english
OPTIMIZING THE ARRAY
Once the design (number of elements and vertical splay angles) has been designed using Shape Designer software, you can effectively optimise
the array depending on the environment and the application by driving it using different DSP presets stored onboard. Typically arrays are
divided in two or three zones depending the design and size of the array.
To optimise and EQ the array, different strategies are used for high frequencies (long throws and short throws) and low frequencies.
19
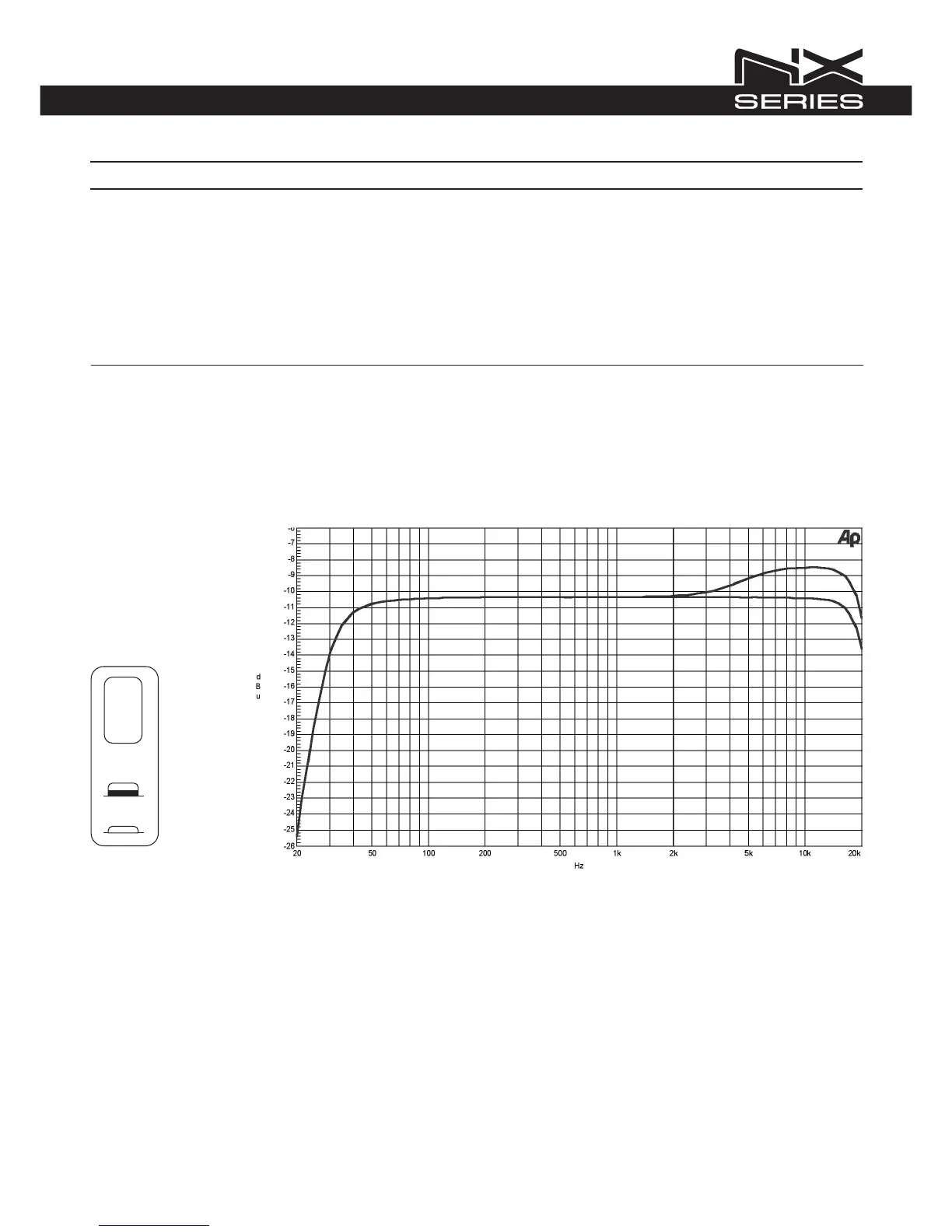
HIGH-FREQUENCY EQUALIZATION STRATEGIES
The longer the distance, the greater the attenuation at high frequencies. Generally, high frequencies need a correction to compensate for
energy lost over distance; the correction needed is usually proportional to the distance and high-frequency air absorption. In the near- to
mid-field, the air absorption is not nearly as critical; in this zone, high frequencies need little additional correction.
In the next figure is shown the equalization that corresponds to HF BOOST settings for LINEAR and ARRAY:
HF BOOST
LINEAR
ARRAY

 Loading...
Loading...