduction.
Always use cables having wires with an adequate cross-section, considering
the cable length and the total loudspeaker power.
Loudspeaker lines must be kept separated from mains cable, microphone
cables or others, in order to avoid inductive phenomena may cause hum
or noises.
Use loudspeaker cables having twisted wires to reduce hum caused by
inductive effects due to coupling with electromagnetic fields.
-
-
-
-
-
-
Pa > Pd x n
+ Va
–
– Vd = Va + – Vd = Va + – Vd = Va +
The total loudspeaker impedance must not be lower than the amplifier
output impedance.
Note: a louDspeaker total impeDaNce equal to the amplifier output oNe permits
to get the maximum DeliVerable power (but aN higher louDspeaker impeDaNce
eNtails less power).
The total impedance of a group of identical loudspeakers linked in parallel is
given by their unit value divided by the loudspeaker quantity.
The total loudspeaker power shall be adequate for the maximum deliverable
power of the amplifier.
The loudspeaker line shall be as short as possible.
-
-
-
-
NOTES ABOUT
LOW IMPEDANCE CONNECTIONS

 Loading...
Loading...